Differences between Omega 3, 6, and 9

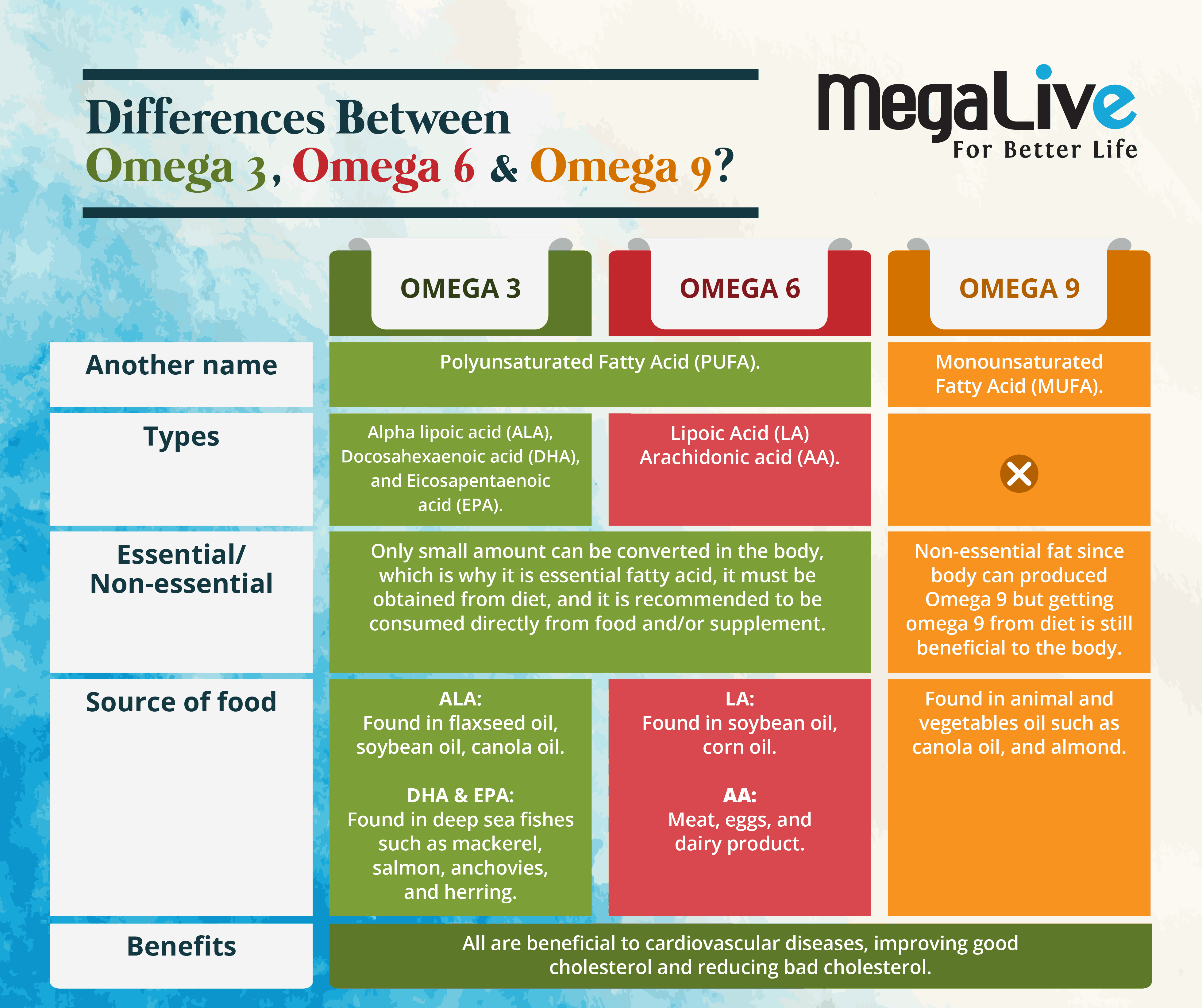
The infographic above explains the types of good and bad fats. But what about the differences between Omega 3, 6, and 9? All these three fats can be considered good fats, but there are certain things that distinguish them from one another.
MUFA or Omega 9
Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), also known as omega 9, is named because of the double bond position, which is on the ninth position from the omega end. It is a type of fat that is found in vegetable and animal fats such as canola oil, sunflower oil, olive oil, and nuts. Unlike polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), omega-9 is a non-essential fat, which means the body is able to produce these types of fat. However, there are also benefits when it is obtained from food, such as reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke, reducing LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol), increasing HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol), and helping to eliminate plaque buildup in the arteries, which can cause heart attacks and strokes.
PUFA or Omega 3 & Omega 6
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) can be divided into Omega 3 and Omega 6. The difference between these two is that the position of the double bond for Omega 3 is in the third position from the end, whereas for Omega 6, it is in the sixth position from the end.
Among the types of Omega 3 with extensive scientific research are eicosapentanoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-lipoic acid (ALA). The difference between these three types of Omega-3 fats is the number of carbon atoms: 18, 20, and 22 for ALA, EPA, and DHA, respectively. ALA can be converted to EPA and then to DHA, but the conversion, which usually occurs in the liver, is less than 15%, which is why it is recommended to consume EPA and DHA directly from foods or dietary supplements. ALA is present in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils. DHA and EPA are present in fish, fish oils, and krill oils. But the DHA and EPA in krill oil do not originate from krill but rather from the ingestion of microalgae.
Whilst, among the types of Omega 6 are linolenic acid (LA) and arachidonic acid (AA), The difference between these two is the position of the double bond in the omega-6 fatty acid chain. Linolenic acid (LA) is the same as ALA; it is an essential fatty acid that cannot be produced by the human body. Sources of food with LA are soybean oil, corn oil, safflower oil, peanut oil, cottonseed oil, and rice bran oil. While the sources of food for AA are peanut oil, meat, eggs, and dairy products,
Omega 3 and Omega 6 are beneficial for cardiovascular diseases because they can help manage cholesterol levels, triglycerides levels, and blood pressure levels. There is also certain supporting data that states that it can help with reducing weight and waist size, improving infant brain development in the foetus, and fighting inflammation. However, other than for cardiovascular health, the finding is quite inconclusive. But as for Omega 3 and 6 (PUFA) and heart health, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that 8–10% of calories should come from PUFA, as there is evidence that eating more PUFA—up to 15% of daily calories—in place of saturated fat can lower the risk of heart disease.
The diagram below shows the comparison between these three types of good fat:
All in all, Omega 3, 6, and 9 are beneficial for cardiovascular health, as they can help with lowering LDL levels (bad cholesterol), increasing HDL levels (good cholesterol), and helping with blood pressure levels. Several other studies also mentioned that certain good fats can help with inflammatory diseases such as joint pain and skin diseases such as eczema. However, consumption of all these fats must be in balance since overconsumption of them can have serious health effects! However, replacing bad fat (or even good fat) with refined carbohydrates does not help your health either. It is so important to note that everything must be in balance, and consuming healthy food is not about one type of food only; it is about variety, quality, and the food source as well!
References
-
Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH). Hyperlipidemia.
-
Harvard T.H Chan. School of Public Health. Types of fat. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/types-of-fat/
-
Harvard T. H Chan. School of Public Health. Saturated fat or not does type of fat matter. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2014/05/15/saturated-or-not-does-type-of-fat-matter/
-
Healthline. Omega 3, 6, and 9. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/omega-3-6-9-overview#omega-6




