A Guide to Heart Health
The heart serves as a pivotal organ within the body, facilitating blood circulation and ensuring the distribution of vital nutrients to all its corners (1). Beyond its circulatory role, the heart plays a vital part in shielding the body against infections (1). Moreover, it contributes to regulating body temperature and upholding fluid equilibrium (2). Given these multifaceted functions, the heart emerges as a cornerstone of bodily well-being; even minor irregularities can set off significant repercussions throughout the human system (2).
There are several effective strategies to ensure the well-being of your heart:
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity and Maintain a Healthy Weight
If you find yourself struggling with excess weight, it's crucial to acknowledge that this condition can elevate your risk of developing high cholesterol and blood pressure, both of which can adversely impact your heart health (3). In light of this, striving for a healthy weight becomes a priority. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that individuals aged 18 to 64 incorporate a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity into their weekly routine. Alternatively, dedicating at least 75 minutes to vigorous-intensity physical activity is also effective. Additionally, breaking down your aerobic exercises into segments of at least 10 minutes each can contribute to optimal results.

- Limit Salt Intake and Minimize Oily Foods
Excessive salt consumption has been linked to elevated blood pressure, which escalates the risk of heart disease. It's advised that adults keep their daily salt intake below 6g, and strive to opt for foods containing no more than 1.5g of salt or 0.6g of sodium per 100g whenever feasible (4). Moreover, it's beneficial to reduce the consumption of oily foods. Oils typically encompass a blend of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fats. Prioritizing options low in saturated fatty acids (SFA) while favoring those rich in unsaturated fats can effectively contribute to lowering cholesterol levels (5). For instance, heart-healthy oils like grapeseed, avocado, and olive oils are commendable choices (5). Embracing a diet low in salt content is pivotal in sustaining optimal blood pressure levels.
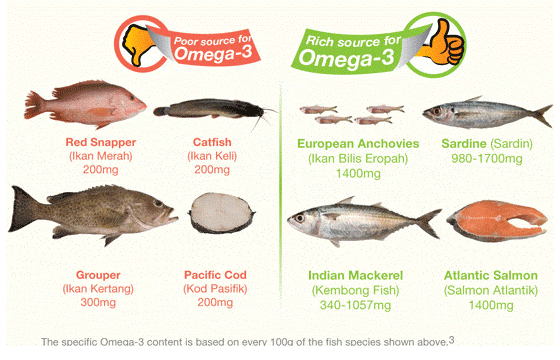
- Incorporate More Fish into Your Diet
Including more oily fish in your diet can offer substantial benefits for your heart health. Oily fish varieties are rich sources of Omega-3 fatty acids, compounds known to effectively lower cholesterol levels, decrease blood pressure, and mitigate the risk of blood clot formation (4). These vital advantages underline the importance of including these types of fish in your meals. Noteworthy examples of fish abundant in Omega-3 fatty acids include:
- Manage your cholesterol level
Maintaining a healthy cholesterol level is pivotal in preventing coronary heart disease. Excess cholesterol can accumulate within your artery walls, potentially leading to the development of plaque—a phenomenon known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this accumulation can narrow the arteries, impeding the smooth flow of blood. Ultimately, reduced blood flow can manifest as chest pain or, in severe cases, a heart attack if a blood vessel becomes completely obstructed (7). Thus, it is imperative to address cholesterol levels to safeguard cardiovascular well-being. Normal total cholesterol levels should ideally remain below 5.2 mg/dL.
References
- News Medical Net (n.d). Structure and Function of the Heart. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Structure-and-Function-of-the-Heart.aspx
- Patient Direct. Anatomy and Physiological Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. https://www.ptdirect.com/training-design/anatomy-and-physiology/major-functions-of-the-cardiovascular-system-2013-a-closer-look
- News Medical Net. Structure and Function of Heart. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Structure-and-Function-of-the-Heart.aspx
- Lloyd Pharmacy. 10 Healthy Ways to Take Care of Heart. http://blog.lloydspharmacy.com/health/10-ways-take-care-heart-health/
- Garavaglia J, Markoski MM, Oliveira A, Marcadenti A. Grape seed oil compounds: biological and chemical actions for health. Nutr Metab Insights. 2016;9:59-64. doi:10.4137/NMI.S32910
- World Health Organization 2010; Global recommendations on physical activity for health.WebMD (n.d). Cholesterol




