L – Carnitine: Can It Improve Diabetes?
L-Carnitine is an amino acid that the body produces. L-carnitine assists the body in converting fat into energy. In other words, L-carnitine aids the body's energy production. L-carnitine is essential for heart and brain function, muscle movement, and a variety of other processes in the body (1).
How does it work?
Many studies have found that L-carnitine can improve insulin sensitivity. It improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to convert food into energy. Here's a general overview of how food is converted into energy or fat in the body.
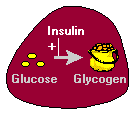
Glycogen is created when food is consumed and stored in the body until it is needed again (2). Insulin is an enzyme that converts the glucose in the food into glycogen.
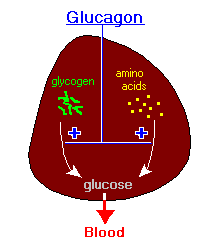
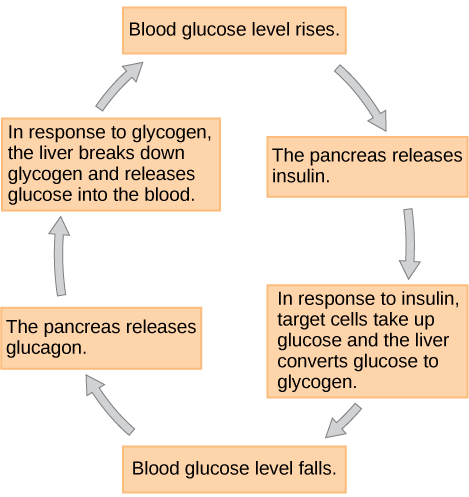
The Overall pathway
This is where L-carnitine plays its role. Mice fed a high-fat diet are able to lower their blood glucose levels when L-carnitine supplementation is given to them, as opposed to mice fed a high-fat diet without the supplement (3).
Another human study found the same result, which is that L-carnitine supplementation reduces insulin resistance and improves insulin sensitivity. The study also suggests that current diabetes patient management, which includes diet modification, medication administration, and physical activities, may be improved in the future with the consumption of supplements such as L-Carnitine (4). The study also suggests that consuming 3g of L-carnitine per day may improve diabetes symptoms, but this must be accompanied by medical professional consultation (4). However, some studies suggest that L-carnitine consumption may have some side effects, so the safe consumption level is less than 2g/day.

Due to the possibility that the general public might mistake it for a "magic pill" that would allow diabetes patients to eat whatever they wanted after taking it. The answer is no! A diabetes patient must still adhere to the diabetes diet, physical activity, and diabetes medication, but because diabetes is a progressive disease where the condition can worsen progressively, all actions, including supplement intake, may slow its progression (4).
Where can L-carnitine be found?
Apart from supplemented products, L-carnitines can be found naturally in foods such as beef and fish.
Beef: 81 mg/ 3 ounces
Pork: 24 mg/ 3 ounces
Fish: 5 mg/ 3 ounces
Chicken: 3 mg/ 3 ounces
Milk: 8 mg/ 3 ounces
References
-
WebMD. L – Carnitine. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1026/l-carnitine (Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Feedback Loop of Insulin and Glucagon. https://www.biologycorner.com/2017/08/22/feedback-loops-insulin-andglucagon/ (Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Randall L. Mynat (2009). Carnitine and Type 2 Diabetes. NCBI. PMC Journal. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5707127(Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Mingroe, Graco et al., (1999). L- carnitine Improves Glucose Disposal in Type 2 Diabetes Patient. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10067662/#:~:text=Conclusions%3A%20L%2Dcarnitine%20constant%20infusion,also%20observed%20in%20normal%20subjects (Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Healthline. L – Carnitine: Benefits, Sides Effects, Sources and Dosage.https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/l-carnitine (Accessed on July 13,2020).




