Find out more about your health here from our health professionals!


Healthy hair, radiant skin, and strong nails rely on specific nutrients, and several scientifically-backed compounds play vital roles in enhancing these features.
Fish Collagen Peptides
Collagen is a structural protein essential for skin elasticity and hydration. Fish collagen peptides are particularly effective at promoting collagen synthesis and improving skin texture. They also support nail strength and hair health by maintaining the protein matrix that underlies these tissues
Hyaluronic Acid
Known for its unparalleled hydrating properties, hyaluronic acid retains moisture in the skin, improving suppleness and reducing fine lines. This hydration benefits not only the skin but also the scalp, fostering an optimal environment for healthy hair growth
L-Cysteine
This amino acid is a precursor to keratin, a fundamental protein in hair and nails. By reducing oxidative stress and enhancing keratin production, L-cysteine supports resilience and growth in both hair and nails
Zinc and Selenium
Both zinc and selenium are critical for maintaining the structural integrity of skin, hair, and nails. Zinc regulates oil production in the skin and strengthens hair follicles, while selenium acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage
Biotin (Vitamin B7)
Biotin is celebrated for its role in metabolic processes, aiding the formation of healthy keratin. This makes it a powerhouse nutrient for combating brittle nails and promoting thicker, shinier hair
Together, these ingredients offer a synergistic approach to enhancing the health of hair, skin, and nails, combining hydration, structural support, and antioxidant protection.


Herbal remedies have long been revered for their ability to promote health and vitality, especially for women. A combination of potent natural extracts like Cynanchum wilfordii, Angelica gigas, Phlomis umbrosa, and Humulus lupulus offers a holistic approach to addressing the unique health challenges women face at various stages of life.
Key Ingredients and Their Benefits
Holistic Health Benefits: A Natural Solution for Every Stage of Life
The synergy of these herbs provides comprehensive support for women across different stages of life, from hormonal imblances during menstruation to the challenges of menopause. From enhancing energy and managing hormonal changes to supporting bone and joint health, these extracts offer a natural and effective approach to overall well-being. Their use in traditional medicine, combined with modern research, underscores their safety and effectiveness in supporting women’s health.
However, as with any herbal-based supplement, it is important to note that some herbal ingredients may be contraindicated with certain medications, particularly for women in menopause. The older we get, the more health concerns we may encounter, often requiring medication. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal remedies into your routine, ensuring they are compatible with your current health regimen.
References

Skin is the largest organ in our body. Not only that it functions as to protect our body from microbes and the elements, it also helps to regulate body temperature and permits the sensation of touch, heat and cold.
There are many factors influencing skin condition, but in this post, we are going to share on tips on how to make your skin glow!
As much as smoking is bad to your lung so does it to your skin
Cigarette smoke contain many harmful substances to our body, as we know. However as for the skin, it releases carbon monoxide which displace oxygen in your skin and nicotine which reduce blood flow which will make skin dry and discolored. Smoking also triggers the destruction of collagen in the skin hence skin loss its elasticity and produce wrinkles and fine lines!
When you are younger and a smoker you cannot really see the difference but as you get older, the damage on your appearance will be obvious and you will be looking older as compared to your actual age (1).

Sunscreen is a must
Malaysia is a humid and warm country all year long; thus, wearing sunscreen is a must! Sunscreen helps protect skin from premature ageing like wrinkles, fine lines, and hyperpigmentation. Studies show that people who are under 55 years old and wear sunscreen regularly can lower their risk of premature ageing by 24% as compared to those who wear sunscreen occasionally or not at all.
If you are a newbie looking for sunscreen, look for sunscreen with at least SPF 30 (Sun Protecting Factor) and choose sunscreen according to your skin type, such as aqua sunscreen, which is meant for dry skin, etc. You also must apply sunscreen every 2 hours or after exercise. Sunscreen should also be applied at least 30 minutes before going out, as it requires time to be absorbed by the skin and activated in order to protect your skin (2).
Move, Move, Move
We know that exercising regularly can keep our bodies fit and healthy, but did you know that it can also keep your skin healthy?
Exercise increases blood circulation and flow throughout the body, hence making your skin radiant and glowing. Pssttt…you can kill twoi birds with one stone by doing this; you can keep your body lean while also getting healthy skin! (3)
Keep your body hydrated
Our skin is exposed to various conditions: cold due to the air conditioner, warm due to the water, etc., so drinking plenty of water will make our skin condition better. Everybody is born with a particular skin type, whether it is dry, oily, or a combination; however, all these surrounding factors and age factor can change skin condition as well (4, 5).
In order to see whether your skin is dry, try to pinch it in an area and see whether it has a wrinkle on it after your pinch or whether it bounces back after your pinch, which is an indicator for well-hydrated skin. Wrinkles and less bouncy skin are indicators of dry skin; it can also sometimes be seen based on your urine colour if it is too concentrated, meaning your body does not get a sufficient amount of water (4, 5).
Lifestyle changes can reverse this; drink at least 8 glasses of water per day. Limiting the intake of alcohol and drinking less caffeinated drinks like coffee and tea can improve the dry skin condition (4).
Face and manage your stress.
We used to believe that suppressing our feelings and emotions was better for everyone, including ourselves. However, that is not always the case; we have to deal with it and manage it. Talk to someone if you have a problem; share it with someone that you trust. Think positive.
Pick up some hobbies, distract yourself from overthinking about it, and slowly find solutions. Doing outdoor activities can help calm a person if their mind is too saturated with a lot of stuff, or spending time alone can de-clutter their mind and create more space. Cleaning can sometimes make you a lot happier and help you think better about the solution to your problem.
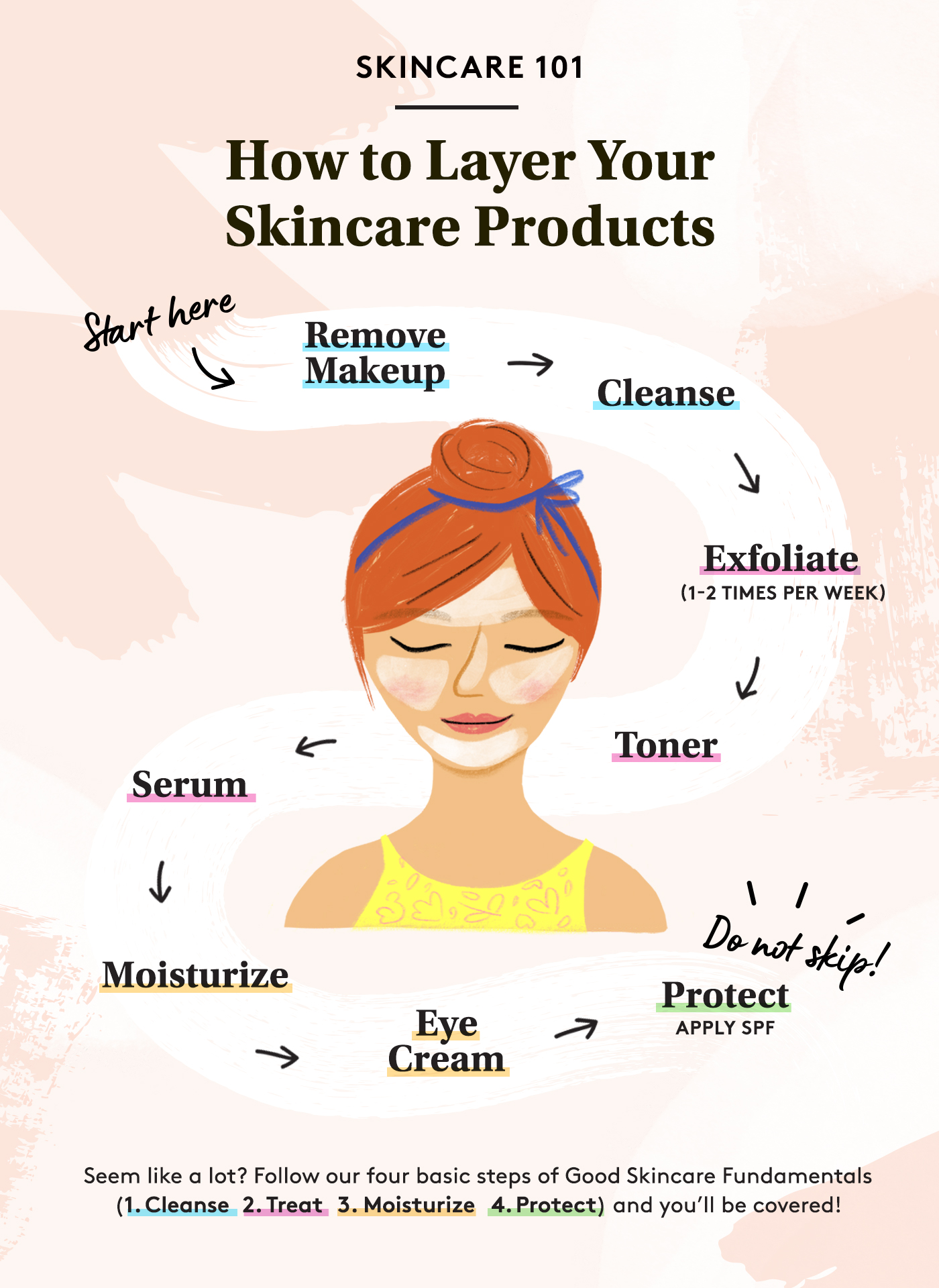
Established a skincare routine
Skin care is essential for keeping skin in good condition. A good skin care routine will improve skin condition, but only if the products used are of high quality.First, you have to find out your skin type. Normal skin, dry skin, oily skin, and combination skin are the four skin types.
To determine your skin type, start by washing your face and then waiting an hour. After it’s been an hour, dab your forehead and nose with a tissue and check to see if any oil has rubbed off. If it did, it’s a sign that you have oily skin. If there isn’t any oil but your face feels dry and tight, you may have dry skin (4,5).
Once you have figured out your skin type, find the right product for it. The common one should have cleanser, moisturizer, toner, sunscreen, exfoliator, and makeup removal. Start with cleansing your face at least twice per day. If you need to exfoliate your skin at least twice a week, this is a good time to remove all of the dead cells, dirt, and blemishes on your face (5).
Once you have done these, your skin is now ready to absorb all the good nutrients from your skincare, so now is the time for you to apply toner and moisturizer. Toner and moisturiser are good for hydrating the skin. After that, the skin is completely moisturized.You can now apply sunscreen.After sunscreen, it is time for you to wear makeup. If you are wearing make-up, make sure to thoroughly clean it at the end of the day using make-up removal and start your nighttime skin care routine as per daytime (5).
The only difference between a daytime and nighttime skincare routine is that moisturiser used on the skin is encouraged to be applied thickly at night so that the skin is not dry in the morning!
There are also people who want to give extra care and a boost to their skin; they can try to use serum. Serum is a product that is very concentrated with good vitamins for the skin, like vitamin A, C, and E. It’s usually used to fade scars or add more vitamins to the skin. However, the correct order of using skincare products is important; if not, skin cannot absorb the nutrients that the product has, and it will just go to waste (5).
Diet vs skin condition
As much as sugary food is bad for your waistline, so is it for your skin! Acne and breakouts can be exacerbated by sugary foods.Sugar and foods high on the glycemic index (meaning foods that, once ingested, convert quickly into glucose and cause your body’s insulin levels to elevate) lead to a burst of inflammation that goes throughout your entire body (6).
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is a very common vitamin used to make skin become radiant and glow. Vitamin C-rich foods are often used to boost skin conditions. Fruits like guava are really rich with vitamin C; it even has twice the content of vitamin C in an orange!
However, if one is a picky eater, it is also best to actually consume a vitamin C supplement rather than apply it topically (topical application). On the market, there are many types of vitamin C supplements. Most of it has really high vitamin C content, such as 500 mg or 1000 mg. However, according to the RNI (recommended nutrient intake), our body only needs about 70 mg of vitamin C, so the higher dosage of the vitamin will just be excreted through urine.
On the supplement ingredients list, you can see whether the supplement is made from natural or synthetic ingredients.Synthetic vitamin C is called ascorbic acid; it usually irritates the stomach and has a higher dosage of vitamin C as compared to vitamin C that is derived from natural fruits like berries, guavas, oranges, etc.
Synthetic vitamin C or ascorbic acid is also usually coloured with food colouring to make the supplement look as if it has a high content of vitamin C. If you notice that your soluble vitamin C supplement stains your glass of water after being diluted in it, there is a high probability that the supplement that you are taking has food colouring in it.
So be wise in choosing your vitamin C supplements. In order to make your skin glow, know how to find good vitamin C. Remember, it has to be derived from a natural source with no coloring, and the content of the vitamin C does not need to be too high!
References

Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer deaths especially among women around the world. The development of breast cancer is a multi-step process involving multiple cell types, and its prevention remains challenging in the world. In general, breast cancer results from abnormal and uncontrolled division of the cells in the lobules (milk producing glands) or the ducts (11).
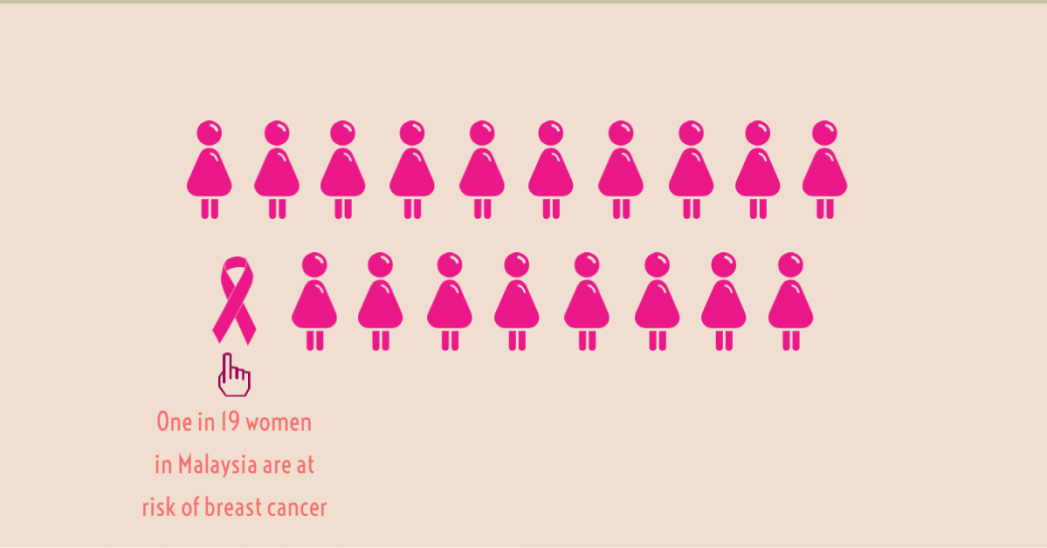
Breast cancer is the most common cancer affecting women in Malaysia. One in 19 women in Malaysia are at risk compared to one in eight in Europe and the United States. According to Malaysia Breast Cancer Foundation, female breast cancer cases reported 65% of women were between age of 40 to 60 years old whereas a total number of incidents with 59.7 Chinese women, 55.8 Indian women and 33.9 Malay women per 100,000 respectively. Unfortunately, 40% of the reported new cases were already in the very advanced stages of the disease (4).
However, of all breast disorders, palpable breast lump is the second most common presentation and important cause of anxiety and fear of cancer (8). Breast lump often found during breast self-exam or breast exam by medical professional. Lumps found one of these ways are called palpable masses or palpable lesions where something that you can touch or feel (11).
How to know if a breast lump is normal or abnormal?
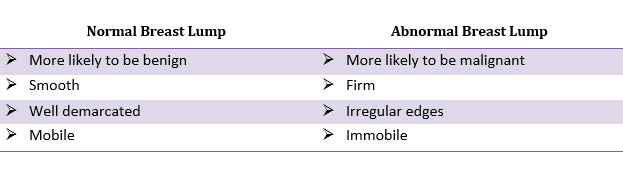
By comparison to breast cancer (carcinomas), benign breast lump often smooth, well demarcated dominant masses that are mobile whilst breast cancer is more likely to be malignant include firmness with poorly defined margins, irregular edges, immobility, or fixation to the surrounding tissues (3,10).
“The most common causes of breast lump or palpable masses can be cysts, fibroadenomas, and carcinomas. Breast cysts is a fluid filled sacs or a water- filled balloon inside the breasts. Cysts are normally round or oval which has distinct edges, smooth, firm, and mobile (9). Meanwhile, fibroadenomas commonly found in women in their 20’s and 30’s, but they can be found in women at any age. They tend to shrink after a woman goes through menopause (2). Both cysts and fibroadenomas are generally benign or harmless but it is important for women to have regular breast exams or imaging test before any symptoms appear. Of all breast disorders, carcinomas are a type of malignant breast lump where a tumor or mass start in the epithelial cells that line organtissues such as adenocarcinoma (3).”
In short, breast self-exam, or regularly examining your breasts on your own, can be an important way to find a breast cancer early, when it is more likely to be treated successfully.

Sign and Symptoms of Breast Cancer (1)
The most common symptom breast cancer is a new lump or mass that is painless, hard and has irregular edges. However, it can also be tender, soft, or round and can even be painful.
Women need to be aware of changes in your breast and to know signs and symptoms of breast cancer. This is because sometimes mammograms or regular breasts check do not find every breast cancer.
Other possible symptoms of breast cancer may include:
Although some of the symptoms may be caused by things other than breast cancer, if you have them, they should be reported to health care professional and have screening tests.
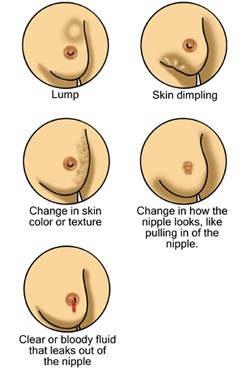
Source: Breast Cancer Foundation
Risk Factors of Breast Cancer (5,11)
No one knows for certain what causes breast cancer. However, a number of risk factors are known to increase the chance of developing breast cancer. Some of the risk factors are beyond control, while some are linked to cancer-causing factors in the environment or due to lifestyle and personal choices such as pregnancy, smoking and drinking.
Woman is the most significant risk factor for developing breast cancer. This is due to women’s breast cells are constantly changing and growing as a results of the activity of the female hormones estrogen and progesterone.
As we age, you could be at higher risk of getting breast cancer. From age 30 to 39, the risk is 1 in 228, or .44%. That jumps to 1 in 29, or just under 3.5%, by the time you are in your 60s.
If you have a first-degree relative (mother, daughter, sister) or multiple relatives affected by breast or ovarian cancer (especially before they turned age 50), you could be at higher risk of getting breast cancer.
Women who have no children (nulliparity) or who had their first child after age 35 have a higher breast cancer risk.
Multiple pregnancy or become pregnant at an early age reduces breast cancer as breastfeeding will reduce their estrogen level and hence reduce the possibility of breast cancer risk.
Pregnancy changes the lobules inside the breast and that the lobules of women who have carried a pregnancy to term differ from those of a woman has not been pregnant. Thus, it may be that breast-feeding reduces breast cancer risk by changing the mammary gland in specific ways.
Women using oral contraceptive have a slightly greater risk of breast cancer than women who have never used them.
Long-term use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) after menopause, particularly oestrogen and progesterone combined, may slightly increase your risk of breast cancer.
Use of alcohol slightly increased risk of developing breast cancer.
Obesity has been found to be a breast cancer risk factor especially for women after menopause. Having more fat tissue can increase your estrogen levels and increase your likelihood of developing breast cancer as fat tissues will produce estrogens as well.
Studies of fat in the diet have not clearly shown that this is a breast cancer risk factor. However, most studies found that breast cancer is less common in countries where the typical diet is low in total fat, low in polyunsaturated fat, and low in saturated fat.
REFERENCES

This is because, breastmilk is the ideal food for infants. Breastmilk provides all the energy and nutrients that the infant needs for the first months of life, and it continues to provide up to half or more of a child’s nutritional needs. From the age of 6 months, children should begin eating safe and adequate complementary foods while continuing to breastfeed for up to 2 years and beyond. Other than that, breastmilk also contains antibodies which help protect against many common childhood illnesses.

Breastfed children perform better on intelligence tests, are less likely to be overweight or obese and less prone to diabetes later in life. Women who breastfeed also have a reduced risk of breast and ovarian cancers.
However, how about the mother nutrition, should lactating mother eat more, for the sake of the baby?
Breastfeeding mothers generally need more calories to meet their nutritional needs while breastfeeding. An additional 450 to 500 kilocalories (kcal) of healthy food per day is recommended for well-nourished breastfeeding mothers, compared with the amount they were consuming before pregnancy (approximately 2,300 to 2,500 kcal per day for breastfeeding women verses 1,800 to 2,000 kcal per day for moderately active, non-pregnant women who are not breastfeeding). The number of additional calories needed for an individual breastfeeding woman is also affected by her age, body mass index, activity level, and extent of breastfeeding (exclusively breastfeeding verses breastfeeding and formula feeding).
To get these extra calories, focus on making healthy choices to help fuel your milk production. Choose for protein rich food, such as lean meat, eggs, dairy, beans, lentils and seafood low in mercury. Choose variety of whole grains as well as fruits and vegetables.
Eating a variety of foods while breast-feeding will make your baby have variety of complete nutrients through the breastmilk. But, if you are picky eater or a juggler who does not have time to eat, then discuss with your healthcare provider for daily multivitamin to consume until you wean your baby.

Another essential thing for mother when it comes to breastfeeding, is water consumption, it is very important for a breastfeeding mother especially to drink enough water in order to produce milk and to not making your dehydrate as well.

Be wary of juices and sugary drinks, however. Too much sugar can contribute to weight gain — or sabotage your efforts to lose pregnancy weight. Too much caffeine can be troublesome, too. Limit yourself to no more than 2 to 3 cups (16 to 24 ounces) of caffeinated drinks a day. Caffeine in your breast milk might agitate your baby or interfere with your baby’s sleep.
If you are exclusive pumping breastmilk for your baby, consider pumping your breastmilk every few hours in order to make sure the milk supply imitate the baby breastfeeding hour.
What foods and drinks should I limit or avoid while breast-feeding?
Certain foods and drinks deserve caution while you are breast-feeding. For example:
Alcohol. There is no level of alcohol in breast milk that is considered safe for a baby. If you drink, avoid breast-feeding until the alcohol has completely cleared your breast milk. This typically takes two to three hours for 12 ounces (355 milliliters) of 5% beer, 5 ounces (148 milliliters) of 11% wine or 1.5 ounces (44 milliliters) of 40% liquor, depending on your body weight. Before you drink alcohol, consider pumping milk to feed your baby later.
Caffeine. Avoid drinking more than 2 to 3 cups (16 to 24 ounces) of caffeinated drinks a day. Caffeine in your breast milk might agitate your baby or interfere with your baby’s sleep.
Fish. Seafood can be a great source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. Most seafood contains mercury or other contaminants, however. Exposure to excessive amounts of mercury through breast milk can pose a risk to a baby’s developing nervous system. To limit your baby’s exposure, avoid seafood that is high in mercury, including swordfish, king mackerel and tilefish.
Remember, there is no need to go on a special diet while you are breast-feeding. Simply focus on making healthy choices — and you and your baby will reap the rewards.
References

There is actually no specific study that has confirmed whether foods that have these lactogenic properties are able to increase milk production. However, usually foods that are suggested to be consumed in order to increase milk production are food that is rich in specific ingredients which can stimulate hormones used for milk production.
Factors influencing breastmilk production.
Breastmilk production is based on supply-demand system. The more the baby needs the more milk will be produced. However, this is also depending on the many factors as well such as hydration, stress level, separation between mother and child, new pregnancy and many more.
Mechanism of action of breastmilk production
Production of milk is directly influence by two types of hormones, oxytocin and prolactin. There are other hormones which influence production of milk indirectly such as oestrogen and progesterone. When a baby suckles at the breast, sensory impulse pass from the nipple to the brain. In response, part of brain will then secrete prolactin and another part will produce oxytocin.
Prolactin is important for the secretion of milk by the cells. The level of prolactin hormone in blood increases markedly during pregnancy and stimulates the growth and development of the mammary tissue, in preparation of the production of milk. However, milk is not secreted then because progesterone and oestrogen, these hormones of pregnancy, block action of prolactin. After delivery, the levels of progesterone and oestrogen will fall rapidly, thus prolactin is no longer blocked, and milk secretion begins.
Oxytocin hormone is the one who control the reflex in the breast for breastfeeding which call the “let-down reflex” or the “milk ejection reflex.” Oxytocin is produced more quickly than prolactin. It makes milk that is already in the breast flow and helps the baby to get the milk easily. Oxytocin starts working when a mother expects a feed as well as when the baby is suckling. The reflex becomes conditioned to the mother’s sensations and feelings, such as touching, smelling, or seeing her baby, or hearing her baby cry, or thinking lovingly about him or her. If a mother is in severe pain or emotionally upset, the oxytocin reflex may become inhibited, and her milk may suddenly stop flowing well. If she receives support, is helped to feel comfortable and lets the baby continue to breastfeed, the milk will flow again. It is important to understand the oxytocin reflex, because it explains why the mother and baby should be kept together and why they should have skin-to-skin contact. Oxytocin makes a mother’s uterus contract after delivery and helps to reduce bleeding. The contractions can cause severe uterine pain when a baby suckles during the first few days.
Lactogenic foods and breastmilk production
Thus far, there is no study established that lactogenic foods or galactagogues foods can increase breastmilk production. Since production of breastmilk is based on ‘demand-supply’ system. Thus, the frequent the breast is emptied the more milk will then be produced. However, eating healthy food, helps in transferring all the good nutrients to the baby. Food that is high with vitamins and minerals can help baby in their development as well, thus breastfeeding mother is suggest to eat healthily and increase her calorie intake to 2300 to 2500kcal per day as compared to moderately active women which is about 1800 to 2000 kcal. Breastfeeding mother also need to need avoid certain food such as caffeinated drinks.
Mother is suggested to consume protein-rich foods, such as lean meat, eggs, dairy, beans, lentils and seafood low in mercury. Choose a variety of whole grains as well as fruits and vegetables.
Eating a variety of foods while breast-feeding will change the flavor of your breast milk. This will expose your baby to different tastes, which might help him or her more easily accept solid foods down the road.
To make sure both mother and baby are getting all of the vitamins you need, it is recommended to continue take daily multivitamin such as vitamin B12 if you are vegetarian or if you are underweight, you may try to achieve the 2500 kcal diet, or you may use oral nutrition supplement to top up, your daily nutrient intake.
If you find that, certain food has that lactogenic properties on your body, you may continue consume it as it can increase your milk supply, but what works for you might not works for others. It can also be said that, eating food that you like can make you happy thus less stress and make you produce more milk, but again do not over consume it!
References

Function of Calcium?
Body needs calcium for strong bones and teeth. Calcium is also required to carry out important function such as for muscle to move, for nerves system to carry messages between brain and body parts, for blood vessels to move blood throughout the body, and for body to help release hormones and enzyme that affect almost every function in the human body (1,2,3).
How much calcium is needed?
Normal adult need about 1000 mg of calcium daily, however there are certain condition which require to consume up to 1300 mg of calcium daily such as for pregnant lady, lactating mother, post-menopausal women, and man who is above 70 years old of age (1,2,4).
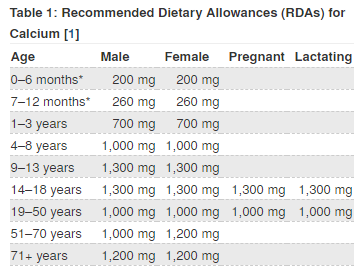
Calcium and diet
Body does not produce calcium, so it needs to be consumed from foods. Luckily, calcium can be found in variety of foods such as dairy products, dark leafy vegetables, fish, and many other fortified food products (1,2,3). As for our local food products sardine, anchovies, cencaluk, budu, tofu, tempeh, broccoli, kalian, and tapioca leaves are among food that is high with calcium (4).
It is also important to take note that in order to absorb calcium, body needs vitamin D. Only a few foods containing small amount of natural vitamin D, such as egg yolks and salmon with bones. Mostly, we rely on the exposure to sunlight in order to get enough vitamin D, of course in Malaysia the country with sun all year long have no problem with this! However, as currently we are still in the so to say the ‘lockdown’ phase thus it is very important to remind everyone to get the sunlight every day at least 20 minutes for its vitamin D and calcium absorption (1,2,4).
Though all the foods stated above are easily found, but there are conditions which hinder individuals from getting enough calcium from diet thus require it from calcium supplementation.
Condition for calcium supplementation
Before considering calcium supplement, individuals must understand how much calcium needs by the body (stated above). Then individuals must seek help from nutritionist, dietitian, pharmacist, or doctors, where they will assess your calcium consumption from your diet through diet recall. If the calcium intake falls short thus you need to top up calcium from supplement.
Hypertensive individuals and diet with large amounts of sodium.
Several literature reviews on topic of total calcium intake from food and supplements with regards to hypertension suggested that there is possible link to lowering high blood pressure. However, since most of the study design have small number of subjects, and were tested with people from different background, and not to mention possess various kind of biases thus making it difficult for scientist to draw conclusion (1,2).
However, a large study subject (Women’s Health Study), found out that calcium intake was inversely associated with risk of hypertension in middle-aged and older women, in terms of preventing hypertension (1,2).
The consumption of high sodium food lead to more calcium excretion through the urine, which will lead to constriction of blood vessels, which in the end resulting in high blood pressure. Drinking large water after consuming salty food, is not enough, as it may be making blood pressure return to its slightly normal condition, but it is not helping with the loss of calcium (1,2,5).
Pregnant and lactating mother
Often times, pregnant women is being reminded of how important is folic acid for the baby, even from the trying to conceive period, healthcare providers already advise them to consume folic acid, in order to prevent spina bifida to the baby. However, calcium is as well very important for mothers throughout pregnancy and lactating period especially for mother who is lack of calcium from diet (1).
Several professional organizations recommend calcium supplements during pregnancy for women with low calcium intakes to reduce the risk of preeclampsia (a condition where gestational hypertension always occur). For example, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (ACOG) states that daily supplementation with 1,500–2,000 mg calcium may reduce the severity of preeclampsia in pregnant women who have calcium intakes less than 600 mg/day. Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 1,500–2,000 mg calcium for pregnant women with low dietary calcium intakes, particularly those at higher risk of gestational hypertension (1).
As for normal healthy mother, the consumption of calcium is especially important during lactating period, mother may notice symptoms such as cramps which indicates lack of calcium during pregnancy and lactation period. Also if a mother is on iron supplementation as well, it is advisable to not consume both at the same time, it is best to gap several prior the consumption of these two since it can interfere with the absorption (1,2).

Throughout the lifespan, bones are constantly being broken down and built up in a process known as remodelling. Bone cells called osteoblasts build bone, while other bone cells called osteoclasts break down bone if calcium is needed. In healthy individuals who get enough calcium and physical activity, bone production exceeds bone destruction up to about age 30. After that, destruction typically exceeds production. This is sometimes called “negative calcium balance,” which can lead to bone loss. Women tend to experience greater bone loss than men later in life due to menopause, a condition that lowers the amount of hormones that help to build and preserve bone (5).
Getting enough dietary calcium at all ages may help to slow the degree of bone loss, but calcium intakes at any level are not known to completely prevent bone loss. Calcium is less easily absorbed at later ages, and therefore eating a very high amount of calcium will not always resolve the problem (5).

Individuals with lactose intolerance and limit dairy products
Individuals with lactose intolerance usually, is unable to consume food that has high amount of calcium especially if it come from milk and dairy source of food. Thus, lactose intolerance individuals need to consume it form dark leafy vegetables and soy-based product. However, in most cases the consumption is not enough or individuals with lactose intolerance consume not enough vegetable rich with calcium or other food source rich with calcium, thus for this specific population calcium supplementation is needed either from fortified food product such as ready to eat cereals or from calcium supplementation tablet itself.
Individuals receiving treatment on certain medication in the long period
Well, there are certain medication which can influence the absorption of calcium. Medication such as to treat osteoporosis (bisphosphonates), antibiotics (fluroquinolone), medication to treat low thyroid problem (levothyroxine), anticonvulsant (phenytoin), diuretic medication (Lasix and bumex), antacids containing aluminium and magnesium and also glucocorticoids (prednisone). These are all either causing calcium loss in the urine or cause calcium depletion in the bone. Thus, if you are on these medication, it is advisable to take calcium rich foods four hours prior or after the intake of medication, so that it would not interfere with the absorption of calcium, it is also best if you consume calcium supplementation if you do have poor intake of calcium rich food as well (2).
In conclusion, in these situations, calcium supplements may help you meet your calcium requirements. Talk with your doctor or dietitian about whether calcium supplements are right for you.
References

Omega-3-rich foods
The term "good fat" usually refers to omega-3 fatty acids. It regulates skin oil production, improves hydration balance, controls breakouts, and reduces signs of ageing. Furthermore, when applied topically, it can help soften rough, dry skin and soothe irritation and dermatitis. Omega-3-rich foods can improve skin composition by balancing its inflammatory response to sun damage, as well as improve sensitive skin condition by making it less dehydrated and dry.
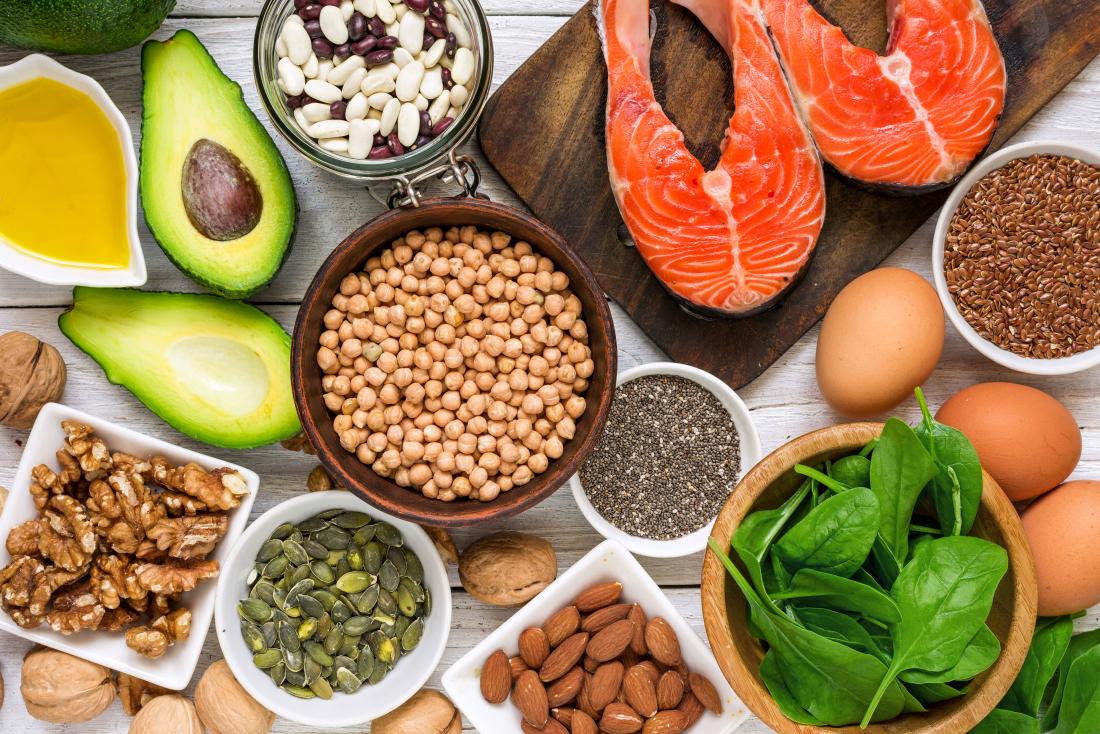

Fish is high in Omega 3 fatty acids. Specifically, fish oil. As a result, if an individual does not consume fish at all or prefers not to consume fish, it is recommended that they take Omega 3 and 6 supplements for their heart health. Omega-3-rich fish include mackerel, tuna, sardine and anchovies, salmon, and herring. Freshwater fish rich in omega 3 are also available in Malaysia, including catfish (ikan keli), patin fish, and terubok fish.
Aside from that, certain plant-based foods, such as spinach (bayam), mustard leaf (sawi), and 'salad roket,' contain high levels of omega 3. There are also omega-3-rich oils that can be used in cooking, such as canola oil. Also, if you want to improve the health of your skin, instead of snacking on chips or other unhealthy foods, try eating walnuts, which are high in omega 3.
Antioxidant and vitamin-rich foods
Plant-based foods, such as vegetables and fruits, are typically high in antioxidants and vitamins. Fruits and vegetables high in vitamins like C, E, and A are known as skin best friends.' All of these vitamins work in the same way when they engulf free radicals or reactive oxygen species (ROS). Free radicals can be produced naturally in the body, or as a result of UV radiation exposure, among other things. In other words, it is something that happens to everyone. As a result, it is critical to consume foods high in vitamins and antioxidants to combat all of the problems caused by free radical formation.
The Malaysian Ministry of Health recommends eating two servings of fruits and three servings of vegetables per day. The cupped hand size is used to determine vegetable serving size. As a result, 2 cupped hand size equals 2 servings. While the serving size for fruit varies depending on the type of fruit, 1 serving is equivalent to 1 fruit for medium-sized fruit such as apple, pear, and orange, while larger fruit is dependent on the normal cut sized. To simplify things, if you eat two apples, two pear, two bananas, or two oranges per day, you've already met the daily serving requirement.
Guava, orange, and lemon are examples of vitamin C-rich foods. Did you know that guava has twice the vitamin C content of an orange of the same size? Consuming 2 servings of guava or 1 small guava already meets your daily vitamin C requirement (75mg).

Almond, pumpkin, corn, collard, red bell pepper, and soy-based foods are examples of vitamin E-rich foods. According to research, Vitamin E or tocopherol works synergistically with Vitamin C to protect against UV radiation or sun damage.
Since most of the antioxidant- and vitamin-rich foods are mainly fruits and vegetables, it is essential to consume fruits and vegetables as suggested to have young looking skin!
Sugar
Sugar, as many people already know, is bad for your health because it raises your blood sugar level, which can lead to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other metabolic diseases. But it's also bad for your skin.
Sugar, in any form, has an impact on the two main causes of acne: hormones and inflammation. When you consume refined and processed carbohydrates, such as white sugar, your blood sugar levels rise faster, and your pancreas responds by releasing insulin. By avoiding sugar, you may be able to reduce the amount of insulin your body produces, which will reduce the oil and acne production.
Desserts such as cakes, tarts, cookies, 'traditional' kuih, and bakery products are high in sugar. Our daily staple foods are also high in refined carbohydrates or refined sugar. White rice, white bread, noodles, and flour-rich foods are all high in refined carbohydrates, which can harm the skin condition in the long run.
In conclusion, eating a healthy and well-balanced diet is the best way to achieve younger-looking skin. Consuming a lot of fresh products, limiting processed foods, oily foods containing trans fat, and sugary foods will help you not only have younger looking skin but also a healthier body!
References

Culturally, humans rarely consume placenta, but recently there has been growing interest in consuming placenta, be it from humans or animals. Mammals have been consuming placenta since years ago; it is called placentophagia, while in humans it is called placentophagy. The placenta could be served raw, cooked, or encapsulated and taken as a supplement as it contains various nutritional benefits.
Rave on this started when many Hollywood celebrities started using placenta therapy as part of their skincare routine treatment. Celebrities like Kim Kardashian, Victoria Beckham, and even male celebrities like Harry Styles from One Direction have said they have been using this for their skin to get baby-soft skin.
Placenta consumption in Malaysia.
In Malaysia, it is rare for people to consume raw placenta. Usually, it comes in health supplement form and is derived from deer or sheep. Hence, as it is in health supplement form, any products containing placenta extract in a pharmaceutical dosage will require to be registered with the Drug Control Authority (DCA) before they are sold or used in Malaysia.

Benefits of placenta consumption.
Findings from research reported that nutrients that are delivered via the placenta could be retained even after the process of delivering the baby. The research also stated that the placenta contains collagen, elastin, laminin, and vitamins such as B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, B6, B7, and B12. All these vitamins, better known as B complex vitamins, play roles in cell metabolism, cell division, cell development, and energy production.
Due to this aspect as well, it is said that it gives a lot of benefits to skin health. Placenta is even used in clinical settings, such as for burn injuries and wound healing. In one study, researchers compared the efficacy of topical placental extract dressings versus povidone iodine dressings in diabetic wounds in a variety of patients. Placenta wound dressings could significantly accelerate the rate of wound healing when compared to povidone-iodine dressings as they contained amino acids, vitamins, and nucleotides, which accelerated wound healing recovery by seven to ten days.
Due to all these effects, many skincare products have recently incorporated placenta, be it from sheep or deer, in their skincare or supplement products.

Caution with regard to placenta in the supplement
When it comes to placenta consumption as a health supplement, it is evaluated based on its safety of use and product quality. To be safe, sheep placenta products must be hormone-free. Because placenta typically contains hormones such as testosterone, oestrogen, and progesterone, being hormone-free is much more important for a placenta-based supplement. To confirm whether the products you are considering or consuming have been notified by the Ministry of Health, you can conduct an online product search on the National Pharmaceutical Registration Agency (NPRA). However, if the product is not listed in the DCA, it is not recommended that you consume it because its safety and quality have not been evaluated, and it may pose a health risk.
References
-260x200.jpg)
But, what if it is not in good condition? Is it hormonal in nature? Is it related to food? Is it hereditary? Is it any of these?
Yes, it is indeed all of these!
Skin that appears younger is closely related to lifestyle and genetics. According to research, there is a gene in the human body that controls our skin condition. Have you ever wondered why certain people of similar age but different appearances appear younger than their actual age while others appear older? The study by dermatologist professor Alexa B. Kimball from Harvard revealed that this has something to do with gene expressions.
According to the study, people with rapid gene expression speed up the skin-repairing process when exposed to external or internal stress, which is why they can maintain younger-looking skin. It has also been observed that some people who appear young have rapid gene expression that mimics those who are younger than their chronological age. According to the professor, the skin appears younger because it behaved younger (1)!
To elaborate, the one described above is known as intrinsic skin ageing, and it represents chronological ageing, with the same pattern affecting all internal organs. Extrinsic skin ageing, also known as aged skin, is caused by external factors such as environmental influence, particularly chronic sun exposure and ultraviolet (UV) irradiation, but also smoking, pollution, sleep deprivation, and poor nutrition. As a result, when it comes to skin, the best way to avoid harm is to avoid all of these extrinsic factors (1).
A study that compared sun-exposed skin (face and forearm) to sun-protected skin (buttock) among women aged 20 to 70 years old discovered that ultraviolet (UV) exposure is a major driver and accelerator of skin ageing. Although sun exposure without any skin protection, such as sunscreen, is harmful to the skin, there is a recommended amount of time spent outdoors without sunscreen so that UVB from the sun can activate vitamin D3 in the skin. The recommended exposure time is 5 - 30 minutes between 10 a.m. and 3 p.m., at least twice a week, to the face, arms, legs, or back (2). In Malaysia, where the weather is sunny all year, excessive sun exposure can cause skin damage. As a result, if one of your 2021 resolutions is to avoid sun damage, you should start wearing sunscreen religiously!
Apart from smoking and pollution, which can both cause skin damage, sleep deprivation can also cause skin to appear older. Sleep serves as a reset button for our entire health, including our skin. During sleep, the blood flow to the skin increases, and the organ rebuilds collagen and repairs UV damage, reducing wrinkles and age spots. According to research, sleep deprivation affects wound healing, collagen growth, skin hydration, and skin texture. Inflammation is also higher in sleep-deprived individuals, causing acne outbreaks, eczema, psoriasis, and sin allergies. To combat this, health experts recommend 7 to 9 hours of beauty sleep per day to achieve fluffy baby skin (3,4)!
Poor nutrition is also a major contributor to the appearance of older skin, and the worst culprit of all is sugar! Glycation is the process by which sugar interacts with skin. Younger-looking skin is always associated with firm and elastic skin, which refers to the cross-linking structure of skin fibres. This structure can repair itself naturally; however, when sugar is consumed, the glycation process renders the structure and renders the skin unable to remodel into its original structure. As a result, the youthful skin condition has vanished! This explain, sugar consumption is not only bad for metabolic conditions like diabetes mellitus, but also for skin conditions.
To summarise, the skin is the largest and most delicate organ; it may appear strong and capable of withstanding all of the external and internal harm that we inflict on it, but it, too, requires pampering. A good skincare routine will help with its condition, but it also requires good food, hydration, and sleep to keep everything in check and balance!
References


Functions of EPO in Women’s Health.
There are various functions of EPO, such as treating eczema, a condition in which the skin becomes inflamed, itchy, scaly, and flaky due to allergies or irritation. Besides, it has also been used to treat acne, psoriasis, and other skin conditions. Which explains why it is commonly used among women since a pretty appearance is something every woman desires (1, 2, 3).
Apart from this, it has also been used to relieve the physical and psychological symptoms of pre-menstrual syndrome (PMS), such as cyclical mastalgia (breast pain), mood swings, headaches, depression, food cravings, period cramps, irritability, bloating, fatigue, irritable bowel syndrome, and hormonal acne. According to the study, 85% of menstruating women are affected by these symptoms, and the study shows that there is significant improvement in the severity and duration of PMS in the group using EPO as compared to the placebo group (1, 2, 4). Researchers believe that some women experience PMS because they are sensitive to the level of prolactin that is produced during ovulation and increases during the luteal phase. So, what EPO does is that the active ingredients inside it (GLA) convert to prostaglandin E1 in the body, which is able to help prevent prolactin from triggering PMS (4).

As for women during menopausal age, EPO has been seen to help with menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes (the most common symptoms in the menopausal syndrome). A study among 56 menopausal women in the age range of 45–59 observed that there is a significant reduction in hot flash symptoms among menopausal women using EPO (4).

Dosage and what to be cautious of with EPO
Evening primrose oil is classified as a herbal supplement, and the dosage is determined by a variety of factors. Many studies currently recommend a daily dose of 1 -3g (1,4). There are some studies that mention or use higher dosages of EPO, but using higher dosages of EPO requires advice from pharmacist or doctor because it may have side effects. Consumption of medication such as schizophrenic medications, antiplatelet medication, anticoagulant medication, and seizure medication is also contraindicated with EPO consumption, which is why it is best to seek professional advice before consuming EPO as it may interfere with medication that you are consuming (1,4).
In conclusion,
EPO can help women with their hormone regulation from they reach their puberty age, post-delivery of the baby, and during menopausal age. Which is why it can be said as women B.F.F (best friend forever) throughout their healthy journey!
References

Numerous studies have shown that grape seed extract contains a high level of antioxidants. Using punctured wounded mice, researchers discovered that mice treated with GSE in the wound affected area grew tissue faster than mice treated with only normal saline. Another difference between GSE-treated mice and placebo-treated mice was more organized tissue formation and a higher rate of collagen deposition.
Topical application of 2% GSE cream in the area of a post-surgery surgical wound heals the wound completely in an average of 8 days, compared to 14 days for placebo. This is due to GSE's vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) properties, which promote the regeneration of damaged blood vessels while increasing the amount of free radicals present at the wound site. Free radicals aid in the killing and removal of pathogenic bacteria and endotoxin from the site, as well as in the healing of wounds
Apart from wound healing and skin health properties, it also has anti-ageing properties. GSE proanthocyanidins delay skin ageing by reducing lipid oxidation on the skin structure.
Cardiovascular and antihypertensive properties.
Cardiovascular disorders (CVD) are among the major problems that arise due to modern, unhealthy lifestyles, which are the primary cause of death worldwide. It is a disorder that affects the condition and function of the heart and blood vessels in general. Changes in these two can result in cardiac arrest, heart stroke, hypertension, chest pain, and other complications. Studies show that GSE may prevent atherosclerosis (a condition where there is a build-up of fats, cholesterol, etc. in the blood vessel walls, which can restrict blood flow), inhibit or limit the oxidation of LDL (bad cholesterol), reduce inflammation, inhibit platelet aggregation, and lower blood pressure. It lowers blood pressure by suppressing oxidative stress and inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and nitric oxide, which mediate vasodilation, hence making the constricted blood vessels dilate and improving blood pressure.

Antimicrobial activity
GSE has been shown to have antimicrobial properties; for example, when applied topically, resveratrol in GSE increases the production of cathelicidin, which inhibits the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. In another study, quercetin, caffeic acid, and quercetin-3-0-rutinoside in GSE were responsible for the inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes. It is also worth noting that GSE had the highest inhibition activity against almost all Listeria species. The review on the benefits of GSE also reported that the antimicrobial effect of GSE is attributed to changes in cell morphology and DNA content.
Cosmetic and nutraceuticals
Skin ageing is a natural process which occurs due to the external and internal factors involving genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. GSE is rich in proanthocyanidin help to reduces the lipid oxidation of cellular structure of the skin and inhibit the production of free radicals. A study was carried out in which the anti-ageing effect of GSE was investigate. The study concluded that GSE has a promising role as an anti-ageing compound.
GSE help skin structure by strengthening the collagen-based tissue (by increasing the collagen cross links). It also increases the synthesis of collagen and the conversion of collagen from soluble into insoluble one.
In conclusions,
GSE has various benefits to health due to its high antioxidant properties, it is able to scavenge the free radicals which an essential feature that could help with various body functions.
References

Consumption of fish is important as it is a good source of protein. It is recommended to consume one fish per day, according to the Malaysian food pyramid. This is because the consumption of fish in Malaysia is rarely equated with a risk of contamination with mercury, etc., unlike in western countries. This might be due to the types of fish and sizes of fish that we are consuming here as compared to other parts of the world. It is said that the bigger the fish, the more contamination it has; hence, there is a recommendation for pregnant mothers to consume small fish rather than big fish to avoid the risk of contamination.
Research on the benefits of fish oil supplementation also varies greatly, which is why in this article we are going to list out who might need a fish oil supplementation in their daily lives!
The benefits of ingesting fish oil can differ significantly between studies. A study found a connection between these omega-3 fatty acids and mental health disorders and that EPA and DHA can speed up brain development even in young children. Additionally, studies have demonstrated that it can help treat cardiovascular diseases, joint pain, and eczema. The question is, is it true that all of these effects can be obtained from fish oil consumption? (1)

Individual with mental health problems/disorders
In three lengthy studies spanning the years 1988 to 2008, researchers looked at the relationship between fatty acid intake and suicide risk among more than 205 000 participants. They discovered no proof that eating fish or fatty acids reduced the risk of suicide. "The vast majority of earlier research on whether fatty acid intake has any positive effects on mental health has been based on results from depression screening. The only time this relationship has been studied with concrete data on suicide mortality is in our study, which is also the largest of its kind.” (2)
While a study found that eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly are better for brain health than taking fish oil or omega-3 fatty acid supplements, A study of 3073 elderly people at risk of macular degeneration, an age-related cause of vision loss, found little benefit from omega-3 supplements on memory. Omega 3 supplements or a placebo were given to study participants at random for a five-year period. According to the researcher, a healthy diet cannot be replaced by a supplement; therefore, if you eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and marine fish, you probably don't need to take a fish oil supplement. According to this study, the overall dietary pattern is more important than a single nutrient (2).
Individuals with cardiovascular disease
Recently, there have been many studies suggesting that Omega 3 will not lower the risk of heart problems. To answer this, Dariush Mozaffarian, cardiologist from Harvard Medical School, said that he gathered 20 previous studies involving more than 68, 000 patients since 1989 and found that, overall, fish oil supplements did neither harm nor good since they did not significantly reduce people’s risk of mortality, cardiac death, heart attack, or stroke. But according to him, the research link between fish oil supplementation and heart problems is rather complex since it does not only take fish oil to shield the heart from various problems and diseases; it also takes weight status, exercise frequency, cigarette or substance use, and many more (3,4,5).

Which is why, interpreting the study, we would still recommend customers and patients consume more fish as a first-line measure. But if you do not like fish, or you feel like your consumption of fish is not enough, or you simply want to be sure that your body is getting omega 3, there is no harm in taking fish oil; it will certainly help with the essential nutrient, since omega 3 is a nutrient that your body cannot produce and can only get from diet (3,4,5).
Individuals with skin problem
A systematic review for the treatment of atopic dermatitis or eczema using fish oil supplementation is very scarce; the studies available are all small-sample studies. Not only are these three studies small, but they are also described as poor methodological studies by the reviewer, as they have many confounding factors. However, the outcomes of these studies show positive outcomes for eczema and overall daily living as compared to placebo (6, 7).
Another convincing relationship between consumption of fish oil and skin health is that in a study where pregnant women were given fish oil during pregnancy and followed up for 6 years, it was found that consumption of fish oil during pregnancy led to a positive skin health outcome for babies skin. The study also concluded that maternal supplementation with fish oil might have prophylactic potential for long-term prevention of asthma in offspring (6, 7).

In conclusion, consumption of fish oil has mixed results in studies depending on what kind of problem we are looking to solve with fish oil. Since there are various factors influencing a particular health problem, There is no magic pill in this world, honey! You need to, however, eat healthily, consume a lot of vegetables and fruits, and exercise, but if you think that you do not get enough omega 3 from your diet because you dislike fish, are afraid to consume fish regularly due to contamination, etc., or simply would like to make sure that your body has enough omega 3, then there is no harm in taking fish oil supplementation. It's just that in order to make sure you get the right omega 3 for your body, buy it from a pharmacy, make sure the product has a Ministry of Health (MOH) notification number, and simply ask a healthcare professional which omega 3 supplementation suits you, simply for the dosage and perhaps current medication that you are on, and you are good to go!
References
Harvard T.H Chan. School of Public Health. Fish: Friend or Foe? https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/fish/
Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. No mental health benefit from fish oil. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/no-mental-health-benefit-from-fish-oil/\
Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/fish-stroke-risk-mozaffarian/
Harvard T.H Chan. School of Public Health. Major Meta Analysis in Clinical Trial Omega 3 Supplemeny link with lower risk of CVD. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/press-releases/in-major-meta-analysis-of-clinical-trials-omega-3-fish-oil-supplements-linked-with-lower-cardiovascular-disease-risk/
Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. Fish Oil Supplementation and Heart Health. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/mozaffarian-fish-oil-supplements-heart-health/
Schlichte, M. J., Vandersall, A., & Katta, R. (2016). Diet and eczema: a review of dietary supplements for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Dermatology practical & conceptual, 6(3), 23–29. https://doi.org/10.5826/dpc.0603a06
Huang, T. H., Wang, P. W., Yang, S. C., Chou, W. L., & Fang, J. Y. (2018). Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications of Fish Oil’s Fatty Acids on the Skin. Marine drugs, 16(8), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080256

Collagen is a fibre-like structure that is used to make connective tissue, which connects other tissues together. It is a major component of bone, skin, muscles, tendons, and cartilage. Collagen is a component that helps make tissue strong, resilient, and able to withstand stretching (1).
Although the saying that our bodies make less collagen as we age is true, the production of collagen drops most not only because of this but also due to excessive exposure to the sun, smoking, including secondhand smoke, excessive consumption of alcohol, lack of sleep, and lack of exercise. As the collagen levels in our skin diminish, the deep skin layers change from a tightly organised network of fibres to an unorganised maze. Environmental exposure to the skin, such as harsh weather, can also damage collagen fibres by reducing their thickness and strength, which can lead to wrinkles on the skin surface (1).

Research on collagen supplementation focuses mostly on joint and skin health. Although studies pertaining to this using human subjects are still lacking, some randomized controlled trials have found that collagen supplementation improves skin elasticity. In one study, women who took a supplement containing 2.5–5 grammes of collagen for 8 weeks experienced less skin dryness and a significant increase in skin elasticity as compared to those who did not. Another study found that women who consumed it for 12 weeks experienced increased skin hydration and a significant reduction in wrinkle depth as compared with a control group (1, 2, 3, 4).
Trials on collagen supplements and joint health also found that they can improve joint mobility and decrease joint pain in people with osteoarthritis or in athletes (5). Collagen comprises about 60% of cartilage, a very firm tissue that surrounds bones and cushions them from the shock of high-impact movements, so a breakdown in collagen could lead to a loss of cartilage and joint problems.

Other than the consumption of collagen-based supplements, there are also foods that are rich in collagen or that encourage collagen production other than the lifestyle modifications mentioned above. Foods such as tough cuts of meat full of connective tissue like pot roast, brisket, and chuck steak. However, a high intake of red meat is not recommended as part of a long-term healthy diet. Collagen is also found in the bones and skin of freshwater and saltwater fish. Bone broth, which requires animal bones to simmer in water with a small amount of vinegar for 4–24 hours, is also said to have high collagen properties. However, the amount of amino acids will vary among batches depending on the types of bones used, the cooking period, and many other factors. Other foods that can help with the production of collagen are foods that are rich in zinc, such as legumes, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and vitamin C-rich foods, such as citrus fruits, bell peppers, and tomatoes.

Although studies on the effectiveness of collagen for health are still lacking, many available studies have not shown negative side effects in individuals given collagen supplements (6). Thus, it is worth trying for its said benefits, especially if the benefits are your health concerns! But be sure to talk to your healthcare professionals about this based on your medication intake and your health issues before consuming any health supplement.
References

Calories are a unit of measurement for the amount of energy in food and beverages.
We put energy into our bodies when we eat and drink. This energy will then be used in our daily activities, such as breathing, sleeping, and running.
To maintain a stable weight, we must balance the energy we put into our bodies with the energy we use through normal body functions and daily activities. Simply put, the more calories you put into your body, the more activities you need to do to burn them off, and vice versa.

General calories intake
Men on average need about 2500 kcal per day, while women need about 2000 kcal per day. However, as mentioned above, the amount of recommended nutrient intake varies from person to person based on their daily activities, occupation, frequency of exercise, lifestyle habits, and also body metabolism.
The more vigorously you engage in an activity, the more calories you will expend. Fast walking, for example, burns more calories than moderate walking. If you're gaining weight, it could be because you've been eating and drinking more calories than you've been burning. To lose weight, you must expend more energy than you consume; this can be accomplished by eating less or exercising more vigorously. Doing this consistently over time will get you to your desired weight.
When people try to lose weight, they tend to restrict their food intake and often do not enjoy their diet changes. A healthy diet should also be a sustainable diet, which means gradually but consistently reducing unhealthy food consumption, consuming more healthier food options, and being mindful of the amount of food consumed.
Calorie counter
Nowadays, there are various apps that can be used on a mobile phone to track not only your calorie intake but also your steps, exercise, and the energy that you burn. Using all these apps and gadgets is helpful in making sure that you are on track with your diet and exercise.
One of the apps developed by the Ministry of Health Malaysia that is compatible with the Malaysian variety of foods is My Nutri Diary 2.0. The app is helpful in monitoring your calorie intake and your weight progress. Often, when we use calorie tracking apps, it frustrates users that the app does not know how many calories a nasi lemak has (or any local food), but with my nutri diary, it covers a variety of Malaysian food options, which can be helpful for our daily food consumption.
Gap between unhealthy diet and body needs
While trying to lose, put on, or maintain weight, imbalanced consumption of foods may lead to the loss of some essential nutrients. Hence, to bridge the gap between the lack of nutrients in food and what the body needs, consumption of multivitamins and multiminerals is helpful.
Other conditions include denture problems, loss of appetite, a hectic lifestyle, and many more.

Anemia is a common blood disorder. It is a condition when the body does not have enough red blood cells and is unable to deliver enough oxygen throughout the body.
Anemia is diagnosed by a low haemoglobin or hematocrit level in a blood test. The main protein in red blood cells is haemoglobin. It transports and distributes oxygen throughout your body. Your haemoglobin level will be low if you have anaemia. If it falls below a certain level, your tissues or organs may not receive enough oxygen.
Symptoms of anemia
Lethargic or tiredness are the most common symptoms of anemia. Other symptoms include pale skin, an irregular or fast heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, headache, and light-headedness.
Types of anemia
Among the types of anemia are sickle cell anemia, iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, aplastic anemia, and many more.
Each of these types of anemia has its own cause.
In conclusion,
anemia must be treated depending on the cause, ranging from taking supplements to having medical procedures.
Most importantly, anemia can be prevented by consuming a healthy and varied diet.
Iron-rich foods include boiled cockles, chickpeas, fried soy bean curd, liver, dried anchovies, bitter gourd, spinach, and kangkung.

Iron is a mineral found in many proteins and enzymes that the body needs in order to stay healthy. Most of the iron in the body is found in haemoglobin, the pigment of red blood cells. Haemoglobin transports oxygen to all of the tissues and organs in the body. If there is an insufficient amount of iron in the blood, the amount of haemoglobin in the blood decreases too. This will reduce the oxygen supply to cells and organs.
During pregnancy, a haemoglobin level of 11 g/dl or above is considered normal. Between 3 to 6 months of pregnancy, a small drop of 10.5 g/dl is also considered normal. Lower levels of haemoglobin are usually due to a lack of iron (iron deficiency). Usually, the level of iron in the blood is measured in order to find out whether a low haemoglobin level is due to a lack of iron.
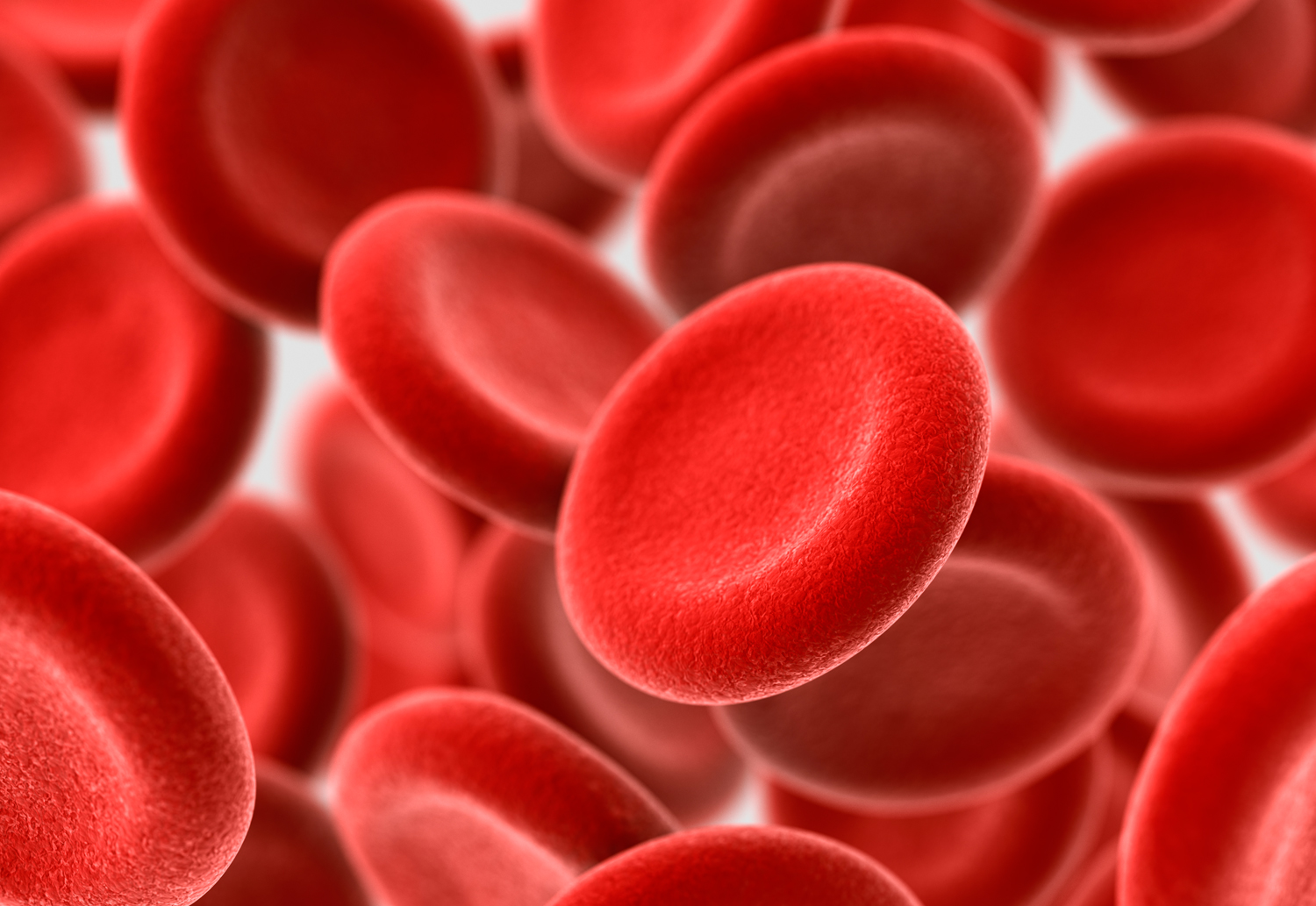
For a pregnant lady with a normal level of iron in her blood, it is not compulsory to consume an iron supplement; some people might consume it as a precautionary measure, but studies involving more than 40, 000 women show that there are no noticeable health benefits for the pregnancy or the baby. Although iron supplements were found to lower the risk of anaemia, they did not influence the number of preterm births, the number of babies with low birth weights, or infections in pregnant women.
However, it is important to know some of the examples of iron-rich foods that can be beneficial during pregnancy and for overall health, such as pistachios, sesame, rolled oats, whole grain rice and pasta, tofu, strawberries, tuna, shrimp, lettuce, chickpeas, peas, meat, and internal organs (liver).
In conclusion, we normally get iron from the food we eat. Meat has a lot of iron in it from haemoglobin in the animal’s body. The liver (internal organ) is particularly high in iron. Other than these foods, iron can be taken in the form of iron supplement too.
Reference:
1. Pregnancy and birth: Do all pregnant women need to take iron supplements? December 22, 2009. Last update March 22, 2018. National Library of Medicine. National Centre of Biotechnology Information. National Institute of Health (NIH).