Erectile Dysfunction: Is it taboo or a health concern?
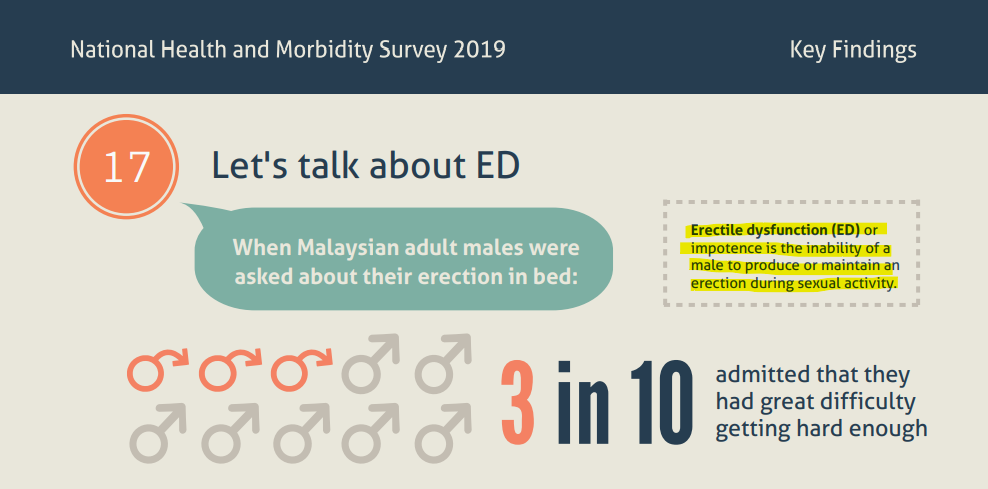
Globally, it is estimated that 100 million men have ED problems, but even with such a figure, ED is considered a taboo topic to discuss because it is considered an embarrassment, and people do not want to seek medical help for it. It is not taboo to discuss ED because it is a health issue. Sexual well-being is one component of overall health, and as we age, our bodies do not function as well as they used to, which is why ED is common in men aged 40 and older.
ED can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical, psychological, and social factors. Physical factors such as heart disease, atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, liver or kidney problems, Peyronie's disease, and alcoholism are common among older men. These medical conditions typically affect the nerves and blood vessels that control erections, which explains why people with such conditions are more likely to develop ED. Psychological factors can also contribute to ED. Worry about being unable to achieve or maintain an erection, as well as prolonged emotional distress related to economic, professional, social issues, relationship conflicts, and depression can all distract a man of any age from becoming aroused.
Stendra (avanafil), Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra or Staxyn (vardenafil) are some of the most commonly prescribed erectile dysfunction treatments. Aside from medication, lifestyle changes such as exercise, healthy eating, stress management, and adequate sleep will also aid in the treatment of this condition.
According to the study, not all types of exercise help with ED; exercise such as cycling might not be helpful for ED, according to the National Health Service, UK; however, weight-bearing exercise can increase the natural production of testosterone, which is a significant factor in erectile strength and sex drive. Apart from weight-bearing exercise, kegel exercises, which improve your pelvic floor, yoga, and aerobic exercise, which are targeted to improve stamina and overall fitness, also help. In general, exercise will improve sexual health as it improves blood circulation, hormone regulation, stamina, and endurance, thus improving sex drive and erection problems.

Apart from exercise, nutrition also plays an important role in ED. A study found that men with a 42-inch waist are 50% more likely developing ED than men with a 32-inch waist. Also, being obese increases men's risk of getting vascular diseases and diabetes, which contributes to ED. Reduce or stop smoking, and consuming alcohol has also shown tremendous positive effects on ED problems. Smoking for a long time affects the vascular health; it causes the blood supply to the penis to become restricted due to blockage or narrowing of the arteries, thus causing the erection problem. While, as for the consumption of alcohol, it suppresses the central nervous system that is responsible for releasing nitric oxide (a chemical that is responsible for producing and maintaining an erection), which is why the more men drink alcohol, the more likely they are to have an ED problem.
In conclusion, talk to your doctor regarding your condition. You might think that your condition is too petty to discuss, but by letting your doctor know about it, it gives a different perspective to your whole treatment plan.
References
- Everyday Health (n.d). Naturqal Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.everydayhealth.com/pictures/lifestyle-changes-natural-treatments-erectile-dysfunction/ (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Healthline (n.d). Erection Problems. https://www.healthline.com/health/erection-problems (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Medical News Today (n.d). Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/5702 (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- National Health Service, United Kingdom. Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/erection-problems-erectile-dysfunction/ (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- National Institute of Health (NIH), National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive, and Kidney Disease (NIDDK). Symptoms & Causes of Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/symptoms-causes (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Mayo Clinic. Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/erectile-dysfunction/symptoms-causes/syc-20355776 (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Everything you need to know about ED. https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction#symptoms (Accessed on March 2, 2021).




