Normally, uric acid dissolves in the blood and passes through kidneys and excreted in urine. But when there is too much uric acid in the body, uric acid crystals (monosodium urate) will build up in joints, fluids, and tissues within the body. The build up will become sharp needle like crystal compound in joint or in the surrounding tissue that will cause pain, inflammation and swelling in the affected joint area.
Sometimes hyperuricemia does not cause gout, which also refer to as asymptomatic hyperuricemia. This condition does not need to be treated but efforts should be made to lower the uric acid levels by encourage individuals to make changes in their diet or lifestyle.
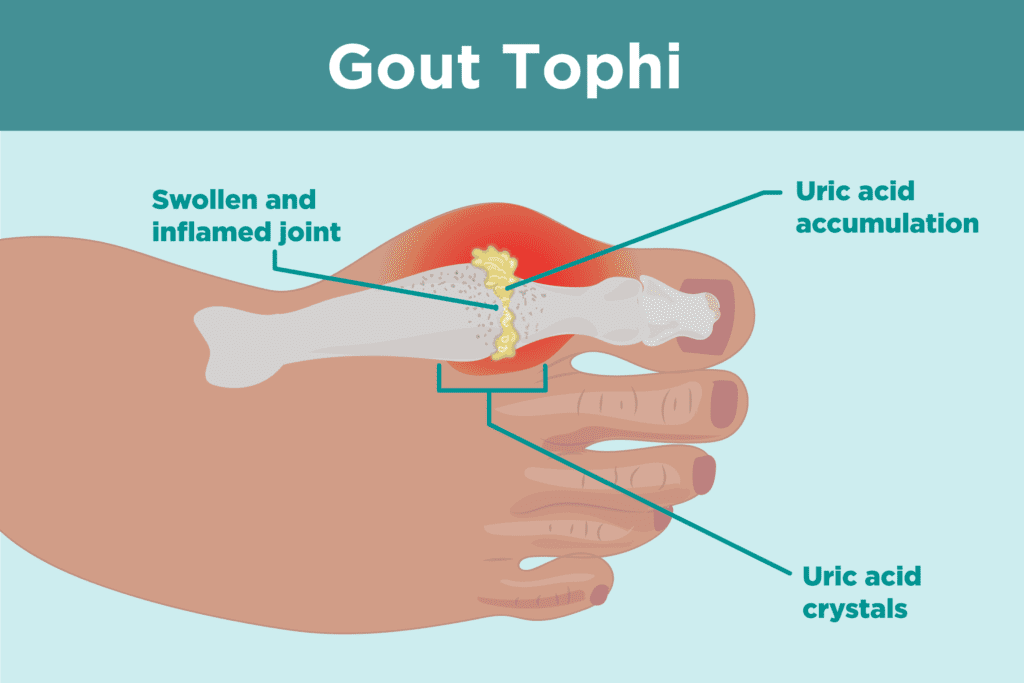
What are the sign and symptoms for gout? (1,4)
Sign and symptoms for gout occur when there is appearance of inflammation and swelling in the joint are, this condition usually refers to as acute gout attack. Usually during this condition symptoms below can be seen:
Intense joint pain. Usually it affects the large joint in the big toe area, but it can occur in any joint. Other commonly affected joints include the ankles, knees, elbows, wrists, and fingers. The pain is likely to be most severe within the first 4 to 12 hours after its presence.
Lingering discomfort. After the most severe pain subsides, some joint discomfort may last from a few days to a few weeks.
Inflammation and redness. The affected joint or joints become swollen, tender, warm and red.
Limited range of motion. As gout progresses, individuals may not be able to move joints normally, as it will becoming stiff.
For gout there will be times when symptoms get worse, known as flares, and times when there are no symptoms at all, known as remission. Repeated attack of gout can lead to gouty arthritis, a worsening form of arthritis.
What are the risk factors for gout (5)?
There are factors which makes individuals are more susceptible to gout as compared to others:
- Male
- Being Obese

- Have certain health condition such as hypertension, diabetes, and poor kidney function
- Using certain medication such as diuretic pills
- Excessive drinking of alcohol
- Frequently have diet that is high with purine
How gout is diagnosed? (1,5)
Doctor usually diagnose gout based a review of your medical history, physical examination, and the symptoms. However, as for gout as people in Malaysia rarely do blood test thus the only time, they found out that they have gout is when their big toe is already at stake. Usually when you meet doctor with presence of tophi or podagra, the doctor usually will manage or treat the condition as gout until proven otherwise. Doctor will usually further confirm this via X-ray to see if there is any stone, or through your blood result where your uric acid level will be measure. Sometimes doctor can also take fluid sample from your joint to confirm whether it contains uric acid (4).
How gout is treated? (1,5)
Gout is usually treated by managing the pain of flare. Treatment of flare consists of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID), like ibuprofen, steroids, and the anti – inflammatory drug colchicine.
However as to prevent from the future flare, changes in lifestyles is a must. Losing weight, eat less purine-rich food (like red meat or organ meat), limit alcohol consumption, and drinking plenty of water will help to prevent future attack.
In order to prevent gout from happening, it is none other than to live a healthy lifestyle, eat diet in balance, variety, and moderation manner. Exercise frequently. Always make sure your weight is in the healthy range of weight for your height and frequently conduct medical check up to see if there is any changes in your blood result as our age increases.
References
- Centre of Disease Control (CDC). Gout. https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/gout.html (Accessed on November 26, 2020).
- What is gout? https://www.webmd.com/arthritis/arthritis-gout (Accessed on November 26, 2020).
- American Family Physician Foundation (AAFP). Gout and Hyperuricemia. https://www.aafp.org/afp/1999/0215/p925.html#:~:text=The%20peak%20incidence%20occurs%20in,changes%20in%20diet%20or%20lifestyle. (Accessed on November 26, 2020).
- Mayo Clinic. Gout. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gout/symptoms-causes/syc-20372897 (Accessed on November 26, 2020).
- Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG). Gout. Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH).




