Health Articles
Find out more about your health here from our health professionals!

Is artificial sweetener good for health?
Artificial sweeteners are low-calorie or calorie-free chemical substances used instead of sugar to sweeten foods and drinks. Sacharin, was the first artificial sweetener discovered in John Hopkin. It was then use widely, to the point that it was used during world war II when there was a sugar shortage, and when the shift in the perspective viewing thin figure as beauty. Sacharine is 300 times sweeter than sucrose but it has bitter after taste, which makes scientist discover cyclamate, aspartame and many more. As of 2018, there are eight Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved artificial sweeteners which are, acesulfame K (Sunnet), aspartame (Nutrasweet), saccharin (Sweet and Low, Necta sweet), neotame (New tame), sucralose (Splenda), stevia (Truvia), advantame, and Luo Han Guo fruits extract (Nectresse).
With the advancement in the technology of discovering all these non-calorie artificial sweeteners, thousands of products ranging from drinks, desserts, ready to eat food, baby food, frozen food, and toothpaste start to use this non-calorie artificial sweeteners. But,

Is artificial sweetener healthy? (2, 4, 5)
Although it has been approved by FDA that it is safe to consume artificial sweeteners within the Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI), but the healthiness of artificial sweeteners is somewhat questionable though many individuals with diabetic are consuming it as a means to control their blood sugar level.
Several large-scale studies using artificial sweetener come up that the consumption of artificial sweeteners had no effect on energy intake unlike glucose or sucrose, when it does not possess any effect on the energy intake or consumption of food, it trigger a response to keep the overall energy consumption constant.
We can see this clearly in the rat model study, where rodent that is supplemented with saccharin had significantly elevated total energy intake and gain more weight with increase body adiposity (fat) compared to those that conditioned with glucose. It was seen that, rodent that was given saccharin consume more food than those that is not given saccharin.
While in the human studies, the San Antonio Heart Study that examined 3, 682 adult over seven to eight year period of time found out that BMI of those who consumed artificial sweetener is significantly increased as compared to those who do not. Nurses’ Health Study reported similar observation among children.

Why is that so? (2)
The explanation on this is owe to on how our brain function when we consume food. When we consume food, it is not only that our digestive system is activated but as well as our mind. Food reward system shares the same brain circuitry with other pleasurable activities such as sex and drug administration, thus share the same behavioural paradigm such as binging, withdrawal, and craving. Food rewards consist of two branches: sensory and postingestive (after eating). When we eat, our mind activates in order to tell our body that we are already full, or we feel full (satiety) or when we are satisfied with the food (mesolimbic dopamine system). Mesolimbic dopamine system is a system that is activated whenever a pleasant taste causes us to be satisfied with the food that we consumed.
However, when we consume food from artificial sweetener, it is somehow does not activate mind into signalling that we are satisfied with the food, thus those who consume artificial sweetener tend to consume more food, this trick has cause individuals to eat even more, some more thinking that they consume non-calorie artificial sweeteners, thus making them easily gain weight.

In conclusion (1)
Data on artificial sweeteners is still scarce as compared to other kind of things, where even health professionals have different take on whether it is okay for the body. To make thing safe, whatever things that we consume must always be in moderation, balance, and variety. It is very essential for individuals with diabetes to know on how to estimate their calorie intake and identify the food that can instantly spike their blood glucose level and food that will slowly increase the blood glucose level, so that they can manage their blood glucose better.
Different kind of artificial sweeteners have different level of sweetness as compared to sucrose; it also has different side effect in terms of its bitter after taste. Some of it even is not suitable to certain cooking temperature like baking. Some of it is even not suitable to certain medical condition such as phenylketonuria (PKU), a condition when an individual is unable to metabolize amino acid phenylalanine, thus cannot consume food that has phenylalanine such as aspartame.
Also, if you are considering taking artificial sweetener, do consult medical professional so they may calculate the amount needed based on your body weight per day.
References
- National Health Service (NHS). U.K. The Truth About Sweeteners. https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/are-sweeteners-safe/ (Accessed on September 9, 2020).
- Qing Yang (2010). Gain weight by “going diet?” Artificial sweeteners and the neurobiology of sugar cravings. Department of Molecular, Cellular and Developmental Biology, Yale University. YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 83 (2010), pp. 101-108.
- S Food and Drugs Administration (FDA) (2018). Additional Information about High-Intensity Sweeteners Permitted for Use in Food in the United States. https://www.fda.gov/food/food-additives-petitions/additional-information-about-high-intensity-sweeteners-permitted-use-food-united-states (Accessed on September 9, 2020).
- Mc Clave, S., Obert, J., Casey, L. (2017). The Association Between Artificial Sweeteners and Obesity. Nutrition and Obesity. Current Gastroenterology Reports volume 19, Article number: 64 (2017).
- Brown, R. J., De Banate, M. A., & Rother, K. I. (2010). Artificial sweeteners: a systematic review of metabolic effects in youth. International Journal of Pediatric Obesity, 5(4), 305-312.

Do you know why fiber is important?
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that our body is unable to digest. Though most carbohydrates are broken down into sugar molecules, fiber cannot be broken down into sugar molecules, and instead it passes through the body undigested. Fiber helps regulate sugars in the body and helps keep hunger and blood sugar in check.
Children and adults need at least 20 to 30 grammes of fiber per day for good health. It can be obtained by consuming a diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and fruits.
There are two types of fiber: soluble fiber and insoluble fibre.
-
Soluble fiber is a type of fiber that dissolves in water and can help lower glucose levels and blood cholesterol levels. Foods with soluble fiber include oatmeal, nuts, beans, lentils, apples, and blueberries.
-
Insoluble fiber is a type of fiber that does not dissolve in water. It can help food move through the digestive system, promoting regularity and helping to prevent constipation. Foods with insoluble fibers are wheat, whole wheat bread, whole grain couscous, brown rice, legumes, carrots, cucumbers, and tomatoes.
There are various studies confirming that consumption of a diet high in fiber helps to make the overall body function healthier.
Heart Health
In a Harvard study with over 40, 000 male health professionals, researchers found that consumption of a high-fiber diet reduced the risk of getting coronary heart disease by 40%. Another study conducted by Harvard among female nurses also found similar findings: a high-fiber diet lowers the risk of metabolic syndrome (a combination factor of heart disease and diabetes). These factors are high blood pressure, high insulin levels, excess weight, a high triglyceride level, and a low HDL level (good cholesterol level).

Diabetes Mellitus Type 2.
A diet low in fiber and high in carbohydrates and fat can cause a sudden spike in blood sugar, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Both Harvard studies with female nurses and male health professionals found that this type of diet increased more than double the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Other studies, such as the Black Women’s Health Study and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition, have shown similar results.
Constipation.
It is believed that the fibre in wheat bran and oat bran is more potent than the fibre found in fruits and vegetables. In addition, because fibre absorbs water, experts advise increasing beverage intake along with fibre intake rather than doing so abruptly.
Cancer.
Fiber is shown to decrease the risk of breast cancer through a large-scale study in 2016, where the findings indicate that higher fiber intake reduces breast cancer risk, suggesting that fiber intake during adolescence and early adulthood may be particularly important.
In other words, women who consume higher fiber foods during adolescence and young adulthood, including vegetables and fruits, may have a significantly lower breast cancer risk than those who eat less dietary fiber when young.
In conclusion, consumption of sufficient fiber can give various benefits to the human body. According to the Malaysia Food Pyramid 2020, it is recommended to consume 3 servings of vegetables and fruits daily. However, according to the National Health Morbidity Survey (NHMS), about 95% of Malaysians do not consume enough vegetables and fruits daily, which is why sometimes consumption of fiber supplements can help to bridge the gap of poor dietary intake.
Reference
1. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Fiber. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/
2. National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) (2019). Chapter 09, Of fruits, veggies, and plain water. http://iptk.moh.gov.my/images/technical_report/2020/4_Infographic_Booklet_NHMS_2019_-_English.pdf
3. Malaysia Food Pyramid 2020. Ministry of Health Malaysia. Nutrition Division. http://nutrition.moh.gov.my/piramid-makanan-malaysia-2020-mendidik-rakyat-mengambil-makanan-dengan-betul/

Diet Suku – Suku Separuh ?
Suku – suku separuh diet adalah saranan diet oleh Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) untuk cara pemakanan sihat. Pelbagai langkah dan inisiatif telah dilakukan bagi mempromosikan amalan pemakanan sihat kepada rakyat Malaysia.
MegaLive menyambut baik saranan ini dengan turut sama mempromosikan amalan pemakanan sihat ini kepada semua.
Suku – suku separuh adalah diet yang merangkumi suku jumlah karbohidrat seperti nasi, mee, bihun, capati, roti dll, suku jumlah protein seperti ayam, ikan, sotong dll dan separuh jumlah sayur – sayuran dan buah – buahan. Pinggan yang dirujuk dalam saranan diet ini adalah pinggan berukuran 10 inci/ 25sm.
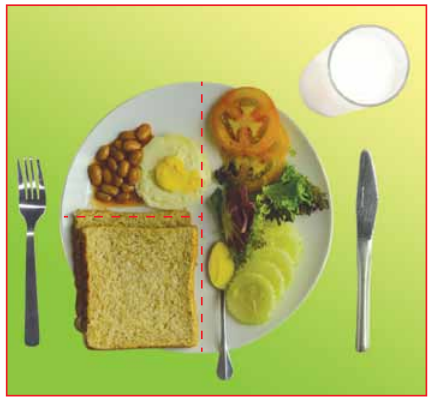
Contoh hidangan suku – suku separuh:
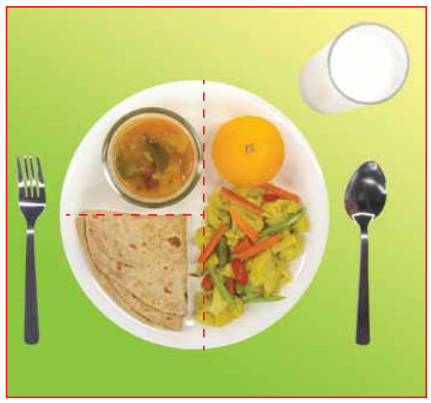

Capati dengan kuah dhal.
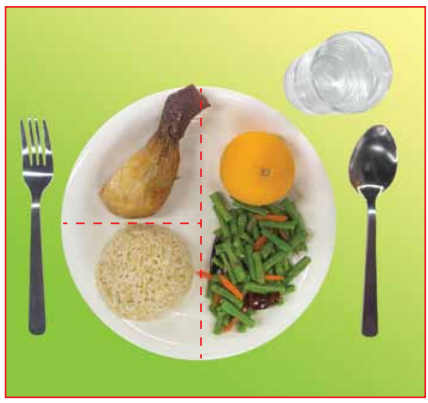
Nasi beras perang dengan ayam tanpa kulit dan sayur.
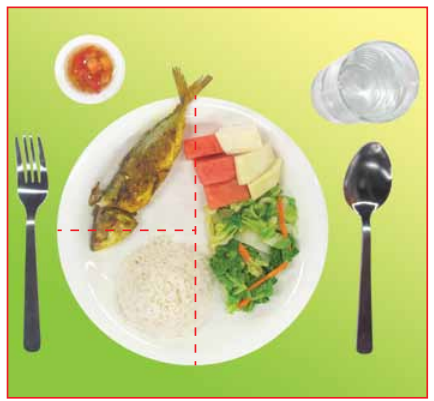
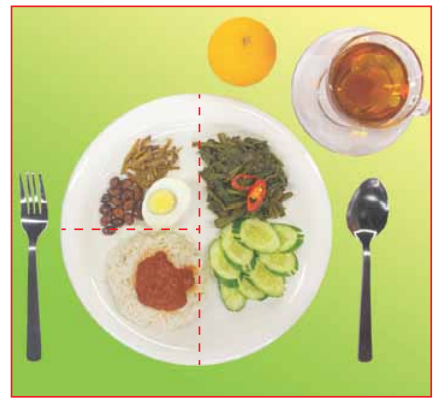


Nasi lemak

Terdapat 5 mesej utama dalam amalan diet suku – suku separuh.
Mesej Utama 1: Makan 3 Hidangan Utama yang sihat dalam sehari.
Makan sarapan, makan tengah hari, dan makan malam dengan sihat dengan mengikut konsep suku – suku separuh.
Makan pada waktu yang tetap juga membantu pengawalan porsi/ saiz hidangan makanan. Berikut adalah contoh waktu makan seharian.
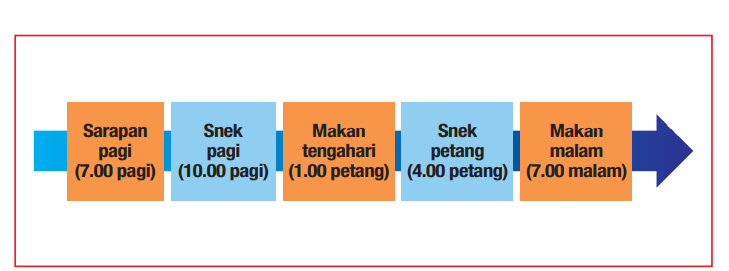
Mesej Utama 2: Makan 1-2 Snek yang Sihat di antara Waktu Makan Jika Perlu
Bagi menggalakan pemakanan secara sihat secara holistik atau sebagai gaya hidup, anda juga digalakkan untuk mengambil snek sihat 1-2 kali dari sumber buah – buahan, kekacang, dan sayur – sayuran.
Contoh snek sihat yang boleh di ambil 1-2 sajian ialah:

Mesej Utama 3: Makan Sekurang-kurangnya Separuh Daripada Bijirin Anda Sebagai Bijirin Penuh
Malaysia adalah negara di mana, makanan rujinya adalah nasi, oleh itu tidak hairanlah jika kebanyakkan rakyat Malaysia masih berasa tidak kenyang selagi tidak makan nasi. Oleh yang demikian, Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) menggariskan pengambilan karbohidrat hendaklah diambil kebanyakkannya dari sumber bijirin penuh, seperti dari sumber nasi beras perang, roti bijirin mil penuh, jagung, barli dll.
Contoh makanan berkarbohidrat yang tinggi serat:
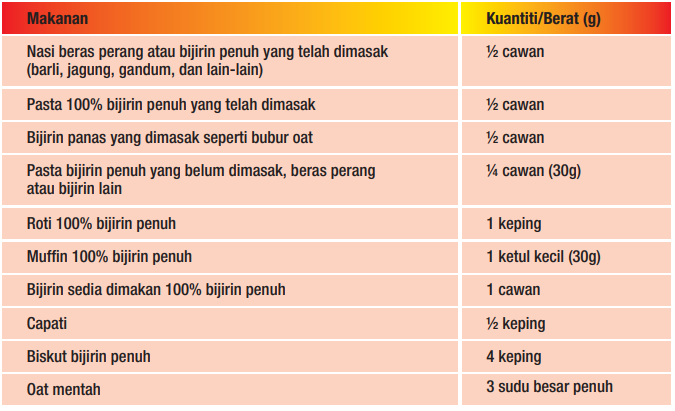
Mesej Utama 4: Makan Hidangan Tidak Bergoreng dan Tanpa Santan Setiap Hari
Seterusnya, lauk -pauk di Malaysia begitu sinonim sekali dengan jenis lauk -pauk yang bergoreng menggunakan minyak yang sangat banyak iaitu menggunakan kaedah ‘deep -frying’. Makanan bergoreng dengan minyak banyak yang digunakan secara berulang – ulang dan makanan yang mengandungi jumlah santan yang tinggi boleh meningkatkan masalah kesihatan seperti masalah jantung, darah tinggi, kolesterol dan kanser.
Justeru, pengambilan makanan dengan cara masakan dan kandungan santan yang tinggi seperti masak lemak, kari, gulai, dan masakkan bergoreng hendaklah dihadkan.
Cara mengantikan pengambilan minyak dan santan dalam masakan dan makanan:

Mesej Utama 5: Makan Makanan yang dimasak di Rumah Lebih Kerap
Makanan yang dibeli di luar secara amnya mempunyai kandungan gula, garam, sos, kicap, perasa, dan monosodium glutamate (MSG) yang tinggi, ia juga kebanyakannya menggunakan kaedah memasak yang kurang sihat iaitu dengan cara menggoreng dengan minyak yang banyak dan berulang- ulang.
Kandungan makanan yang tinggi garam, gula, sos, kicap, perasa dan MSG boleh menyebabkan tinggi risiko kepada masalah kesihatan seperti diabetes, dan juga darah tinggi.
Selain daripada itu, pengambilan makanan dari luar juga seringkali mempunyai jumlah porsi yang tidak mengikut spesifikasi suku – suku separuh, hal ini menyebabkan individu lebih cenderung untuk makaan secara berlebihan dan mendapat lebih risiko untuk menjadi obes.
Cadangan hidangan harian di rumah:
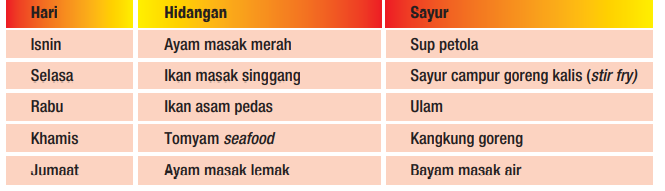
Rujukan:
- Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). Bahagian Pemakanan. Panduan Pinggan Sihat Malaysia. https://bit.ly/3HHHdU6

How to improve your blood circulation ?
Individuals with poor blood circulation typically experience numbness and coldness in their extremities, particularly their hands and feet. It is often the result of an underlying condition to a more serious condition, such as uncontrolled diabetes or low blood pressure, but it can also be the result of poor posture, among other things.
Here are some tips on how to
improve your blood circulation:
1. Go on regular walks
Walking can improve blood
circulation. Contraction of the calf muscle causes venous blood to be pushed
back up to the heart. The arteries dilate when patients walk and improve blood
flow throughout the body. Aim for a minimum of 30 minutes of walking three
times per week.
2.
Reduce your weight
Being obese or overweight poses a
greater health risk to your circulatory system because it increases your risk
of hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes, all of which lead to blood
circulatory problems.
Consumption of food in moderation,
balance and exercise regularly can help to prevent being obese and overweight.
3.
Take more breaks at work
Taking more work breaks allows you
to develop the habit of alternately sitting, standing, and walking. This
reduces the demand on the circulatory system because sitting causes blood flow
to slow and pool in your legs, resulting in muscle pain and fatigue. Thus,
taking more breaks while working in an office is beneficial for improving blood
flow and keeping your stress level in check.
Try to stretch every 15 to 20
minutes and get up and move every hour—even if it's just a power walk around
your house.
4. Stay
hydrated
When your body is dehydrated, it affects the amount of blood that
circulates through it. It also causes your blood to retain more sodium, causing
it to thicken and making it much more difficult for your circulatory system to
function properly.
Checking your pee is the simplest
way to ensure that you are getting enough fluid. A yellow light or clear urine
indicates that you are drinking enough water; anything darker indicates that
you need to up your water intake game!
5.
Manage your blood pressure
High blood pressure causes your blood circulation to go haywire,
putting more strain on your heart and blood vessels. If you do not manage your
blood pressure properly, the heart and circulatory system will have to work
harder to supply blood flow throughout the body.
High blood sugar levels can harm
the lining of small blood vessels, causing blood circulation issues. This
condition will also encourage the formation of plaque in your blood vessels,
further complicating matters.
Exercise, limiting sodium intake,
reducing stress, getting enough sleep, and making changes to your lifestyle can
all help to lower your blood pressure and improve your circulation. Ideally,
your blood pressure should be less than 120/80 mmHg.
6.
Elevate your legs.
Elevating your legs relieves
pressure on your veins because the blood does not have to work against gravity
to return to the heart.
When you are watching TV or taking
a nap, the most convenient time to elevate your legs is when you are lying down
and prop your legs above your heart level for 15 minutes or more at a time.
This will greatly improve overall blood circulation.

The Detrimental Effects of Junk Food on Health
The Detrimental Effects of Junk Food on Health
In accordance with the Oxford dictionary, junk food is defined as food with negligible nutritional value, commonly found in the form of packaged snacks or hastily prepared meals. Think of salty, oily snacks, burgers, sausages, and candies.
The Cognitive Consequences: Loss of Memory and Learning Impairments
Delving into the implications of consuming junk food, it becomes apparent that its effects extend far beyond just satisfying cravings. Studies published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition reveal a disturbing correlation between a junk food-heavy diet and cognitive performance. Individuals who frequently indulge in junk food exhibit lower scores on cognitive tests. Even more alarming is the detrimental impact on memory and brain function. The excessive consumption of junk food can trigger inflammation in the hippocampus—a crucial brain region responsible for memory and recognition. This inflammatory response has been linked to memory loss and even amnesia, inhibiting the ability to learn and recall new information.
The Weighty Dilemma: Escalating Obesity Rates
One cannot ignore the excessive sugar, calorie, and fat content prevalent in junk food. These culprits contribute significantly to weight gain and the alarming rise of obesity. The consequences of obesity are not limited to mere aesthetics; they extend to a multitude of severe health conditions. Diseases ranging from high cholesterol and diabetes to heart problems and hypertension find their roots in obesity.
This health crisis is particularly perilous for children, whose physical development is at stake. The consumption of junk food can lead to unhealthy weight gain, consequently fostering self-esteem issues. The relationship between self-esteem and junk food may seem indirect, but it is noteworthy. Unhealthy weight gain can pave the way for diminished self-esteem, which in turn can pave the way for depression.
A Nutritional Void: Depleting Essential Nutrients and Amplifying Mental Health Issues
Behind the delectable façade of junk food lies an insidious nutritional void. Excessive intake of sugar and fats robs the body of essential nutrients and amino acids—critical components that trigger vital chemical reactions in the brain. This deprivation of nutrients results in the impairment of brain function, rendering it less capable of handling stress and emotional well-being. Consequently, individuals who overindulge in junk food often find themselves grappling with increased stress and susceptibility to depression.
In conclusion, the ramifications of consuming junk food are manifold and deeply entrenched. From cognitive decline and memory impairment to obesity-related health complications and deteriorating mental health, the allure of quick and tasty eats should be approached with caution. To safeguard our physical and mental well-being, a conscious effort to prioritize nutritious and wholesome alternatives is imperative.
References
- Icilombard (n.d). 5 Harmful Effects of Junk Food. https://www.icicilombard.com/insurance-information/health-insurance-info/article/5-harmful-effects-of-junk-food
- Icilombard (n.d). Harmful Effects of Junk Food. https://www.icicilombard.com/insurance-information/health-insurance-info/article/5-harmful-effects-of-junk-food
- Jamesclear (n.d). Science of Junk Food. https://jamesclear.com/junk-food-science
- Healthy eating (n.d). Junk Food affect children. https://healthyeating.sfgate.com/junk-food-affects-children-5985.html

Unveiling the truth about salt and your health
We're talking about something that might not seem like a big deal, but it's hiding in our food and affecting our health - salt. You know, the stuff we sprinkle on our fries? It's causing some trouble, and here's how.

Changing Eating Habits: What's Going On?
As our cities grow and change, so does our food. We're eating more and more processed foods that are easy to grab on the go. This change in what we eat is causing problems with our health. We're not getting the good stuff we need, like nutrients, from our food. Instead, we're loading up on things like fats, sugars, and salt. These are the things that make our food taste good but aren't always good for our bodies.
Too Much Salt: A Sneaky Problem
Did you know that too much salt can be bad for us? We're not just talking about the salt we shake onto our food. It's hiding in lots of other foods too, like instant noodles, snacks, sausages, and more. Eating too much salt can mess with our health, especially our blood pressure. And high blood pressure isn't a good thing – it can lead to heart problems and even stroke.
Who's Most Affected?
Different groups of people can be affected by too much salt. In some places, like Malaysia, the traditional foods we love can be really salty. This can lead to problems like high blood pressure. For example, Malays are more likely to have high blood pressure than Chinese folks. It's because their traditional foods often have lots of salt.
What Can We Do About It?
Cutting back on salt doesn't mean our food has to be boring. Here are some simple tips:
- Fresh is Best: Try to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables. These are good for us and have less salt.
- Check Labels: When you're buying packaged food, look at the labels. They'll tell you how much salt is inside. Choose foods with less salt.
- Spice it Up: Use herbs and spices to make your food taste great without adding too much salt. Things like garlic, onions, and lemongrass can be awesome flavor boosters.
- Cook at Home: Try making your own meals at home. This way, you can control how much salt goes into your food.
- Less Fast Food: Eating out a lot can mean more salt in your diet. Try to eat out less and cook at home more often.
- Go Slow: Don't cut out all the salt at once. Your taste buds need time to adjust. Gradually use less salt in your cooking and you might not even miss it.

Salt Myths Busted:
- Sweating Doesn't Mean More Salt: Hot day? You might think you need more salt. Nope, just drink more water.
- Sea Salt vs. Regular Salt: It doesn't matter where the salt comes from – it's the sodium in it that can be a problem.
- Taste Can Be Tricky: Sometimes, salty foods don't even taste salty. Read labels to know for sure.
- Age Doesn't Matter: Too much salt is bad for everyone, young or old.
The Takeaway:
Salt might make food taste great, but too much isn't so great for our health. Let's be mindful of how much salt we're eating, read labels, cook more at home, and enjoy the flavors of fresh foods. Your body will thank you for it, and your taste buds might even adjust to the new, healthier flavors.

References
- Balkish, M., N., Muhammad, F., M., Y., Sarimah, A., Kamarul Imran, M., Najib Majdi, Y., Maria, S., M., Norhafizah, S. and Tahir, A. 2019. Factors associated with the severity of hypertenstion among Malaysian adults. PLoS ONE 14(1): e0207472. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal. pone.0207472
- Mayo Clinic. 2019. Healty Lifestyle: Nutrition and healthy eating [online]. Available from: https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/sodium/art-20045479 [Accessed on 6 April 2020].
- Ministry of Healthy Malaysia. 2018. Guidelines for Healthcare Professionals: Health Education and Communication Tools to Reduce Salt Intake in Malaysia [online]. Available from http://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Rujukan/NCD/Garam/Guideline_for_healthcare_professionals.pdf [Accessed on 6 April 2020].
- Ministry of Health Malaysia. 2018. Manual Penggunaan Bahan Pendidikan Kesihatan: Penjagaan Pemakanan Dalam Pengawalan Pengambilan Garam [online]. Available from http://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/Rujukan/NCD/Garam/Buku_manual.pdf [Accessed on 6 April 2020].
- National Coordinating Committee on Food and Nutrition. 2013. Malaysian Dietary Guidelines for Children and Adolescents [online]. Available from http://nutrition.moh.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/penerbitan/buku/MDG_Children_adolescent_2014.pdf [Accessed on 6 April 2020].
- National Coordinating Committee on Food and Nutrition. 2017. Recommended Nutrient Intakes for Malaysia [online]. Available from http://nutrition.moh.gov.my/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/FA-Buku-RNI.pdf [Accessed on 6 April 2020].
- New Straits Times. 2019. 4 out of 5 Malaysians eat too much salt [online]. Available from https://www.nst.com.my/news/nation/2019/04/479149/4-out-5-malaysians-eat-too-much-salt [Accessed on 6 April 2020].
- World Health Organization. 2016. Salt reduction [online]. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/salt-reduction [Accessed on 6 April 2020].

A Guide to Heart Health
The heart serves as a pivotal organ within the body, facilitating blood circulation and ensuring the distribution of vital nutrients to all its corners (1). Beyond its circulatory role, the heart plays a vital part in shielding the body against infections (1). Moreover, it contributes to regulating body temperature and upholding fluid equilibrium (2). Given these multifaceted functions, the heart emerges as a cornerstone of bodily well-being; even minor irregularities can set off significant repercussions throughout the human system (2).
There are several effective strategies to ensure the well-being of your heart:
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity and Maintain a Healthy Weight
If you find yourself struggling with excess weight, it's crucial to acknowledge that this condition can elevate your risk of developing high cholesterol and blood pressure, both of which can adversely impact your heart health (3). In light of this, striving for a healthy weight becomes a priority. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that individuals aged 18 to 64 incorporate a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity into their weekly routine. Alternatively, dedicating at least 75 minutes to vigorous-intensity physical activity is also effective. Additionally, breaking down your aerobic exercises into segments of at least 10 minutes each can contribute to optimal results.

- Limit Salt Intake and Minimize Oily Foods
Excessive salt consumption has been linked to elevated blood pressure, which escalates the risk of heart disease. It's advised that adults keep their daily salt intake below 6g, and strive to opt for foods containing no more than 1.5g of salt or 0.6g of sodium per 100g whenever feasible (4). Moreover, it's beneficial to reduce the consumption of oily foods. Oils typically encompass a blend of monounsaturated, polyunsaturated, and saturated fats. Prioritizing options low in saturated fatty acids (SFA) while favoring those rich in unsaturated fats can effectively contribute to lowering cholesterol levels (5). For instance, heart-healthy oils like grapeseed, avocado, and olive oils are commendable choices (5). Embracing a diet low in salt content is pivotal in sustaining optimal blood pressure levels.
- Incorporate More Fish into Your Diet
Including more oily fish in your diet can offer substantial benefits for your heart health. Oily fish varieties are rich sources of Omega-3 fatty acids, compounds known to effectively lower cholesterol levels, decrease blood pressure, and mitigate the risk of blood clot formation (4). These vital advantages underline the importance of including these types of fish in your meals. Noteworthy examples of fish abundant in Omega-3 fatty acids include:
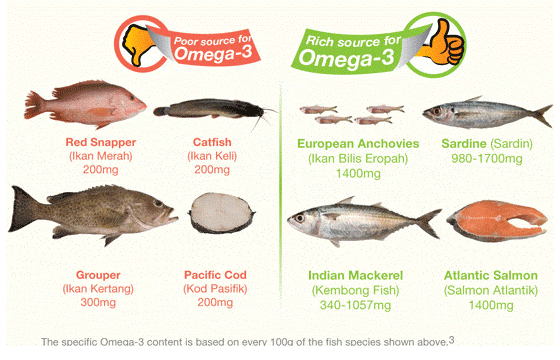
- Manage your cholesterol level
Maintaining a healthy cholesterol level is pivotal in preventing coronary heart disease. Excess cholesterol can accumulate within your artery walls, potentially leading to the development of plaque—a phenomenon known as atherosclerosis. Over time, this accumulation can narrow the arteries, impeding the smooth flow of blood. Ultimately, reduced blood flow can manifest as chest pain or, in severe cases, a heart attack if a blood vessel becomes completely obstructed (7). Thus, it is imperative to address cholesterol levels to safeguard cardiovascular well-being. Normal total cholesterol levels should ideally remain below 5.2 mg/dL.
References
- News Medical Net (n.d). Structure and Function of the Heart. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Structure-and-Function-of-the-Heart.aspx
- Patient Direct. Anatomy and Physiological Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. https://www.ptdirect.com/training-design/anatomy-and-physiology/major-functions-of-the-cardiovascular-system-2013-a-closer-look
- News Medical Net. Structure and Function of Heart. https://www.news-medical.net/health/Structure-and-Function-of-the-Heart.aspx
- Lloyd Pharmacy. 10 Healthy Ways to Take Care of Heart. http://blog.lloydspharmacy.com/health/10-ways-take-care-heart-health/
- Garavaglia J, Markoski MM, Oliveira A, Marcadenti A. Grape seed oil compounds: biological and chemical actions for health. Nutr Metab Insights. 2016;9:59-64. doi:10.4137/NMI.S32910
- World Health Organization 2010; Global recommendations on physical activity for health.WebMD (n.d). Cholesterol

Stress: How to handle it
Stress can be defined as the body’s reaction to any change that requires an adjustment or response. The body reacts to these changes with physical, mental, and emotional responses. Stress is a normal part of life. You can experience stress from your environment, your body, and your thoughts. Even positive life changes such as a promotion, a mortgage, or the birth of a child produce stress. (1)
The human body is designed to experience stress and react to it. Stress can be positive, keeping us alert, motivated, and ready to avoid danger. Stress becomes negative when a person faces continuous challenges without relief or relaxation between stressors. As a result, the person becomes overworked, and stress-related tension builds. The body’s autonomic nervous system has a built-in stress response that causes physiological changes to allow the body to combat stressful situations. This stress response, also known as the “fight or flight response”, is activated in case of an emergency. However, this response can become chronically activated during prolonged periods of stress. Prolonged activation of the stress response causes wear and tear on the body, both physical and emotional. (2)
Stress that continues without relief can lead to a condition called distress – a negative stress reaction. Distress can disturb the body’s internal balance or equilibrium, leading to physical symptoms such as headaches, an upset stomach, elevated blood pressure, chest pain, sexual dysfunction, and problems sleeping. Emotional problems can also result from distress. These problems include depression, panic attacks, or other forms of anxiety and worry. Research suggests that stress also bring on or worsen certain symptoms or diseases. Stress is linked to six of the leading causes of death: heart disease, cancer, lung ailments, accidents, cirrhosis of the liver, and suicide. (3)
Stress also becomes harmful when people engage in the compulsive use of substances or behaviours to try to relieve their stress. These substances or behaviours include food, alcohol, tobacco, drugs, gambling, sex, shopping, and the Internet. Rather than relieving the stress and returning the body to a relaxed state, these substances and compulsive behaviours tend to keep the body in a stressed state and cause more problems. The distressed person becomes trapped in a vicious circle.
It may seem that there is nothing you can do about your stress level. The bills aren’t going to stop coming; there will never be more hours in the day for all your errands, and your career or family responsibility will always be demanding. But you have a lot more control than you might think. In fact, managing stress is all about taking charge of your thoughts, your emotions, your schedule, your environment, and the way you deal with problems. The ultimate goal is a balanced life with time for work, relationships, relaxation, and fun, plus the resilience to hold up under pressure and meet challenges head-on. (4)
Stress management starts with identifying the sources of stress in your life. This isn’t as easy as it sounds. Your true sources of stress aren’t always obvious, and it’s all too easy to overlook your own stress-inducing thoughts, feelings, and behaviours. Sure, you may know that you’re constantly worried about work deadlines. But maybe it’s your procrastination, rather than the actual job demands, that leads to deadline stress.
To identify your true sources of stress, look closely at your habits, attitude, and excuses:
-
Do you explain away stress as temporary (“I just have a million things going on right now”) even though you can’t remember the last time you took a breather?
-
Do you define stress as an integral part of your work or home life (“Things are always crazy around here”) or as a part of your personality (“I have a lot of nervous energy, that’s all”)
-
Do you blame your stress on other people or outside events, or view it as entirely normal and unexceptional?
Until you accept responsibility for the role you play in creating or maintaining it, your stress level will remain outside your control.
Stress management strategy 1: Avoid unnecessary stress
Not all stress can be avoided, and it’s not healthy to avoid a situation that needs to be addressed. You may be surprised, however, by the number of stressors in your life that you can eliminate.
-
Learn how to say “no” – Know your limits and stick to them.
-
Avoid people who stress you out.
-
Take control of your environment – If the evening news makes you anxious, turn the TV off. If traffic’s got you tense, take a longer but less-traveled route.
-
Avoid hot-button topics – If you get upset over religion or politics, cross them off your conversation list.
-
Pare down your to-do list – Analyze your schedule, responsibilities, and daily tasks
Stress management strategy 2: Alter the situation
If you can’t avoid a stressful situation, try to alter it. Figure out what you can do to change things so the problem doesn’t present itself in the future. Often, this involves changing the way you communicate and operate in your daily life.
-
Express your feelings instead of bottling them up. If something or someone is bothering you, communicate your concerns in an open and respectful way.
-
Be willing to compromise. When you ask someone to change their behavior, be willing to do the same.
-
Be more assertive. Don’t take a backseat in your own life. Deal with problems head on, doing your best to anticipate and prevent them.
-
Manage your time better. Poor time management can cause a lot of stress.
Stress management strategy 3: Adapt to the stressor
If you can’t change the stressor, change yourself. You can adapt to stressful situations and regain your sense of control by changing your expectations and attitude.
-
Reframe problems. Try to view stressful situations from a more positive perspective.
-
Look at the big picture. Take perspective on the stressful situation.
-
Adjust your standards. Perfectionism is a major source of avoidable stress.
-
Focus on the positive. When stress is getting you down, take a moment to reflect on all the things you appreciate in your life, including your own positive qualities and gifts.
Stress management strategy 4: Accept the things you can’t change.
Some sources of stress are unavoidable. You can’t prevent or change stressors such as the death of a loved one, a serious illness, or a national recession. In such cases, the best way to cope with stress is to accept things as they are. Acceptance may be difficult, but in the long run, it’s easier than railing against a situation you can’t change.
-
Don’t try to control the uncontrollable. Many things in life are beyond our control, particularly the behaviour of other people.
-
Look for the upside. As the saying goes, "What doesn’t kill us makes us stronger." When facing major challenges, try to look at them as opportunities for personal growth.
-
Share your feelings. Talk to a trusted friend or make an appointment with a therapist.
-
Learn to forgive. Accept the fact that we live in an imperfect world and that people make mistakes.
Stress management strategy 5: Make time for fun and relaxation.
Beyond a take-charge approach and a positive attitude, you can reduce stress in your life by nurturing yourself. If you regularly make time for fun and relaxation, you’ll be in a better position to handle life’s stressors when they inevitably come.
Healthy ways to relax and recharge
-
Go for a walk.
-
Spend time in nature.
-
Call a good friend.
-
Sweat out tension with a good workout.
-
Write in your journal.
-
Take a long bath.
-
Lightly scented candles
-
Enjoy a warm cup of coffee or tea.
-
Play with a pet.
-
Work in your garden.
-
Get a massage.
-
Curl up with a good book.
-
Listen to music.
-
Watch a comedy.
Don’t get so caught up in the hustle and bustle of life that you forget to take care of your own needs. Nurturing yourself is a necessity, not a luxury.
-
Set aside relaxation time. Include rest and relaxation in your daily schedule.
-
Connect with others. Spend time with positive people who enhance your life.
-
Do something you enjoy every day. Make time for leisure activities that bring you joy, whether it be stargazing, playing the piano, or working on your bike.
-
Keep your sense of humor. This includes the ability to laugh at yourself.
Stress management strategy 6: Adopt a healthy lifestyle
You can increase your resistance to stress by strengthening your physical health.
-
Exercise regularly. Physical activity plays a key role in reducing and preventing the effects of stress.
-
Eat a healthy diet. Well-nourished bodies are better prepared to cope with stress, so be mindful of what you eat.
-
Reduce caffeine and sugar. The temporary "highs" caffeine and sugar provide often end with a crash in mood and energy.
-
Avoid alcohol, cigarettes, and drugs. Self-medicating with alcohol or drugs may provide an easy escape from stress, but the relief is only temporary.
-
Get enough sleep. Adequate sleep fuels your mind as well as your body.
References
-
Robinson, L., Smith, M. and Segal, R., 2011. Stress Management: How To Reduce, Prevent, And Cope With Stress | Brainline. [online] BrainLine. Available at: <https://www.brainline.org/article/stress-management-how-reduce-prevent-and-cope-stress> [Accessed 15 April 2020].
-
National Institute of Mental Health. Fact sheet on stress Accessed 12/9/2014.
-
American Psychological Association. Stress: the different kinds of stress Accessed 12/9/2014.
-
Office on Women’s Health. Stress and your health fact sheet Accessed 12/9/2014

Masa untuk berhenti merokok
Pertubuhan Kesihatan Dunia (WHO) telah mewartakan bahawa merokok merupakan risiko yang spesifik bagi komplikasi COVID-19 (1,2). Hal ini adalah kerana, jika virus korona menyerang tubuh badan individu yang merokok, peratus untuk individu tersebut pulih lebih rendah berbanding dengan individu yang tidak merokok manakala peratus untuk individu tersebut untuk mengalami kegagalan paru – paru yang serius pula adalah tinggi.
Umum mengetahui, COVID-19 adalah virus yang menyerang sistem pernafasan, jadi, individu yang merokok atau yang mempunyai masalah pernafasan dan/atau sakit – sakit kronik yang lain seperti masalah jantung, buah pinggang, kencing manis dan lain -lain jika terdedah kepada virus ini, mempunyai sebanyak 80.7% risiko kematian berbanding individu yang tidak menghidapi penyakit kronik (3).
Statistik juga menunjukkan bahawa, warga emas yang berusia 60 tahun ke atas mempunyai lebih 62.6% risiko kematian jika terdedah kepada virus ini berbanding individu berusia 60 tahun ke bawah (3). Lebih menakutkan lagi, jika individu yang berusia 60 tahun ke atas, dan mempunyai sejarah penyakit kronik terdedah kepada virus ini, risiko menghadapi kematian adalah sangat tinggi berbanding dengan individu yang yang berusia kurang dari 60 tahun dan tidak mempunyai sejarah penyakit kronik.
Tabiat merokok itu sendiri yang menyebabkan individu berisiko terdedah kepada pelbagai jenis komplikasi kesihatan, akan tetapi sebelum ini mungkin perokok menghadapi kesukaran untuk berhenti merokok disebabkan faktor rakan sekeliling, tekanan kerja dan sebagainya. Akan tetapi oleh kerana dunia diancam dengan wabak COVID-19, individu yang merokok mempunyai lebih sebab untuk berhenti merokok kerana anda mempunya risiko yang lebih tinggi terdedah kematian jika terdedah kepada virus ini.
Antara cara untuk berhenti merokok, yang telah dikumpulkan oleh Pengkalan Data Cochchrane Edisi Istimewa, mengenai cara – cara berhenti merokok adalah dengan menggunakan terapi kombinasi, iaitu penggunaan ubat dan juga sokongan moral (4).
Penggunaan Ubat – Ubatan seperti Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) telah digunakan sebagai salah satu cara untuk berhenti merokok sekian lama. Terapi ini adalah bagi tujuan untuk menggantikan kebergantungan perokok kepada nikotin dan seterusnya menggurangkan motivasi perokok untuk terus merokok. Ia juga membantu mengawal kesan sampingan berhenti rokok/ kurang merokok (4).
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) ini memberikan nikotin dalam dos yang rendah kepada perokok tanpa apa apa bahan merbahaya yang lain seperti yang terdapat di dalam rokok. Terdapat pelbagai jenis Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT) dipasaran, iaitu sama ada dengan menggunakan gula getah nikotin (nicotine gum), ‘nicotine inhaler’, ‘nicotine lozenge’, ‘nicotine patch’ atau ‘nicotine nasal spray’. Kesemua jenis produk ini mempunyai dos, cara, dan kekuatan yang berbeza (5).
Produk bagi terapi nikotin telah direka dengan pelbagai jenis mekanisma untuk penyerapan dan perembesan nikotin di dalam badan. Sebagai contoh bagi gula getah nikotin, inhaler nikotin, lozenge nikotin dan nasal spray nikotin, ia memberi kesan kepada otak dengan lebih cepat berbanding nicotine patch akan tetapi mempunyai proses perembesan yang lebih lambat berbanding merokok (5). Nicotine patch pula merembeskan dos nikotin secara perlahan – lahan dan secara pasif, oleh kerana itu terapi nicotin patch biasanya digunakan bersama produk yang lain.
Kepelbagaian produk bagi membantu perokok berhenti merokok memberikan perokok beberapa pilihan untuk berhenti merokok dengan kaedah yang paling sesuai, berdasarkan kekerapan perokok merokok dan kebergantungan perokok kepada rokok tersebut (4,5). Kesemua produk ini berkesan jika digunakan mengikut kesesuaian terhadap tahap aktiviti merokok seseorang individu. (5).
Selain daripada penggunaan ubat – ubatan, terdapat beberapa langkah yang biasanya disyorkan oleh Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM), iaitu yang pertama ialah dengan membaca atau mendapatkan informasi mengenai bahaya rokok dari sumber yang sahih, berkenaan bahaya merokok dan kelebihan berhenti merokok.
Terdapat banyak kelebihan berhenti merokok kerana merokok memberi banyak keburukan kepada diri sendiri dan orang sekeliling terutama ahli keluarga, sebagai contoh kanak – kanak yang selalu terdedah kepada asap rokok atau asap rokok basi akan lebih sering sakit seperti batuk – batuk, selsema serta jangkitan telinga, hidung dan tekak. Merokok juga boleh membuatkan paru – paru lemah dan penyakit seperti asma (6).
Selain daripada aspek kesihatan bagi orang yang tersayang, merokok juga boleh menyebabkan anda mendapat pelbagai jenis penyakit seperti, kanser paru – paru, penyakit paru – paru yang kronik, strok dan ulser di bahagian bawah lapisan kulit perut. Individu yang merokok juga mengikut statistik mati lebih awal, kerana statistik menunjukan satu dari dua orang perokok mati disebabkan penyakit berkaitan merokok (6).
Tabiat berhenti merokok juga dapat menjimatkan wang, labur wang anda berbanding membeli rokok sebagai contoh
Wang untuk membeli rokok = RM5.00/sehari
Sebulan = RM 150.00
Setahun = RM 1800.00
Jika anda melabur untuk 10 tahun, anda sudah mempunyai RM18,000.00 dalam akaun simpanan anda) (6).
Selain, Ia juga dapat melindungi alam sekitar – Puntung rokok dibuang oleh perokok boleh menyebabkan kebakaran (6).
Terdapat pelbagai kaedah untuk berhenti merokok. Faktor yang paling penting adalah keinginan anda untuk menjadikannya satu kenyataan. Mula dengan menetapkan tarikh untuk berhenti merokok dan pastikan tarikh tersebut boleh dicapai. Dalam pada masa yang sama, anda mesti yakin dengan keupayaan diri untuk berhenti merokok. Katakan pada diri anda “saya bukan perokok” Ulang beberapa kali sehingga menjadi semangat untuk berhenti merokok. Sentiasa berfikiran positif dan dapatkan sokongan daripada orang sekeliling.
Teknik berhenti merokok yang paling selalu digunakan dan disyorkan oleh Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) ialah dengan mengamalkan Teknik 12M (6).
1. Melengah – lengahkan
Sebagai contoh jika anda terasa seperti mahu merokok, lengah – lengahkan tabiat tersebut seperti tunggu 5 minit atau katakan kepada diri sendiri sebentar lagi “saya akan merokok”.
2. Menarik Nafas Panjang
Tarik nafas 3 kali secara perlahan-lahan. Ulangi perkara yang sama sehingga hilang rasa untuk merokok.
3. Minum air
Anda juga boleh mencuba untuk minum air masak bagi mengalihkan perhatian anda dari tertumpu kepada ketagihan rokok.
4. Menyibukan diri
Buat sesuatu bagi mengalih fikiran untuk melupakan rokok. Buat perkara yang dapat mengalihkan tumpuan anda seperti bersenam atau bermain permainan video.
5. Menjauhkan diri daripada perokok
Oleh kerana musim PKP ini adalah masa yang terbaik untuk berhenti merokok. Anda boleh menjauhkan diri anda dari rakan – rakan dan ahli keluarga yang merokok, gunakan masa yang ada untuk bersama keluarga tersayang.
6. Mengelakkan diri daripada suasana atau situasi yang mendorong kepada merokok
Seperti keadaan berseorangan tanpa berbuat apa – apa (keadaan bosan) atau keadaan tertekan.
7. Mengunyah sesuatu seperti gula getah atau buah-buahan.
Mengunyah dapat membuatkan rongga mulut sibuk dan mengalihkan perhatian dari ketagihan rokok. Elakkan makanan yang manis kerana ia memberi risiko kepada penyakit – penyakit kronik yang lain pula.
8. Membasuh tangan selalu
Membasuh tangan dengan kerap juga dapat menghilangkan ketagihan kerana kita telah mengalihkan perhatian kita daripada keinginan untuk merokok.
9. Mandi dengan kerap
Mandi dengan kerap menyebabkan badan menjadi segar dan dapat melupakan ketagihan yang di alami, seketika.
10. Meregangkan otot
Senaman yang atau regangan otot apabila ketagihan untuk merokok datang dapat menghindarkan diri dari merokok.
11. Meditasi
Meditasi menyebabkan kita ingat kembali sebab – sebab untuk kita berhenti merokok dan boleh membangkitkan kembali semangat kita untuk berhenti merokok.
12. Memohon doa
Memohon doa agar rasa ketagihan dihilangkan dan dipermudahkan urusan untuk berhenti merokok seperti dihindarkan dari perkara – perkara yang boleh menyebabkan keinginan untuk merokok untuk kembali.
Selain daripada langkah - langkah yang telah disyorkan anda juga boleh mendapatkan maklumat yang lebih lanjut di laman sesawang KKM. Terdapat banyak bahan – bahan rujukan cara untuk berhenti merokok yang boleh di muat turun di laman sesawang yang sahih seperti di Portal MyHealth Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM)(5). Selain dari bahan – bahan sokongan yang boleh di muat turun, terdapat juga nombor QuitLine yang boleh dihubungi di nombor 03-88834400 bagi keterangan lanjut mengenai cara berhenti merokok dari kaunselor berhenti merokok atau layari laman web jomquit.moh.gov.my (4,5).
Rujukan
-
The Star. Stub It Out Now, Smoking and Added Health Risk for COVID19. https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2020/04/13/effective-ways-exist-to-quit-smoking-while-under-mco (Diakses 17 April 2020).
-
The Star. Smokers face high infection rate. https://www.thestar.com.my/news/nation/2020/04/13/smokers-face-higher-infection-risk (Diakses 17 April 2020).
-
Ketua Pengarah Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). From the desk of the Director General of Health Malaysia. https://kpkesihatan.com/2020/04/16/kenyataan-akhbar-16-april-2020-situasi-semasa-jangkitan-penyakit-coronavirus-2019-covid-19-di-malaysia/ (Diakses 17 April 2020)
-
Cochrane. COVID-19 Resources. https://www.cochrane.org/news/special-collection-effective-options-quitting-smoking-during-covid-19 (Diakses 17 April 2020)
-
Portal Rasmi My Health Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia. http://www.myhealth.gov.my/en/nicotine-replacement-therapy-nrt/ (Diakses 17 April 2020)
-
Info Sihat. Bahagian Pendidikan Kesihatan. Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). https://www.infosihat.gov.my/index.php/isu-semasa/42-tips-berhenti-merokok (Diakses 17 April 2020)

Leading Causes of Death in Malaysia
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the average human lifespan was reported as 72 years in 2016 (1). Notably, Malaysia's life expectancy stood at 76.07 years in 2019, with a subsequent increase to 76.22 years in 2020, marking a 0.19% rise from the previous year (2). This evolution prompts us to inquire about the factors underpinning this fluctuation in life expectancy within Malaysia. In this discourse, we delve into a comprehensive exploration of the myriad factors that shape life expectancy, focusing specifically on the determinants of mortality in Malaysia.
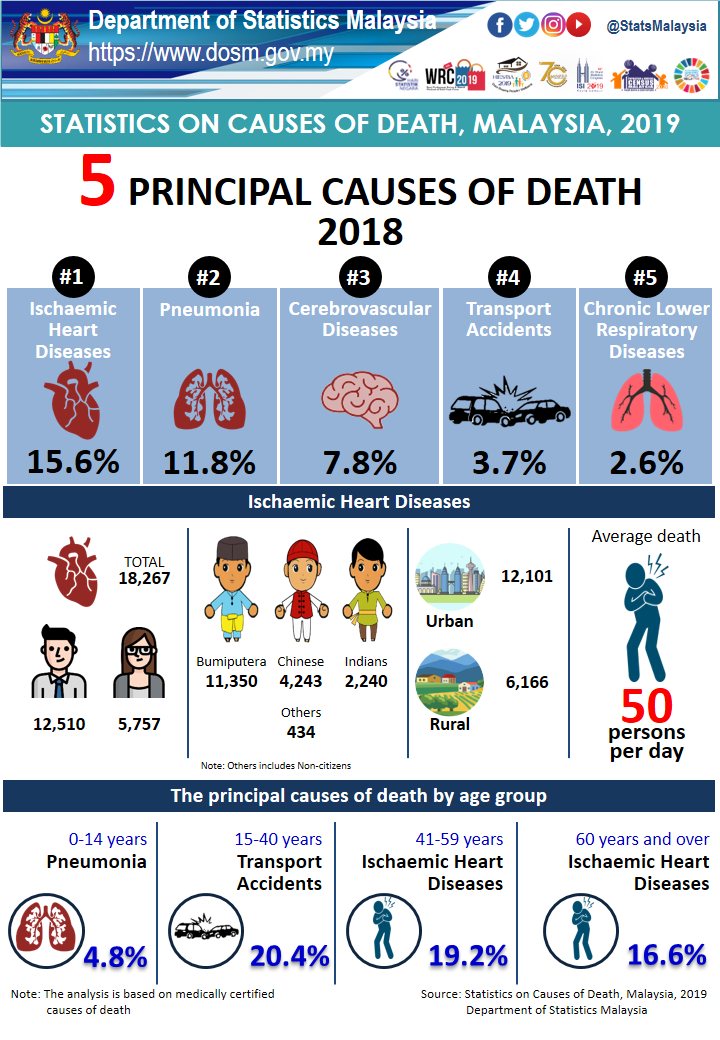
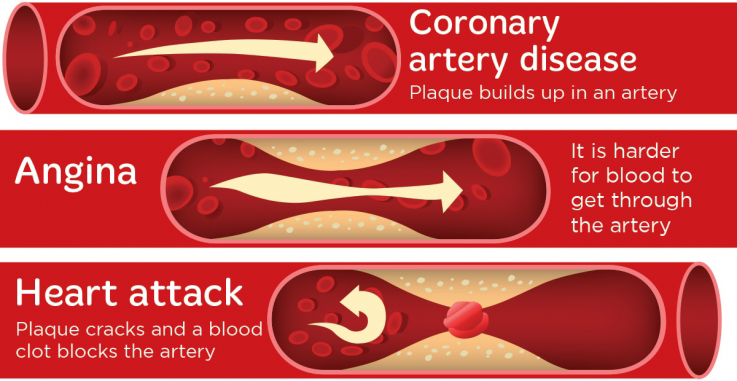
According to the statistics furnished by the Department of Statistics Malaysia on October 30, 2019, Ischaemic heart disease emerged as the leading cause of death, accounting for 15.6% of all fatalities, encompassing both males and females (3). Ischaemic heart disease, characterized by the constriction of heart arteries, results in diminished blood oxygen supply to the heart muscle. This condition, often referred to as coronary artery disease or coronary heart disease, which can ultimately lead to heart attack.
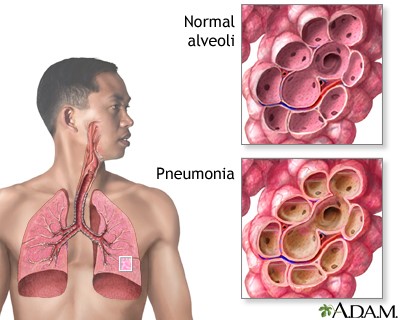
Subsequently, the statistical data reveals another significant contributor to mortality: Pneumonia, equally accounting for 15.6% of deaths (3). Pneumonia, an infection that inflames the air sacs within one or both lungs, can result in the accumulation of fluid or pus within these sacs. This inflammation leads to symptoms like coughing with phlegm or pus, elevated fever, chills, and labored breathing. Pneumonia can be triggered by a spectrum of microorganisms, encompassing bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Its severity spans from mild to life-threatening, posing the most substantial risk to infants, young children, individuals above 65 years of age, and those with underlying health conditions or compromised immune systems (5).
Ranking as the third leading cause of death in Malaysia, cerebrovascular diseases emerge prominently (3). The term "cerebrovascular" amalgamates two components— "cerebro," denoting a substantial part of the brain, and "vascular," signifying arteries and veins. Together, "cerebrovascular" encapsulates the intricate network of blood flow within the brain. This category of disease encompasses all conditions wherein a sector of the brain experiences transient or permanent effects due to restricted blood supply or hemorrhage, with one or more cerebral blood vessels being implicated in the pathological process. The spectrum of cerebrovascular disease spans from strokes to conditions such as carotid stenosis, vertebral stenosis, intracranial stenosis, aneurysms, and vascular malformations (6).
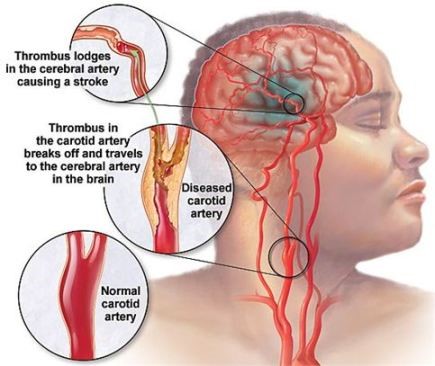
Interestingly, transport accidents accounted for only 3.7% of the total (3). It's noteworthy that the Malaysian fatality rate for transport accidents has remained unaltered since 2007. The Global Status Report on Road Safety, jointly published by the WHO and the World Bank in December 2018, revealed that Malaysia recorded 7,152 deaths in 2016, with males comprising 87% and females 13% of the total. Among road traffic deaths, motorcyclists constituted over half of the casualties. A deeper exploration into motorcycle fatalities highlighted that the majority were riders (89%), with individuals aged 16 to 20 years accounting for 22.5% (7).
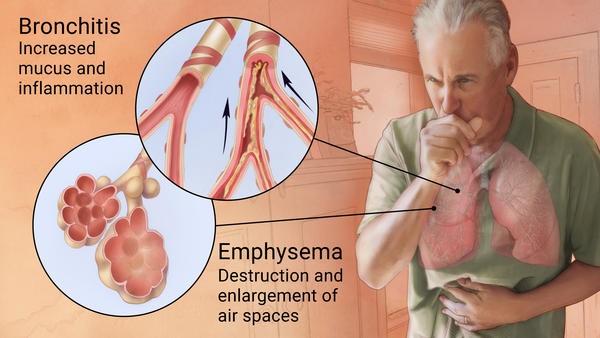
Chronic Lower Respiratory Disease (CLRD) emerges as another notable cause of death in Malaysia (3). CLRD encompasses three key ailments – chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and asthma – all characterized by breathlessness due to airway obstruction. While chronic bronchitis and emphysema involve irreversible obstruction, asthma's obstruction is reversible. Chronic bronchitis is typified by a productive cough occurring most days of the month for at least three consecutive months over two years. Emphysema involves the permanent enlargement of air spaces at the bronchioles' termini, accompanied by the destruction of their walls. Smoking is a primary cause of emphysema, yet approximately half of emphysema patients have an inherited condition known as alpha-1 antitrypsin (ATT) deficiency. ATT, a liver-produced protein, can be deactivated by cigarette smoke. Ordinarily, ATT functions to inhibit elastase, an enzyme that targets elastin, a crucial protein in lung structure. As elastin degradation occurs, alveolar walls may collapse, forming enlarged, irreversibly distended air sacs (8).
We can infer from the above-mentioned statistics that diseases played a significant role among the common causes of death. Malaysians should therefore act wisely in order to increase our average lifespan. By altering our lifestyle, we can take control of a health issue. Additionally, what we eat is important. Have you heard the saying, "You are what you eat"? Change your eating habits today to start taking care of your health.
References
- World Health Organization. 2020. Life Expectancy. [online] Available at: https://www.who.int/gho/mortality_burden_disease/life_tables/situation_trends/en/ [Accessed 17 April 2020].
- DEPARTMENT OF STATISTICS MALAYSIA, 2019. STATISTICS ON CAUSES OF DEATH, MALAYSIA, 2019. [online] Available at: https://dosm.gov.my/v1/index.php?r=column/pdfPrev&id=RUxlSDNkcnRVazJnakNCNVN2VGgrdz09 [Accessed 17 April 2020].

Facts on Fiber
“Eat more vegetables and fruits to get your fiber!” You may have heard these words. But what is fiber, really? How it works to improve our health? Let us take a closer look on it!
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that our body cannot digest undigested. Though most carbohydrates are broken down into sugar molecules but fiber cannot be broken down into sugar and thus it will pass through our body. These carbohydrates often considered beneficial in which mostly come from fruits, vegetables and legumes (1, 3, 6).
Fiber comes in two varieties, both beneficial to health (3):
Soluble fiber
Dissolves in water; absorb water to form a gel like substance that slow the digestion and cause you to feel full. They have been shown to decrease cholesterol and lower blood glucose. Common source of soluble fiber includes beans, oat bran, fruits and vegetables. It is also found in pysllium, a common fiber supplement.
Insoluble fiber
Does not dissolve in water; Increase fecal bulk and appear to help food pass more quickly through the digestive tract so it can be of benefit to those who struggle with constipation and irregular stools.
Facts About Fiber (3,4)
#1 Fiber aids in achieving healthy weight.
#2 Fiber fight diseases. It appears to reduce risk of developing various health conditions including heart disease, diabetes, constipation and breast cancer.
#3 Fiber helps to lower cholesterol.
#4 Fiber helps to regulate blood glucose.
#5 Recommended dietary fiber intake per day for all age group is 20-30g/day. However, if a person is not currently eating enough of fiber, he or she should increase his or her fiber intake slowly to avoid gas and bloating.

#6 More fiber needs more water. When eating a high fiber diet, be sure to drink at least eight or more glasses of water every day.
#7 Fiber aids in improving digestion by increasing stool bulk and regularity. A high-fiber diet may help reduce the risk of hemorrhoids and diverticulitis.
#8 Too much fiber is a bad thing. You may experience abdominal cramping, bloating, gas, constipation and even diarrhea.
#9 Fruit and vegetable peels are rich in several nutrients including fiber. Eating unpeeled fruits and vegetables keep you feel full longer due to its high fiber content. However, certain fruit and vegetable peels may be hard to consume or simply inedible. These peels are best removed and not eaten.
#10 Fruits and vegetable juice has less fiber than whole fruits and vegetable. This is because the skin is removed and thus it is more healthful to eat whole fruit and vegetable.
#11 Fiber cannot be cooked out.
Tips to Increase fiber intake (5,7)
Consume products that have whole grain listed as the first ingredients, high fiber content and low fat and sugar content.
Replace white rice, bread and pasta with brown rice and whole grain products.

Include legumes in your diet (beans, dried peas and lentils)

Eat unpeeled whole fruit and vegetables not juice.
Snack on fruits and vegetables
Take a fiber supplement (e.g psyllium)
In conclusion, fiber is an important dietary substance to your diet. This is because high fiber foods are also good sources of vitamins, mineral and antioxidants which offer many health benefits. Therefore, as one of the key ingredients to healthy eating, fiber is something you cannot skip.
References
-
Cleveland Clinic. 2019. Improving Your Health With Fiber. Available from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/14400-improving-your-health-with-fiber [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Danielle, D. 2018. How much fiber is too much. Medical New Today. Available from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321286#treatment [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Harvard University School of Public Health. (n.d.). Fiber. Available from https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/ [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Karin, L. 2016. 45 Interesting Facts about FIber. Fact Retriever. Available from https://www.factretriever.com/fiber-facts [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Kerri, A., J. 2016. 16 Easy Ways to Eat More Fiber. Healthline. Available from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/16-ways-to-eat-more-fiber [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Mayo Clinic. 2018. Dietary fiber: Essential for a healthy diet. Available from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fiber/art-20043983 [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- My Health Ministry of Health. 2012. SERAT DAN KAWALAN DIABETES. Available from http://www.myhealth.gov.my/serat-dan-kawalan-diabetes/ [Accessed on 23 April 2020]

Red meat: Is it Good or Bad?
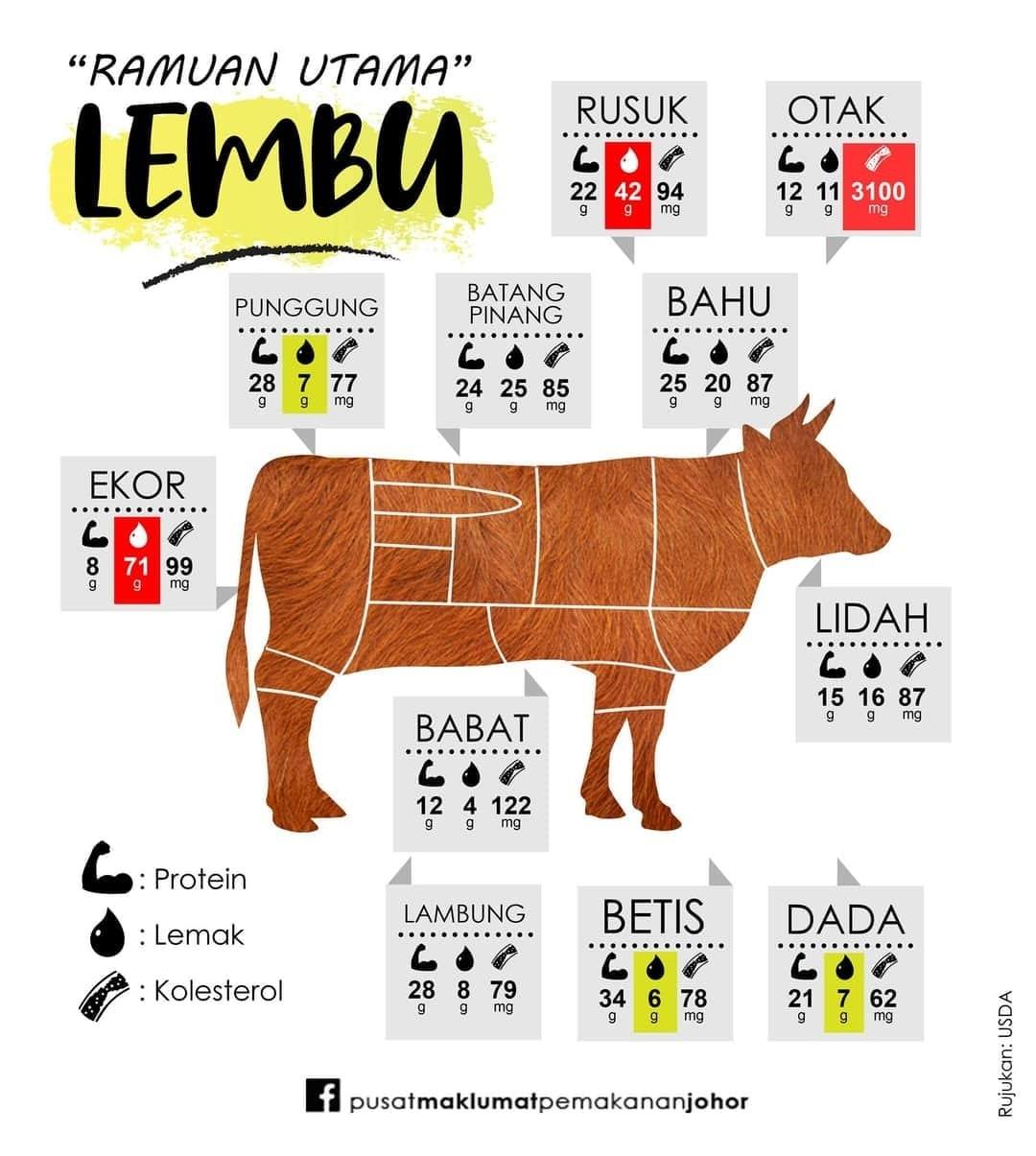
Meat refers to the muscle or organs of an animal consumed as food. In most parts of the world, it comes from animals raised on large industrial farms. As for red meat, it refers to meat from the source of pork, ham, and cuts from pig, lamb, and beef. Red meat is particularly said to have a link with various kinds of disease, such as heart disease and cancer; the question is, is this true?
Well, this statement is partially true. First, there are various kinds of red meat on the market. There is lean meat (meat without its fat), meat with its fat, and processed meat. Processed meat refers to meat that has undergone processes such as salting, curing, fermenting, smoking, and other processes to enhance flavour or improve preservation. Processed meats include ham, salami, bacon, and sausages such as frankfurters and chorizo. Certain minced meats on the market also undergo this kind of processing, which makes them processed foods as well.
Meat itself, referring to lean meat, is a healthy food. It is a good protein source and contains micronutrients such as zinc, vitamin B12, and iron. Iron in meat is easier to absorb, or, in other words, has higher bioavailability, as compared to iron from plant-based foods. Lean meat is also part of the food that is recommended to be eaten in the Malaysian Food Pyramid.

Recommended meat consumption
It is advised to eat 1 to 2 servings of either poultry, meat, or legumes and 1 serving of fish each day, as stated in the food pyramid's section on fish, poultry, meat, and legumes. This is so because the main takeaway from the Malaysian Dietary Guidelines (MDG) is to eat a variety of foods in moderation and with balance. Therefore, it is advised to eat food from a variety of sources, such as foods containing protein, which can come from fish, meat, poultry, and eggs. The protein source for dinner must therefore be meat, poultry, or eggs if you received your protein for lunch that day from a fish source. Another question comes up: how much constitutes one serving?

Example of a serving size of protein.
Serving is loosely translated into ‘sajian’ or ‘hidangan’ in Bahasa Malaysia; thus, the picture above shows how much per serving of protein there is. As for meat, 1 serving of meat is about 2 matchboxes worth of meat. For fish, a medium-sized fish is equivalent to 1 serving, while for chicken, one part of the chicken, such as a drumstick, is considered 1 serving of chicken. As for eggs, 1 egg is considered a serving of protein.
As mentioned earlier, it is not advisable to consume protein from the same source, so it is also not advisable to consume meat every day, since we have protein-based foods from a variety of sources that will give different kinds of nutrients as well, such as ‘tauhu’, ‘tempeh’, eggs, seafood, and many more.

The picture below shows an easy way to know how much you should consume for carbohydrates, vegetables, fruits, and protein just by using your hands.

Good and bad things about meat
The study mostly found out that lean meat has various positive outcomes on individual health, especially for those with strength training exercises like athletes, as compared to if they consumed food from carbohydrates sources like pasta or rice, their muscle growth would be much slower. Another meta- analysis study that focused on the consumption of lean red meat (less than 0.5 servings per day) noted that the consumption of lean red meat does not negatively affect blood lipids or blood pressure. Which means the consumption of lean red meat does not impose a risk of heart problems, provided it is consumed within the recommended intake.
The study mostly found out that lean meat has various positive outcomes on individual health, especially for those with strength training exercises like athletes, as compared to if they consumed food from carbohydrates sources like pasta or rice, their muscle growth would be much slower. Another meta- analysis study that focused on the consumption of lean red meat (less than 0.5 servings per day) noted that the consumption of lean red meat does not negatively affect blood lipids or blood pressure. Which means the consumption of lean red meat does not impose a risk of heart problems, provided it is consumed within the recommended intake.
However, there are also studies that indicate that the consumption of red meat can impose health problems, such as that its saturated fat can lead to colon and breast cancer; the higher the cooking temperature for meat, the more carcinogenic it is; and the heme that is found in meat when cooked can produce compounds that can damage the cells, leading to cancer.
Which is why, when it comes to food, there is not just healthy food and unhealthy food; it is more than that. It depends on the health status of the individual consuming it, the cooking method, and various other factors.
In conclusion
Limiting red meat and processed meat to no more than 70g per day, or 2 servings per day, is the best. Consume protein-based foods from other sources of protein as well, not only red meat and processed meat, just as recommended by the Malaysia Dietary Guidelines (MDG).
References
- Red Meat (2019). https://www.diabetes.co.uk/food/red-meat.html (Accessed on August 4, 2020).
- World Cancer Research Fund. Limit red and processed meat. https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/recommendations/limit-red-processed-meat#:~:text=Dietary%20goal,%2C%20if%20any%2C%20processed%20meat. (Accessed on August 4, 2020).
- The truth about red meat. https://www.webmd.com/food-recipes/features/the-truth-about-red-meat#2 (Accessed on August 4, 2020).
- Is red meat bad for you, or good? An Objective Look. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/is-red-meat-bad-for-you-or-good (Accessed on August 4, 2020).

Is Fat Unhealthy?
Many diseases and health complications are believed to be linked to fat consumption, including obesity, diabetes, heart problems, and cancer. However, fats also play crucial roles in our bodies, such as aiding in the transport and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. Fats also act as insulators for vital organs and as shock absorbers. With these functions in mind, it begs the question: Is fat truly the culprit behind various diseases? (1,2,3).

History of Dietary Fat Recommendations (4)
The confusion surrounding dietary fat intake has its roots in the past, as nutrition scientists struggled to effectively communicate their findings from nutrition studies to the public. Previously, the classic diet-heart hypothesis vilified dietary fat due to two key observations from observational studies and randomized controlled trials.
- Controlled feeding trials showed that dietary saturated fatty acids and cholesterol elevated levels of serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol (considered "bad" cholesterol).
- Dietary fat intake was associated with increased levels of serum total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol, which were predicted factors for cardiovascular disease.

Current Insights on Dietary Fat Intake (4)
Past research focused heavily on singular causal outcomes, but contemporary extensive research has illuminated multiple pathways contributing to the development of cardiovascular diseases. These pathways include factors beyond total cholesterol intake or LDL levels, such as smoking, obesity, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and more.
As a result, recommendations for dietary fat intake among individuals with cardiovascular disease and those seeking to prevent it need to evolve accordingly.

Types of Fats and Cholesterol, Along with Dietary Recommendations (4,5,6)
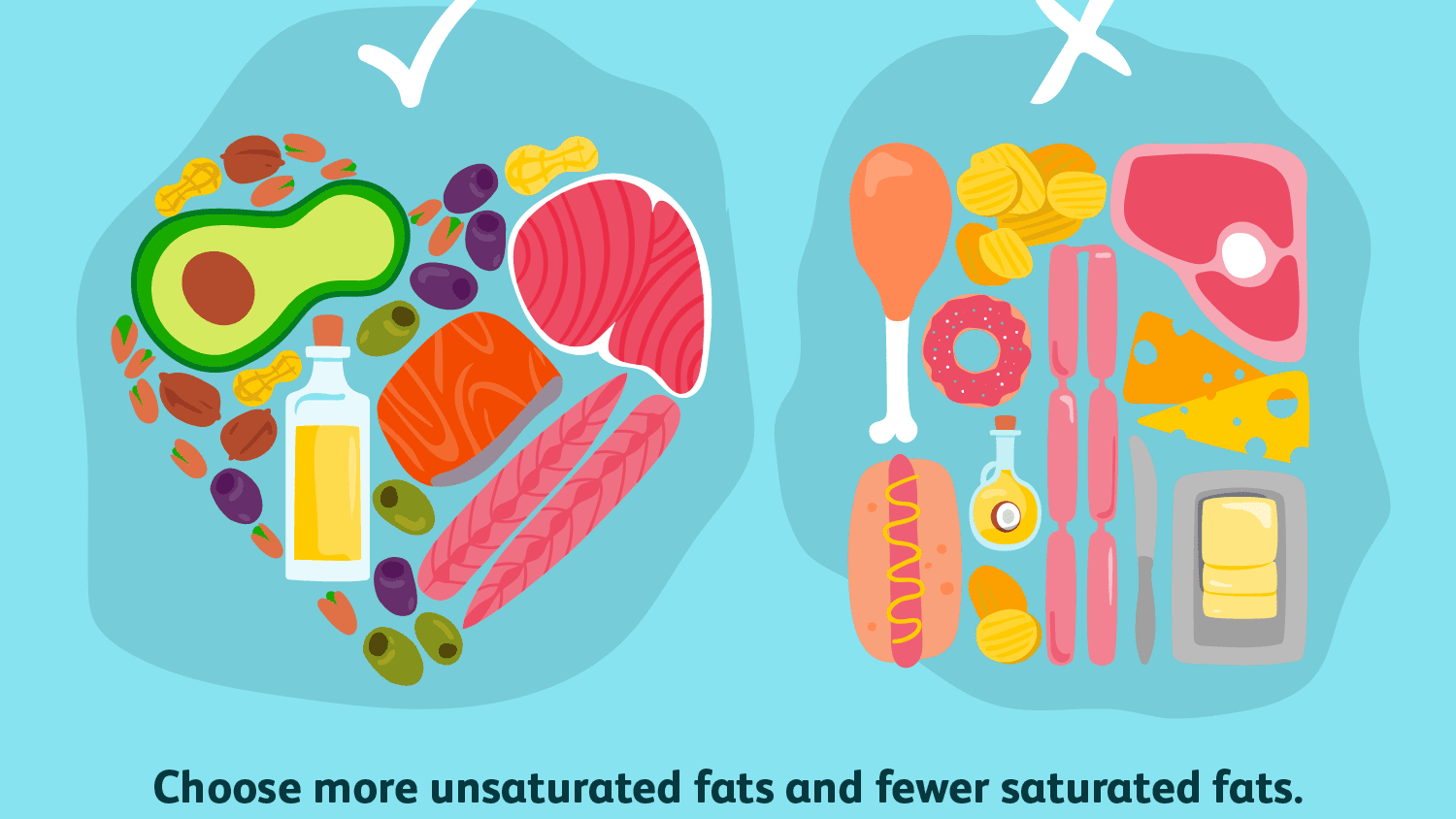
To comprehend dietary recommendations for fat and cholesterol intake, let's first explore the different types. Saturated fat, often labeled as "bad" fat, is solid at room temperature. It can contribute to weight gain and increased levels of LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream. Sources high in saturated fat include meat, chicken skin, margarine, and fatty dairy products.
Unsaturated fats, considered "good" fats, are divided into monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. They can elevate HDL (good cholesterol), lower LDL (bad cholesterol), reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Examples of monounsaturated fats are palm oil, canola oil, olive oil, and cashew nuts. Polyunsaturated fats include corn oil, sunflower oil, and fish oil. For optimal results, studies suggest a 1:1 ratio blend of these two types of oils in cooking, such as combining palm oil and sunflower oil.
Trans fat, the least desirable type, forms during hydrogenation when liquid fats turn solid. Trans fat, or trans-fatty acids, are commonly found in processed and frozen foods to prolong shelf life. Consumption of trans fat should be limited, as it's associated with elevated LDL cholesterol levels, increased cardiovascular disease risk, and certain cancers. Sources of trans fat include margarine, fried foods cooked in unsaturated fats like sunflower oil, as well as ready-to-eat and canned foods.
In Conclusion (4,5)
While there isn't a specific universal standard for each fat type due to various factors, the World Health Organization (WHO) generally recommends fat intake between 20% to 30% of total calories. In Malaysia, this translates to about 45g to 67g of fat, roughly 3 to 5 tablespoons of oil (based on a 2000 kcal/day diet).
As consumers, it's vital to distinguish health-promoting fats from detrimental ones and limit the intake of harmful fats to cultivate a healthy eating lifestyle.
Practical steps include choosing fresh poultry or seafood over processed foods like tempura or finger foods. Cooking methods matter greatly; opt for steaming, baking, boiling, and grilling. When dining out, consider that many eateries reuse cooking oil, making healthier choices paramount.
Limiting trans-fat intake is crucial. Apart from processed and frozen foods, restrict consumption of high-cholesterol items such as mayonnaise, animal organs, and fish heads.
Being mindful of what you fuel your body with is as important as feeding your mind with positive thoughts. Nourish both body and mind with beneficial nutrients by selecting healthy fats.

Calcium Supplementation, Who Needs it?
Calcium is among very common micronutrient heard by public and milk advertisement is the contributor to this. Through this many people know that calcium is very important for bone and teeth. Calcium can be found in various food products nowadays not only milk. It has becoming partly marketing strategy for food company to incorporate calcium in their food product especially if the target consumer is children or elderly since many people know that calcium is vital for these two groups, children, and elderly.
Function of Calcium?
Body needs calcium for strong bones and teeth. Calcium is also required to carry out important function such as for muscle to move, for nerves system to carry messages between brain and body parts, for blood vessels to move blood throughout the body, and for body to help release hormones and enzyme that affect almost every function in the human body (1,2,3).
How much calcium is needed?
Normal adult need about 1000 mg of calcium daily, however there are certain condition which require to consume up to 1300 mg of calcium daily such as for pregnant lady, lactating mother, post-menopausal women, and man who is above 70 years old of age (1,2,4).
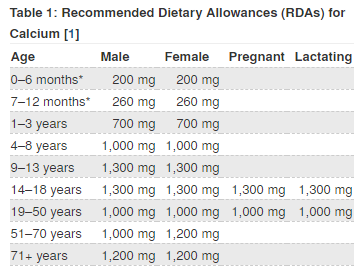
Calcium and diet
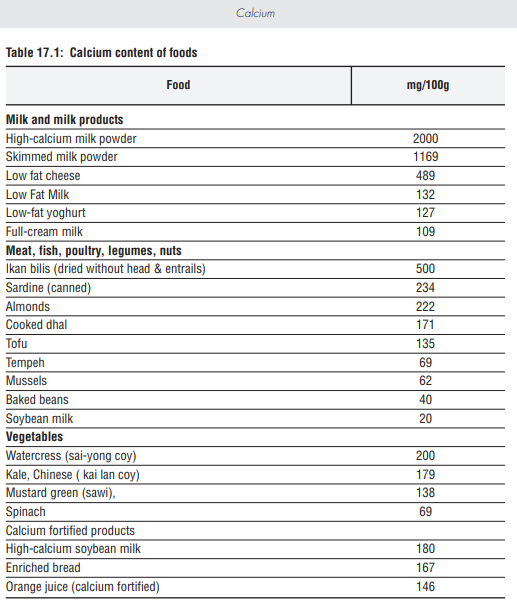
Body does not produce calcium, so it needs to be consumed from foods. Luckily, calcium can be found in variety of foods such as dairy products, dark leafy vegetables, fish, and many other fortified food products (1,2,3). As for our local food products sardine, anchovies, cencaluk, budu, tofu, tempeh, broccoli, kalian, and tapioca leaves are among food that is high with calcium (4).
It is also important to take note that in order to absorb calcium, body needs vitamin D. Only a few foods containing small amount of natural vitamin D, such as egg yolks and salmon with bones. Mostly, we rely on the exposure to sunlight in order to get enough vitamin D, of course in Malaysia the country with sun all year long have no problem with this! However, as currently we are still in the so to say the ‘lockdown’ phase thus it is very important to remind everyone to get the sunlight every day at least 20 minutes for its vitamin D and calcium absorption (1,2,4).
Though all the foods stated above are easily found, but there are conditions which hinder individuals from getting enough calcium from diet thus require it from calcium supplementation.
Condition for calcium supplementation
Before considering calcium supplement, individuals must understand how much calcium needs by the body (stated above). Then individuals must seek help from nutritionist, dietitian, pharmacist, or doctors, where they will assess your calcium consumption from your diet through diet recall. If the calcium intake falls short thus you need to top up calcium from supplement.
Hypertensive individuals and diet with large amounts of sodium.
Several literature reviews on topic of total calcium intake from food and supplements with regards to hypertension suggested that there is possible link to lowering high blood pressure. However, since most of the study design have small number of subjects, and were tested with people from different background, and not to mention possess various kind of biases thus making it difficult for scientist to draw conclusion (1,2).
However, a large study subject (Women’s Health Study), found out that calcium intake was inversely associated with risk of hypertension in middle-aged and older women, in terms of preventing hypertension (1,2).
The consumption of high sodium food lead to more calcium excretion through the urine, which will lead to constriction of blood vessels, which in the end resulting in high blood pressure. Drinking large water after consuming salty food, is not enough, as it may be making blood pressure return to its slightly normal condition, but it is not helping with the loss of calcium (1,2,5).
Pregnant and lactating mother
Often times, pregnant women is being reminded of how important is folic acid for the baby, even from the trying to conceive period, healthcare providers already advise them to consume folic acid, in order to prevent spina bifida to the baby. However, calcium is as well very important for mothers throughout pregnancy and lactating period especially for mother who is lack of calcium from diet (1).
Several professional organizations recommend calcium supplements during pregnancy for women with low calcium intakes to reduce the risk of preeclampsia (a condition where gestational hypertension always occur). For example, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (ACOG) states that daily supplementation with 1,500–2,000 mg calcium may reduce the severity of preeclampsia in pregnant women who have calcium intakes less than 600 mg/day. Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 1,500–2,000 mg calcium for pregnant women with low dietary calcium intakes, particularly those at higher risk of gestational hypertension (1).
As for normal healthy mother, the consumption of calcium is especially important during lactating period, mother may notice symptoms such as cramps which indicates lack of calcium during pregnancy and lactation period. Also if a mother is on iron supplementation as well, it is advisable to not consume both at the same time, it is best to gap several prior the consumption of these two since it can interfere with the absorption (1,2).

Post-menopausal women and elderly
Throughout the lifespan, bones are constantly being broken down and built up in a process known as remodelling. Bone cells called osteoblasts build bone, while other bone cells called osteoclasts break down bone if calcium is needed. In healthy individuals who get enough calcium and physical activity, bone production exceeds bone destruction up to about age 30. After that, destruction typically exceeds production. This is sometimes called “negative calcium balance,” which can lead to bone loss. Women tend to experience greater bone loss than men later in life due to menopause, a condition that lowers the amount of hormones that help to build and preserve bone (5).
Getting enough dietary calcium at all ages may help to slow the degree of bone loss, but calcium intakes at any level are not known to completely prevent bone loss. Calcium is less easily absorbed at later ages, and therefore eating a very high amount of calcium will not always resolve the problem (5).
Studies on calcium intake and bone density in postmenopausal women have mixed results that could be due to various reasons. Because the results of some large trials found that higher calcium intakes (usually achieved with a supplement) was associated with improved bone density and slightly lower risk of hip fractures, the RDA for calcium for postmenopausal women is higher than at younger ages. Some studies suggest that frail elderly (80 years and older living in institutions) may benefit from supplementation more than “younger” elderly who live independently in the community (5).


Individuals with lactose intolerance and limit dairy products
Individuals with lactose intolerance usually, is unable to consume food that has high amount of calcium especially if it come from milk and dairy source of food. Thus, lactose intolerance individuals need to consume it form dark leafy vegetables and soy-based product. However, in most cases the consumption is not enough or individuals with lactose intolerance consume not enough vegetable rich with calcium or other food source rich with calcium, thus for this specific population calcium supplementation is needed either from fortified food product such as ready to eat cereals or from calcium supplementation tablet itself.
Individuals receiving treatment on certain medication in the long period
Well, there are certain medication which can influence the absorption of calcium. Medication such as to treat osteoporosis (bisphosphonates), antibiotics (fluroquinolone), medication to treat low thyroid problem (levothyroxine), anticonvulsant (phenytoin), diuretic medication (Lasix and bumex), antacids containing aluminium and magnesium and also glucocorticoids (prednisone). These are all either causing calcium loss in the urine or cause calcium depletion in the bone. Thus, if you are on these medication, it is advisable to take calcium rich foods four hours prior or after the intake of medication, so that it would not interfere with the absorption of calcium, it is also best if you consume calcium supplementation if you do have poor intake of calcium rich food as well (2).
In conclusion, in these situations, calcium supplements may help you meet your calcium requirements. Talk with your doctor or dietitian about whether calcium supplements are right for you.
References
- National Institute of Health (NIH). Department of Health and Human Service. Calcium. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-HealthProfessional/ (Accessed on November 18, 2020).
- National Institute of Health (NIH). Department of Health and Human Service. Calcium. Fact Sheet for Consumers. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-Consumer/ (Accessed on November 18, 2020).
- Mayo Clinic. Nutrition and Healthy Eating. Healthy Lifestyle. Calcium and calcium supplements: Achieving the right balance. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/calcium-supplements/art-20047097 (Accessed on November 18, 2020).
- Ministry of Health (MOH). National Coordinating Committee on Food and Nutrition. Recommended Nutrient Intake (RNI): A Report of the Technical Working Group on Nutritional Guidelines (2017).
- Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. The Nutrition Source. Calcium. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/calcium/ (Accessed on November 18, 2020).

Grapeseed Extract and its benefits
Grape seed extract (GSE) is derived naturally from grape seed and is commonly used in dietary supplements for a variety of purposes. It is created by removing, drying, and pulverising the bitter tasting grape seeds. It contains a lot of antioxidants like phenolic acids, anthocyanins, flavonoids, and oligomeric proanthocyanidins complexes (OPC). Grape seed extract, in fact, is regarded as one of the best sources of proanthocyanidins. As a result, grape seed extract provides numerous benefits to the human body, including disease prevention, protection against oxidative stress, tissue damage, inflammation, and many more. In this article, we will look in depth at the potential health benefits of grape seed extract (GSE) based on studies:
Wound healing activity and antioxidant properties.
Numerous studies have shown that grape seed extract contains a high level of antioxidants. Using punctured wounded mice, researchers discovered that mice treated with GSE in the wound affected area grew tissue faster than mice treated with only normal saline. Another difference between GSE-treated mice and placebo-treated mice was more organized tissue formation and a higher rate of collagen deposition.
Topical application of 2% GSE cream in the area of a post-surgery surgical wound heals the wound completely in an average of 8 days, compared to 14 days for placebo. This is due to GSE's vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) properties, which promote the regeneration of damaged blood vessels while increasing the amount of free radicals present at the wound site. Free radicals aid in the killing and removal of pathogenic bacteria and endotoxin from the site, as well as in the healing of wounds
Apart from wound healing and skin health properties, it also has anti-ageing properties. GSE proanthocyanidins delay skin ageing by reducing lipid oxidation on the skin structure.
Cardiovascular and antihypertensive properties.
Cardiovascular disorders (CVD) are among the major problems that arise due to modern, unhealthy lifestyles, which are the primary cause of death worldwide. It is a disorder that affects the condition and function of the heart and blood vessels in general. Changes in these two can result in cardiac arrest, heart stroke, hypertension, chest pain, and other complications. Studies show that GSE may prevent atherosclerosis (a condition where there is a build-up of fats, cholesterol, etc. in the blood vessel walls, which can restrict blood flow), inhibit or limit the oxidation of LDL (bad cholesterol), reduce inflammation, inhibit platelet aggregation, and lower blood pressure. It lowers blood pressure by suppressing oxidative stress and inhibiting the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and nitric oxide, which mediate vasodilation, hence making the constricted blood vessels dilate and improving blood pressure.

Antimicrobial activity
GSE has been shown to have antimicrobial properties; for example, when applied topically, resveratrol in GSE increases the production of cathelicidin, which inhibits the growth of Staphylococcus aureus. In another study, quercetin, caffeic acid, and quercetin-3-0-rutinoside in GSE were responsible for the inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes. It is also worth noting that GSE had the highest inhibition activity against almost all Listeria species. The review on the benefits of GSE also reported that the antimicrobial effect of GSE is attributed to changes in cell morphology and DNA content.
Cosmetic and nutraceuticals
Skin ageing is a natural process which occurs due to the external and internal factors involving genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. GSE is rich in proanthocyanidin help to reduces the lipid oxidation of cellular structure of the skin and inhibit the production of free radicals. A study was carried out in which the anti-ageing effect of GSE was investigate. The study concluded that GSE has a promising role as an anti-ageing compound.
GSE help skin structure by strengthening the collagen-based tissue (by increasing the collagen cross links). It also increases the synthesis of collagen and the conversion of collagen from soluble into insoluble one.
In conclusions,
GSE has various benefits to health due to its high antioxidant properties, it is able to scavenge the free radicals which an essential feature that could help with various body functions.
References
- National Institute of Health (NIH). National Centre for Complementary and Integrative Health (NICCH). Grape Seed Extract. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/grape-seed-extract (Accessed on March 15, 2021)
- 10 Benefits of Grape Seed Extract, Based on Science. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/grape-seed-extract-benefits (Accessed on March 15, 2021).
- Gupta, M., Dey, S., Marbaniang, D., Pal, P., Ray, S., & Mazumder, B. (2020). Grape seed extract: Having a potential health benefit. Journal of food science and technology, 57(4), 1205-1215

Differences between Omega 3, 6, and 9

The infographic above explains the types of good and bad fats. But what about the differences between Omega 3, 6, and 9? All these three fats can be considered good fats, but there are certain things that distinguish them from one another.
MUFA or Omega 9
Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA), also known as omega 9, is named because of the double bond position, which is on the ninth position from the omega end. It is a type of fat that is found in vegetable and animal fats such as canola oil, sunflower oil, olive oil, and nuts. Unlike polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), omega-9 is a non-essential fat, which means the body is able to produce these types of fat. However, there are also benefits when it is obtained from food, such as reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke, reducing LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol), increasing HDL cholesterol (good cholesterol), and helping to eliminate plaque buildup in the arteries, which can cause heart attacks and strokes.
PUFA or Omega 3 & Omega 6
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) can be divided into Omega 3 and Omega 6. The difference between these two is that the position of the double bond for Omega 3 is in the third position from the end, whereas for Omega 6, it is in the sixth position from the end.
Among the types of Omega 3 with extensive scientific research are eicosapentanoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-lipoic acid (ALA). The difference between these three types of Omega-3 fats is the number of carbon atoms: 18, 20, and 22 for ALA, EPA, and DHA, respectively. ALA can be converted to EPA and then to DHA, but the conversion, which usually occurs in the liver, is less than 15%, which is why it is recommended to consume EPA and DHA directly from foods or dietary supplements. ALA is present in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils. DHA and EPA are present in fish, fish oils, and krill oils. But the DHA and EPA in krill oil do not originate from krill but rather from the ingestion of microalgae.
Whilst, among the types of Omega 6 are linolenic acid (LA) and arachidonic acid (AA), The difference between these two is the position of the double bond in the omega-6 fatty acid chain. Linolenic acid (LA) is the same as ALA; it is an essential fatty acid that cannot be produced by the human body. Sources of food with LA are soybean oil, corn oil, safflower oil, peanut oil, cottonseed oil, and rice bran oil. While the sources of food for AA are peanut oil, meat, eggs, and dairy products,
Omega 3 and Omega 6 are beneficial for cardiovascular diseases because they can help manage cholesterol levels, triglycerides levels, and blood pressure levels. There is also certain supporting data that states that it can help with reducing weight and waist size, improving infant brain development in the foetus, and fighting inflammation. However, other than for cardiovascular health, the finding is quite inconclusive. But as for Omega 3 and 6 (PUFA) and heart health, the American Heart Association (AHA) recommends that 8–10% of calories should come from PUFA, as there is evidence that eating more PUFA—up to 15% of daily calories—in place of saturated fat can lower the risk of heart disease.
The diagram below shows the comparison between these three types of good fat:
All in all, Omega 3, 6, and 9 are beneficial for cardiovascular health, as they can help with lowering LDL levels (bad cholesterol), increasing HDL levels (good cholesterol), and helping with blood pressure levels. Several other studies also mentioned that certain good fats can help with inflammatory diseases such as joint pain and skin diseases such as eczema. However, consumption of all these fats must be in balance since overconsumption of them can have serious health effects! However, replacing bad fat (or even good fat) with refined carbohydrates does not help your health either. It is so important to note that everything must be in balance, and consuming healthy food is not about one type of food only; it is about variety, quality, and the food source as well!
References
-
Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH). Hyperlipidemia.
-
Harvard T.H Chan. School of Public Health. Types of fat. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/what-should-you-eat/fats-and-cholesterol/types-of-fat/
-
Harvard T. H Chan. School of Public Health. Saturated fat or not does type of fat matter. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/2014/05/15/saturated-or-not-does-type-of-fat-matter/
-
Healthline. Omega 3, 6, and 9. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/omega-3-6-9-overview#omega-6

Benefits of Fish Oil Supplementation
Consumption of fish is important as it is a good source of protein. It is recommended to consume one fish per day, according to the Malaysian food pyramid. This is because the consumption of fish in Malaysia is rarely equated with a risk of contamination with mercury, etc., unlike in western countries. This might be due to the types of fish and sizes of fish that we are consuming here as compared to other parts of the world. It is said that the bigger the fish, the more contamination it has; hence, there is a recommendation for pregnant mothers to consume small fish rather than big fish to avoid the risk of contamination.
Research on the benefits of fish oil supplementation also varies greatly, which is why in this article we are going to list out who might need a fish oil supplementation in their daily lives!
The benefits of ingesting fish oil can differ significantly between studies. A study found a connection between these omega-3 fatty acids and mental health disorders and that EPA and DHA can speed up brain development even in young children. Additionally, studies have demonstrated that it can help treat cardiovascular diseases, joint pain, and eczema. The question is, is it true that all of these effects can be obtained from fish oil consumption? (1)

Individual with mental health problems/disorders
In three lengthy studies spanning the years 1988 to 2008, researchers looked at the relationship between fatty acid intake and suicide risk among more than 205 000 participants. They discovered no proof that eating fish or fatty acids reduced the risk of suicide. "The vast majority of earlier research on whether fatty acid intake has any positive effects on mental health has been based on results from depression screening. The only time this relationship has been studied with concrete data on suicide mortality is in our study, which is also the largest of its kind.” (2)
While a study found that eating a balanced diet and exercising regularly are better for brain health than taking fish oil or omega-3 fatty acid supplements, A study of 3073 elderly people at risk of macular degeneration, an age-related cause of vision loss, found little benefit from omega-3 supplements on memory. Omega 3 supplements or a placebo were given to study participants at random for a five-year period. According to the researcher, a healthy diet cannot be replaced by a supplement; therefore, if you eat a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and marine fish, you probably don't need to take a fish oil supplement. According to this study, the overall dietary pattern is more important than a single nutrient (2).
Individuals with cardiovascular disease
Recently, there have been many studies suggesting that Omega 3 will not lower the risk of heart problems. To answer this, Dariush Mozaffarian, cardiologist from Harvard Medical School, said that he gathered 20 previous studies involving more than 68, 000 patients since 1989 and found that, overall, fish oil supplements did neither harm nor good since they did not significantly reduce people’s risk of mortality, cardiac death, heart attack, or stroke. But according to him, the research link between fish oil supplementation and heart problems is rather complex since it does not only take fish oil to shield the heart from various problems and diseases; it also takes weight status, exercise frequency, cigarette or substance use, and many more (3,4,5).

Which is why, interpreting the study, we would still recommend customers and patients consume more fish as a first-line measure. But if you do not like fish, or you feel like your consumption of fish is not enough, or you simply want to be sure that your body is getting omega 3, there is no harm in taking fish oil; it will certainly help with the essential nutrient, since omega 3 is a nutrient that your body cannot produce and can only get from diet (3,4,5).
Individuals with skin problem
A systematic review for the treatment of atopic dermatitis or eczema using fish oil supplementation is very scarce; the studies available are all small-sample studies. Not only are these three studies small, but they are also described as poor methodological studies by the reviewer, as they have many confounding factors. However, the outcomes of these studies show positive outcomes for eczema and overall daily living as compared to placebo (6, 7).
Another convincing relationship between consumption of fish oil and skin health is that in a study where pregnant women were given fish oil during pregnancy and followed up for 6 years, it was found that consumption of fish oil during pregnancy led to a positive skin health outcome for babies skin. The study also concluded that maternal supplementation with fish oil might have prophylactic potential for long-term prevention of asthma in offspring (6, 7).

In conclusion, consumption of fish oil has mixed results in studies depending on what kind of problem we are looking to solve with fish oil. Since there are various factors influencing a particular health problem, There is no magic pill in this world, honey! You need to, however, eat healthily, consume a lot of vegetables and fruits, and exercise, but if you think that you do not get enough omega 3 from your diet because you dislike fish, are afraid to consume fish regularly due to contamination, etc., or simply would like to make sure that your body has enough omega 3, then there is no harm in taking fish oil supplementation. It's just that in order to make sure you get the right omega 3 for your body, buy it from a pharmacy, make sure the product has a Ministry of Health (MOH) notification number, and simply ask a healthcare professional which omega 3 supplementation suits you, simply for the dosage and perhaps current medication that you are on, and you are good to go!
References
-
Harvard T.H Chan. School of Public Health. Fish: Friend or Foe? https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/fish/
-
Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. No mental health benefit from fish oil. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/no-mental-health-benefit-from-fish-oil/\
-
Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/fish-stroke-risk-mozaffarian/
-
Harvard T.H Chan. School of Public Health. Major Meta Analysis in Clinical Trial Omega 3 Supplemeny link with lower risk of CVD. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/press-releases/in-major-meta-analysis-of-clinical-trials-omega-3-fish-oil-supplements-linked-with-lower-cardiovascular-disease-risk/
-
Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. Fish Oil Supplementation and Heart Health. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/news/hsph-in-the-news/mozaffarian-fish-oil-supplements-heart-health/
-
Schlichte, M. J., Vandersall, A., & Katta, R. (2016). Diet and eczema: a review of dietary supplements for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. Dermatology practical & conceptual, 6(3), 23–29. https://doi.org/10.5826/dpc.0603a06
-
Huang, T. H., Wang, P. W., Yang, S. C., Chou, W. L., & Fang, J. Y. (2018). Cosmetic and Therapeutic Applications of Fish Oil’s Fatty Acids on the Skin. Marine drugs, 16(8), 256. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080256

101: Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q-10 (CoQ-10) is a naturally occurring quinone found in all organisms, from bacteria to mammals. It was discovered in 1940 and isolated in 1957 from the mitochondria of the beef heart. Coenzyme Q10, also known as Coenzyme Q, CoQ, CoQ10, Ubiquinone, Ubiquinone-Q10, Ubidecarenone, or Vitamin Q10, is a type of coenzyme. The number of side chains distinguishes the different types of coenzyme Q. CoQ10 is the most common coenzyme Q. CoQ10 is present in all human tissues, though its level varies.
Why do we need CoQ10?
CoQ10's main function is to act as an energy transfer molecule, where it is a co-factor in the production of energy. Essentially, all cellular functions are dependent on an adequate supply of energy, which explains why coq10 is vital for all tissues and organs. CoQ10 is also one of the most significant lipid antioxidants that prevents the generation of harmful substances in the body, such as free radicals, which can lead to the modification of proteins, lipids, and DNA.
Antioxidant is defined as a substance that inhibits the oxidation process or is a scavenger of free radicals that are produced by normal body processes, hence making the body more stable.
Due to its function as antioxidants, not only can it help neutralize free radicals and prevent the damage caused by free radicals, but it can also improve energy and augment the immune system.
Who needs CoQ10?
There are certain individuals who need to consume more CoQ10 as the amount in their bodies is diminishing.
- Individual who is consuming or on statin medication (medicine used to lower high blood levels of cholesterol or triglycerides to prevent heart problems). This is because studies show that statins interfere with the production of mevalonic acid, which is used to form CoQ10. Thus, individuals who consume statins have low levels of CoQ10 in their bodies.
- Individuals with heart conditions, such as heart failure and angina, may benefit from taking a CoQ10 supplement. A review of 13 studies in people with heart failure found that 100 mg of CoQ10 per day for 12 weeks improved blood flow from the heart.
- As CoQ10 is involved in the production of energy, it can be used by athletes and those who would like to boost physical performance. A 6-week study in 100 German athletes found that those who supplemented with CoQ10 daily experienced significant improvements in physical performance, measured as power output, compared to a placebo group. CoQ10 supplements help reduce the inflammation associated with heavy exercise and may even speed recovery.

How much do we need CoQ10?
A typical CoQ10 dosage is about 30–90 mg per day, taken in divided doses, but the recommended amount can be as high as 200 mg per day. CoQ10 is a fat-soluble antioxidant, so it is better absorbed when taken with a meal that contains oil or fat. The clinical effect of CoQ10 may take up to eight weeks.
Food source with CoQ10?
Primary dietary sources of CoQ10 include oily fish (such as salmon and tuna), organ meats (such as liver), and whole grains. Most individuals obtain sufficient amounts of CoQ10 through a balanced diet, but supplementation may be useful for individuals with particular health conditions. CoQ10 is available as a supplement in several forms, including soft gel capsules, oral spray, hard shell capsules, and tablets.
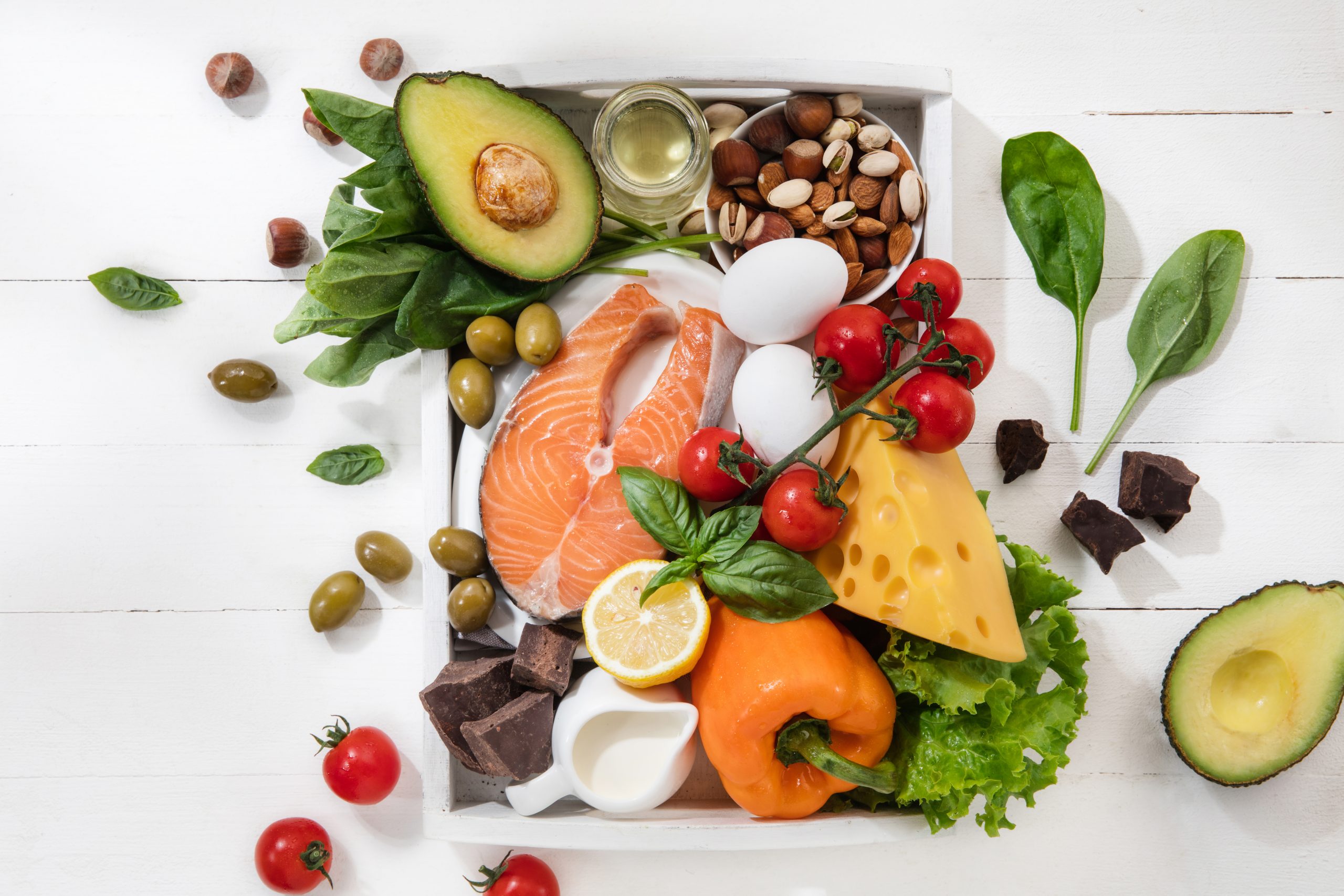

Safety precautions
Consumption of CoQ10 might not really be suitable for individuals who consume warfarin medication, pregnant women, or breastfeeding mothers.
References
- Saini R. (2011). Coenzyme Q10: The essential nutrient. Journal of pharmacy & bioallied sciences, 3(3), 466–467. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.84471
- National Institute Health (NIH). National Centre for Complementary and Integrative Health. Coenzyme Q10. https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/coenzyme-q10
- CoQ10 dosage: How much you should consume per day? https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/coq10-dosage

Benefits of CoQ10 for Heart Health
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a substance that is naturally present in the human body, with the highest levels in the heart, liver, kidneys, and pancreas. It is also naturally present in the foods that we eat, such as cold-water fish like tuna, salmon, mackerel, and sardines, vegetable oils, and meats. Other than these types of foods, individuals can consume CoQ10 through supplementation. Here are some of the benefits of consuming CoQ10 for your heart's health:
Therapeutic benefit in hypertension.
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a condition in which the blood pressure rises above 120/80. CoQ10 has been shown in animal model studies to significantly reduce blood pressure levels while having no effect on other hypertension-related parameters such as plasma renin, serum/urine sodium and potassium, or urinary aldosterone. It is also suggested that varying COQ10 dosage results in a reduced need for medication. In a human study, taking 60 mg of CoQ10 twice daily for 8 weeks reduced blood pressure, plasma inulin, glucose, and several lipid compounds. Other human studies have ranged from 100 to 225mg/day for 4.4 to 10 months.

Therapeutic benefit in coronary artery disease.
Coronary heart disease (CHD) occurs when the coronary arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to your muscles become narrowed due to a gradual buildup of fatty material within their walls. The condition is also referred to as atherosclerosis. Pretreatment with CoQ10 has been shown in animal studies to reduce myocardial ischemia (occurs when blood flow to the heart muscle is obstructed by a partial or complete blockage of plaque buildup (atherosclerosis)) and cardiac dysfunction. In human studies, a dose of 300 mg/day for 7 days straight improves heart efficiency as measured by oxygen consumption per energy formed. Another study on humans using a 150mg dose of CoQ10 found that the supplement increased treadmill exercise tolerance. However, because these two studies involved a small number of subjects, they are not statistically significant.
Therapeutic benefit of congestive heart failure
A small study of 17 patients with congestive heart failure discovered that using 30 mg/day of coenzyme Q10 improved the patients' condition, with 53% of the patients becoming asymptomatic after four weeks of treatment (no symptoms). Another large-scale study involving 2664 patients who took 50-100mg/day of coenzyme Q10 for three months found that 54% of patients improved in their symptoms of insomnia, nocturia, and vertigo.

Is CoQ10 recommended for heart health prevention and treatment?
In conclusion, it appears that CoQ10 may be beneficial for heart health prevention and treatment, particularly for people with coronary heart disease, hypertension, and congestive heart failure. This is due to its ability to prevent LDL oxidation. It also appears that the majority of patients with heart disease are deficient in coenzyme Q10, which can lead to a variety of heart-related complications later on.
References
- Sarter, B. (2002). Coenzyme Q10 and cardiovascular disease: a review. Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing, 16(4), 9-20.

Do you know why fiber is important?
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that our body is unable to digest. Though most carbohydrates are broken down into sugar molecules, fiber cannot be broken down into sugar molecules, and instead it passes through the body undigested. Fiber helps regulate sugars in the body and helps keep hunger and blood sugar in check.
Children and adults need at least 20 to 30 grammes of fiber per day for good health. It can be obtained by consuming a diet rich in whole grains, vegetables, legumes, nuts, and fruits.
There are two types of fiber: soluble fiber and insoluble fibre.
-
Soluble fiber is a type of fiber that dissolves in water and can help lower glucose levels and blood cholesterol levels. Foods with soluble fiber include oatmeal, nuts, beans, lentils, apples, and blueberries.
-
Insoluble fiber is a type of fiber that does not dissolve in water. It can help food move through the digestive system, promoting regularity and helping to prevent constipation. Foods with insoluble fibers are wheat, whole wheat bread, whole grain couscous, brown rice, legumes, carrots, cucumbers, and tomatoes.
There are various studies confirming that consumption of a diet high in fiber helps to make the overall body function healthier.
Heart Health
In a Harvard study with over 40, 000 male health professionals, researchers found that consumption of a high-fiber diet reduced the risk of getting coronary heart disease by 40%. Another study conducted by Harvard among female nurses also found similar findings: a high-fiber diet lowers the risk of metabolic syndrome (a combination factor of heart disease and diabetes). These factors are high blood pressure, high insulin levels, excess weight, a high triglyceride level, and a low HDL level (good cholesterol level).

Diabetes Mellitus Type 2.
A diet low in fiber and high in carbohydrates and fat can cause a sudden spike in blood sugar, which can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Both Harvard studies with female nurses and male health professionals found that this type of diet increased more than double the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Other studies, such as the Black Women’s Health Study and the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition, have shown similar results.
Constipation.
It is believed that the fibre in wheat bran and oat bran is more potent than the fibre found in fruits and vegetables. In addition, because fibre absorbs water, experts advise increasing beverage intake along with fibre intake rather than doing so abruptly.
Cancer.
Fiber is shown to decrease the risk of breast cancer through a large-scale study in 2016, where the findings indicate that higher fiber intake reduces breast cancer risk, suggesting that fiber intake during adolescence and early adulthood may be particularly important.
In other words, women who consume higher fiber foods during adolescence and young adulthood, including vegetables and fruits, may have a significantly lower breast cancer risk than those who eat less dietary fiber when young.
In conclusion, consumption of sufficient fiber can give various benefits to the human body. According to the Malaysia Food Pyramid 2020, it is recommended to consume 3 servings of vegetables and fruits daily. However, according to the National Health Morbidity Survey (NHMS), about 95% of Malaysians do not consume enough vegetables and fruits daily, which is why sometimes consumption of fiber supplements can help to bridge the gap of poor dietary intake.
Reference
1. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. Fiber. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/
2. National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) (2019). Chapter 09, Of fruits, veggies, and plain water. http://iptk.moh.gov.my/images/technical_report/2020/4_Infographic_Booklet_NHMS_2019_-_English.pdf
3. Malaysia Food Pyramid 2020. Ministry of Health Malaysia. Nutrition Division. http://nutrition.moh.gov.my/piramid-makanan-malaysia-2020-mendidik-rakyat-mengambil-makanan-dengan-betul/

Apakah itu antioksida?
Antioksida adalah bahan yang terdapat secara semulajadi dalam badan dan juga boleh diperolehi dari sumber makanan semulajadi. Ia adalah bahan yang dapat mengurangkan, meneutralkan dan melindungi sel badan daripada kerosakan.
Dari masa ke semasa, badan melalui proses pertumbuhan seperti panjangnya kuku dan pertumbuhan rambut yang melibatkan aktiviti pengoksidaan. Proses pengoksidaan ini melibatkan pemberian dan pengambilan elektron, di mana akan menghasilkan elektron bebas yang tidak bergabung dengan mana – mana elektron yang lain. Elektron bebas ini juga dirujuk sebagai radikal bebas. Radikal bebas atau elektron bebas ini adalah elektron yang tidak stabil dan dapat memberikan pelbagai risiko penyakit termasuklah kanser. Fungsi antioksida adalah untuk bergabung dengan elektron bebas atau radikal bebas ini dan meneutralkan atau menstabilkan badan dari risiko pelbagai jenis penyakit.
Kebiasaannya badan dapat menghasilkan antioksida dengan sendiri, akan tetapi setelah lanjut usia, kebolehan badan untuk menghasilkan antioksida semakin berkurangan, ketidakseimbangan antioksida dan radikal bebas boleh meningkatkan risiko penyakit. Justeru, para profesional perubatan sering menasihatkan kita untuk makan makanan dari sumber semulajadi seperti sayur – sayuran, dan buah – buahan dengan banyak. Ini kerana, sayur – sayuran dan buah – buahan mempunyai tinggi sumber antioksida seperti beta karotena, lutein, likopena (lycopene), vitamin c, vitamin E dan pelbagai lagi.
Ikutlah saranan pengambilan makanan sihat oleh Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). Makan 3 sajian sayur dan dua sajian buah setiap hari untuk mendapatkan jumlah antioksida yang diperlukan badan. 1 sajian sayur adalah bersamaan dengan saiz satu saiz tapak tangan manakala, saiz sajian buah adalah mengikut kepada jenis buah tersebut seperti di bawah. Jika anda merasakan pengambilan sayur – sayuran dan buah – buahan anda tidak mencukupi di mana ia dapat memberi kesan kepada jumlah antioksida dalam badan, anda juga boleh menggunakan alternatif suplemen untuk mendapatkan jumlah antioksida yang cukup.


Rujukan
- Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). Portal MyHealth. Antioksida. http://www.myhealth.gov.my/en/antioksida/
- Hello Doktor. Manfaat antioksida. https://hellodoktor.com/pemakanan/fakta-nutrisi/manfaat-antioksidan/
- Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). Bahagian Pemakanan. https://nutrition.moh.gov.my/

Diet Suku - Suku Separuh ?
Diet suku – suku separuh adalah saranan diet oleh Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) untuk cara pemakanan sihat. Pelbagai langkah dan inisiatif telah dilakukan bagi mempromosikan amalan pemakanan sihat kepada rakyat Malaysia.
MegaLive menyambut baik saranan ini dengan turut sama mempromosikan amalan pemakanan sihat kepada semua.
Suku – suku separuh adalah diet yang merangkumi suku jumlah karbohidrat seperti nasi, mee, bihun, capati, roti dll, suku jumlah protein seperti ayam, ikan, sotong dll dan separuh jumlah sayur – sayuran dan buah – buahan. Pinggan yang dirujuk dalam saranan diet ini adalah pinggan berukuran 10 inci/ 25sm.
Contoh hidangan suku – suku separuh:

Capati dengan kuah dhal.

Nasi beras perang dengan ayam tanpa kulit dan sayur.

Nasi putih dengan ikan bakar dan sayur.

Nasi lemak

Roti dengan telur dan salad.
Terdapat 5 mesej utama dalam amalan diet suku – suku separuh.
Mesej Utama 1: Makan 3 Hidangan Utama yang sihat dalam sehari.
Ambil sarapan, makan tengah hari, dan makan malam secara sihat dengan mengikuti konsep suku – suku separuh.
Makan pada waktu yang tetap juga membantu pengawalan porsi/ saiz hidangan makanan. Berikut adalah contoh waktu makan harian.

Mesej Utama 2: Makan 1-2 Snek yang Sihat di antara Waktu Makan Jika Perlu
Bagi menggalakan amalan pemakanan secara sihat secara holistik atau sebagai gaya hidup, anda juga digalakkan untuk mengambil snek sihat 1-2 kali/ hari dari sumber buah – buahan, kekacang, dan sayur – sayuran.
Contoh snek sihat yang boleh di ambil 1-2 sajian ialah:

Mesej Utama 3: Makan Sekurang-kurangnya Separuh Daripada Bijirin Anda Sebagai Bijirin Penuh
Malaysia adalah negara di mana, makanan rujinya adalah nasi, oleh itu tidak hairanlah jika kebanyakkan rakyat Malaysia masih berasa tidak kenyang selagi tidak makan nasi. Oleh yang demikian, Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) menggariskan pengambilan karbohidrat hendaklah diambil kebanyakkannya dari sumber bijirin penuh, seperti dari sumber nasi beras perang, roti bijirin mil penuh, jagung, barli dll.
Contoh makanan berkarbohidrat yang tinggi serat:

Mesej Utama 3: Makan Sekurang-kurangnya Separuh Daripada Bijirin Anda Sebagai Bijirin Penuh
Malaysia adalah negara di mana, makanan rujinya adalah nasi, oleh itu tidak hairanlah jika kebanyakkan rakyat Malaysia masih berasa tidak kenyang selagi tidak makan nasi. Oleh yang demikian, Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM) menggariskan pengambilan karbohidrat hendaklah diambil kebanyakkannya dari sumber bijirin penuh, seperti dari sumber nasi beras perang, roti bijirin mil penuh, jagung, barli dll.
Contoh makanan berkarbohidrat yang tinggi serat:

Mesej Utama 4: Makan Hidangan Tidak Bergoreng dan Tanpa Santan Setiap Hari
Seterusnya, lauk -pauk di Malaysia begitu sinonim sekali dengan jenis lauk -pauk yang digoreng menggunakan minyak yang sangat banyak iaitu menggunakan kaedah ‘deep -frying’. Makanan bergoreng dengan minyak banyak yang digunakan secara berulang – ulang dan makanan yang mengandungi jumlah santan yang tinggi boleh meningkatkan masalah kesihatan seperti masalah jantung, darah tinggi, kolesterol dan kanser.
Justeru, pengambilan makanan dengan cara masakan dengan kandungan santan yang tinggi seperti masak lemak, kari, gulai, dan masakkan bergoreng hendaklah dihadkan.
Cara mengantikan pengambilan minyak dan santan dalam masakan dan makanan:

Rujukan:
- Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia (KKM). Bahagian Pemakanan. Panduan Pinggan Sihat Malaysia. https://bit.ly/3HHHdU6

How can exercise improve blood circulation?
Many experts recommend doing exercise or at least moving around to improve blood circulation. This is because exercise leads muscles to require more oxygen, which improves blood circulation.
Current medical science proves the old adage that "a man is as old as his arteries (blood vessels)," because we now know that blood vessels transport vital oxygen-rich blood to all body tissue. Maintaining artery health (blood vessel health) is thus analogous to maintaining overall health.
Endothelial cells line the inside of blood vessels and perform a variety of functions, the most important of which is the production of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is essential for keeping the lining of blood vessels smooth and slippery, preventing white blood cells and platelets from adhering and causing inflammation or blood clots. Aside from that, it relaxed the muscle cells in blood vessels to prevent spasms and keep arteries open.
A study of four groups of healthy people: young exercisers, young non-exercisers, elderly exercisers, and elderly non-exercisers discovered that while age had a significant impact on endothelial function and nitric oxide production, it had a smaller and more gradual impact on people who exercised regularly. This demonstrates that exercise does, in fact, keep blood vessels young!

Regular exercise benefits blood vessels by increasing nitric oxide production in endothelial cells, thereby maintaining oxygen supply throughout the body and heart health!
When you have a poor blood supply, your extremities, such as your hands and legs, are often affected.
Here are some exercises to improve blood circulation in your extremities;
- Ankle rotation
- Walking
- Heel and toe raises
- Knee flexions
- Squat
- Using exercise ball
- Yoga movement that requires movement of hands and legs
In conclusion, because exercise is essential for maintaining healthy blood vessels, body movement will help in some ways to maintain healthy blood vessels. So get moving and don't be a couch potato!

What Is Anemia?
Anemia is a common blood disorder. It is a condition when the body does not have enough red blood cells and is unable to deliver enough oxygen throughout the body.
Anemia is diagnosed by a low haemoglobin or hematocrit level in a blood test. The main protein in red blood cells is haemoglobin. It transports and distributes oxygen throughout your body. Your haemoglobin level will be low if you have anaemia. If it falls below a certain level, your tissues or organs may not receive enough oxygen.
Symptoms of anemia
Lethargic or tiredness are the most common symptoms of anemia. Other symptoms include pale skin, an irregular or fast heartbeat, shortness of breath, chest pain, headache, and light-headedness.
Types of anemia
Among the types of anemia are sickle cell anemia, iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, aplastic anemia, and many more.
Each of these types of anemia has its own cause.
In conclusion,
anemia must be treated depending on the cause, ranging from taking supplements to having medical procedures.
Most importantly, anemia can be prevented by consuming a healthy and varied diet.
Iron-rich foods include boiled cockles, chickpeas, fried soy bean curd, liver, dried anchovies, bitter gourd, spinach, and kangkung.




