Health Articles
Find out more about your health here from our health professionals!

Is Your Daily Routine Secretly Causing Dry and Strained Eyes?

In our modern world, many people suffer from dry and strained eyes, especially with the rise of digital device use and changing environmental factors. These common eye problems can cause discomfort, affect productivity, and reduce quality of life if left unaddressed. Understanding their causes and how to prevent or treat them is essential for maintaining good eye health.
What Causes Eye Strain?
Eye strain happens when your eyes get tired from intense use. It commonly occurs during activities like reading, working on a computer, or focusing on detailed work for long periods without breaks.
Common causes of eye strain include:
1. Prolonged Screen Time (Digital Eye Strain)
1.1 Reduced Blinking: When we focus on digital screens, we tend to blink less, leading to dry eyes and eye strain.
1.2 Poor Screen Resolution and Contrast: Low-quality screens with poor contrast or improper brightness can strain the eyes.
1.3 Glare: Reflections from screens can cause discomfort and eye strain.
1.4 Improper Viewing Distance: Being too close to a screen or having improper screen positioning can exacerbate eye strain[1].
1.5 Oxidative stress:Oxidative stress remains a significant concern, particularly for vulnerable populations such as the elderly or individuals with preexisting retinal conditions. Cumulative blue light exposure from both digital devices and sunlight may contribute to retinal cell damage and potentially increase the long term risk of age related macular degeneration (AMD)[6].
2. Intense Focus Activities
2.1 Reading: Reading for extended periods, especially without breaks, can fatigue the eye muscles.
2.2 Driving: Driving long distances or engaging in other activities that require continuous focus can cause eye strain.
2.3 Detailed Work:Tasks involving close-up work, such as sewing or crafting, can strain the eyes. [2].
3. Environmental Factors
3.1 Bright Light or Glare: Excessive exposure to bright light or glare can tire the eyes [3].
3.2 Dry Air: Dry or polluted environments and places with fans and heating and cooling units may irritate or dry out eyes, leading to eyestrain[4].
Conclusion
Strained eyes are common in today’s digital age but don’t have to interfere with your daily life. By understanding their causes and adopting healthy habits in our upcoming health articles, you can protect your eyes, reduce discomfort, and maintain clear, comfortable vision.
References:
-
Kaur, K., Gurnani, B., Nayak, S., Deori, N., Kaur, S., Jethani, J., Singh, D., Agarkar, S., Hussaindeen, J. R., Sukhija, J., & Mishra, D. (2022). Digital eye strain—A comprehensive review. Ophthalmology and Therapy. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9434525/
-
American Academy of Ophthalmology. (n.d.). Computers, digital devices, and eye strain. Retrieved May 23, 2025. https://www.aao.org/eye-health/tips-prevention/computer-usage
-
BenQ. (n.d.). Protective peepers: The best eye-caring desk lamps for comfortable computing and study. BenQ. Retrieved May 23, 2025, from https://www.benq.com/en-my/knowledge-center/knowledge/eye-caring-desk-lamp-for-computer-and-studying.html
-
Silver, N. (2024, August 29). Eyestrain: Causes, tips for prevention, and treatments. Healthline. Retrieved May 23, 2025, https://www.healthline.com/health/eye-health/eye-strain#eye-drops
-
Chakravarthy, H., Georgyev, V., Wagen, C., Hosseini, A., & Matsubara, J. (2024). Blue light-induced phototoxicity in retinal cells: Implications in age-related macular degeneration. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11685196/

Proactive Steps to Maintain Liver Health

The liver is one of the most vital organs in the human body, responsible for filtering toxins, metabolizing nutrients, and supporting digestion. However, poor lifestyle choices, an unhealthy diet, and certain medical conditions can put the liver at risk of disease. Taking proactive steps to maintain liver health can prevent serious complications and promote overall well-being. Here are some key ways to protect the liver and reduce the risk of liver disease.
1. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake is a leading cause of liver damage, leading to conditions such as fatty liver disease, hepatitis, and cirrhosis [1]. It is recommended to:
-
Take alcohol-free days to allow the liver to recover.
-
Quit alcohol completely if diagnosed with liver disease to prevent further damage.
2. Practice Safe Medication Use
Overuse or misuse of medications, especially pain relievers like acetaminophen, can damage the liver. Always follow dosage recommendations, consult a doctor before mixing medications, and avoid self-medicating [2].
3. Incorporate Milk Thistle Extract
Milk thistle is an herbal supplement known for its potential liver-protecting properties. It contains silymarin, which supports liver health through its antioxidant activity [3]. Including milk thistle extract as part of a healthy routine may aid in maintaining liver function.
4. Get Enough Sleep
Quality sleep plays a crucial role in liver health. During sleep, the body undergoes essential repair and detoxification processes, helping the liver function optimally [4]. Aim for 7-9 hours of restful sleep each night to support overall liver function.
By making these lifestyle changes, individuals can safeguard their liver health and prevent the onset of serious liver diseases. A proactive approach ensures a longer, healthier life with optimal liver function.
References
-
World Health Organization. (n.d.). Alcohol. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/alcohol
-
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). Don’t Overuse Acetaminophen: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/dont-overuse-acetaminophen#:~:text=But%20taking%20too%20much%20acetaminophen,take%20several%20days%20to%20appear
-
Gillessen, A., & Schmidt, H. H.-J. (2020). Silymarin as supportive treatment in liver diseases: A narrative review. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7140758/
-
Um, Y. J., Chang, Y., Jung, H.-S., Cho, I. Y., Shin, J. H., Shin, H., Wild, S. H., Byrne, C. D., & Ryu, S. (2021). Sleep duration, sleep quality, and the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A cohort study. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8528229/

Natural Support for Lifelong Movement

Our joints do so much for us every day—whether it is walking, bending, stretching, or simply getting through our daily activities. Taking good care of them is one of the best ways to maintain mobility, flexibility, and a pain-free life. As we age, or due to factors like lifestyle and activity levels, our joints may start to feel stiff or uncomfortable. But the good news is that nature provides us with ingredients that can help keep our joints strong and supple.
Let us take a closer look at three ingredients—hydrolyzed fish collagen, sodium hyaluronate, and Boswellia serrata—that can support joint health and overall well-being.
1.Hydrolyzed Fish Collagen
Collagen is like the glue that holds our joints together, providing strength and structure to cartilage and connective tissues. As we grow older, our body’s natural collagen production declines, which can lead to joint stiffness and discomfort. Hydrolyzed fish collagen is a type of collagen that has been broken down into smaller peptides, making it easier for our bodies to absorb. Research has shown that supplementing with hydrolyzed collagen may help improve joint comfort, flexibility, and even skin health [1].
2.Sodium Hyaluronate
Have you ever heard of hyaluronic acid? It is a substance that keeps our joints cushioned and hydrated. Sodium hyaluronate, a form of hyaluronic acid, acts like a natural lubricant inside our joints, helping them move smoothly. When our bodies do not produce enough of this essential compound, joints can feel dry and achy. Studies suggest that taking sodium hyaluronate as a supplement can support joint lubrication and even reduce discomfort in conditions like osteoarthritis [2].
3. Boswellia Serrata
Boswellia serrata, also known as Indian frankincense, has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for its ability to control inflammatory responses. The active compounds in this plant, called boswellic acids, have been found to help ease joint stiffness and improve mobility. Scientific studies show that Boswellia serrata extract may help individuals with joint discomfort regain their flexibility and enjoy daily activities more comfortably [3].
Whether through proper nutrition, gentle movement, or natural supplements, there are many ways to support joint health and maintain an active lifestyle. Small steps today can lead to a future where you continue to move freely, do what you love, and embrace life with ease.
Before adding any new supplements to your routine, it is always a good idea to check in with a healthcare professional to ensure they align with your individual needs. Here is to happy, healthy joints and a life full of movement and joy!
References
-
Guillerminet, F., Fabien-Soulé, V., Even, P. C., Tomé, D., & Lebecque, P. (2012). Hydrolyzed collagen improves bone metabolism and biomechanical parameters in ovariectomized mice: An in vitro and in vivo study. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21927918/
-
Kalman, D. S., & Hewlings, S. J. (2016). A review of the effects of oral hyaluronan on chronic knee pain. Nutrition Journal, https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12937-016-0128-2
-
Sengupta, K., Alluri, K. V., Satish, A. R., Mishra, S., Golakoti, T., Sarma, K. V. S., Dey, D., & Raychaudhuri, S. P. (2008). A double blind, randomized, placebo controlled study of the efficacy and safety of 5-Loxin® for treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Research & Therapy. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18667054/

5 Loving Ways Reclaim Your Energy

Feeling drained? It is okay—you are not alone! Life can be exhausting, but the good news is that small changes can make a big difference. Here are five gentle, science-backed ways to help you feel refreshed, recharged, and ready to take on the day.
1. Prioritize Restful Sleep
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep every night to restore your energy and mood. Regularly sleeping less than 7 hours per night on a regular basis is associated with adverse to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, depression, weakened immunity, impaired performance, and greater risk of accidents. [1] Try creating a cozy bedtime routine: dim the lights, drink milk, and put your phone away to help your mind unwind.
2. Stay Hydrated
Sometimes, fatigue is simply your body asking for more water. A lack of fluids can also cause your heart to work harder to pump oxygen all throughout your body [2]. The expended energy can make you feel tired and less focused. Sip on at least 8 glasses of water a day to keep your mind and body energized. Hydration = self-care.
3. Nourish Your Body with Panax Ginseng Root Extract
Panax ginseng supports the body with natural energy. Studies suggest that it helps improve energy levels and effectively relieve fatigue [3]. Adding a little ginseng to your routine may gently enhance your stamina and overall well-being.
4. Move with Love & Joy
Light jogging, aerobic workouts, cycling, swimming, or dancing to your favorite song with jumps and turns can wake up your system and brighten your mood. Moderate-intensity exercise interventions lasting at least six weeks are, on average, beneficial for fatigue, energy, and vitality [4]. Even small moments of movement can bring more energy and joy to your day.
Nourish your body and soul! When you prioritize rest and self-love, you will feel refreshed and recharged.
References
-
Consensus Conference Panel, Watson, N. F., Badr, M. S., Belenky, G., Bliwise, D. L., Buxton, O. M., Buysse, D., Dinges, D. F., Gangwisch, J., Grandner, M. A., Kushida, C., Malhotra, R. K., Martin, J. L., Patel, S. R., Quan, S. F., & Tasali, E. (2015). Recommended amount of sleep for a healthy adult: A joint consensus statement of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and Sleep Research Society. Sleep. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4434546/#:~:text=):843%E2%80%93844.-,CONSENSUS%20STATEMENT,should%20consult%20their%20healthcare%20provider
-
National Council on Aging. (n.d.). 10 reasons why hydration is important. https://www.ncoa.org/article/10-reasons-why-hydration-is-important/
-
Zhang, G., Lu, B., Wang, E., Wang, W., Li, Z., Jiao, L., Li, H., & Wu, W. (2023). Panax ginseng improves physical recovery and energy utilization on chronic fatigue in rats through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Pharmaceutical Biology. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9879180/#:~:text=Short%2Dterm%20EEP%20supplementation%20resulted,a%20therapy%20herb%20against%20fatigue.
-
Wender, C. L. A., Manninen, M., & O'Connor, P. J. (2022). The effect of chronic exercise on energy and fatigue states: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9206544/
-260x200.png)
How to Help Your Parents Prevent Osteoporosis
.png)
How to Help Your Parents Prevent Osteoporosis
As our parents get older, their bones naturally become weaker, making them more prone to osteoporosis—a condition that causes bones to become fragile and break easily. The good news is that there are simple ways to help them maintain strong bones and reduce the risk of fractures. By making small lifestyle changes and keeping up with regular health checkups, we can ensure our loved ones stay healthy and active. Here are some key ways to prevent osteoporosis.
- Ensure They Get Enough Calcium
Calcium is the building block of strong bones, and getting enough of it every day is essential. If our parents do not get enough calcium, their bodies will start taking it from their bones, making them weaker over time. It is recommended that adults over 50 consume 1,000 to 1,200 mg of calcium daily through calcium-rich foods or supplements. Encourage them to drink milk, eat yogurt, and enjoy cheese, as well as fortified foods like tofu and plant-based milk, are great choices. If they do not eat enough calcium-rich foods, a doctor might recommend a supplement to make up for the difference [1].
- Help Them Get Enough Vitamin D
Vitamin D is just as important as calcium because it helps the body absorb calcium properly. Without it, even a good diet will not be enough to keep bones strong. The best way to get vitamin D is through sunlight—just 10 to 30 minutes of sunlight a few times a week can help. But if our parents do not get much sun exposure, they can eat foods rich in vitamin D, such as salmon, eggs, and fortified dairy products. If necessary, a vitamin D supplement can also be helpful, especially for older adults [2].
- Encourage Regular Exercise
Exercise helps maintain bone density, build muscle, and improve balance, reducing the risk of falls and fractures [3]. Strength training and balance exercises, such as walking, are especially beneficial. Research has shown that tailored exercise plans, including Tai Chi, can significantly help prevent falls and improve balance in older adults [4].
By taking these simple steps, we can help our parents stay strong, active, and independent for years to come. Keeping their bones healthy is one of the best ways to show we care. A little encouragement and support can go a long way in ensuring they live a healthy and happy life!
References
- National Institutes of Health. (n.d.). Calcium - fact sheet for Health professional. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-HealthProfessional/
- Giustina, A., Bouillon, R., Dawson-Hughes, B., Ebeling, P. R., Lazaretti-Castro, M., Lips, P., Marcocci, C., & Bilezikian, J. P. (n.d.). Vitamin D in the older population: A consensus statement. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9607753/
- Giangregorio, L. M., & Ponzano, M. (n.d.). Exercise and physical activity in individuals at risk of fracture. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1521690X21001305
- Chen, W., Li, M., Li, H., Lin, Y., & Feng, Z. (2023). Tai Chi for fall prevention and balance improvement in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Public Health. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10509476/#:~:text=Conclusion,with%20exercise%20time%20and%20frequency.
-260x200.png)
How to Choose a High-Quality Fish Oil Supplement
.png)
Fish oil supplements are a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, which play a crucial role in brain function, joint support, heart health, and inflammation reduction. However, not all fish oil supplements are created equal. With so many options available, choosing a high-quality product is essential to maximize health benefits and avoid contaminants.
This guide will help you identify what to look for when selecting a premium fish oil supplement to ensure purity, potency, and effectiveness.
1. EPA & DHA Content
The two most beneficial omega-3 fatty acids in fish oil are Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA) and Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA). These essential fatty acids support heart health, brain function, and inflammation reduction【1】.
Tip: Some lower-quality fish oil supplements contain more fillers than actual omega-3s. Always check the label for EPA and DHA amounts, not just total fish oil content.
2. Choose Molecularly Distilled Fish Oil
Since fish can contain heavy metals and environmental toxins, it is crucial to choose a supplement that undergoes molecular distillation. This process helps remove mercury, lead, and other harmful contaminants, ensuring a pure and safe product.
Tip: Look for supplements labeled as “molecularly distilled” or “pharmaceutical grade,” as these have been purified to remove potential toxins【2】.
3. Enteric-Coated or Reflux-Free Formulas
A common issue with fish oil supplements is the fishy aftertaste or burps that some people experience. Enteric-coated capsules help prevent this by ensuring the oil is released in the intestines rather than the stomach, leading to reduced reflux【3】.
Tip: If you experience digestive discomfort after taking fish oil, try an enteric-coated supplement or taking it with meals.
By following these guidelines, you can make an informed decision and select a safe, effective, and high-quality fish oil supplement to support your overall health.
References
- Swanson, D., Block, R., & Mousa, S. A. (2022). Omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA: Health benefits throughout life. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2161831322009620
- Technology Networks. (2024). Fish vs fish oil supplements: Which is better for your health? Retrieved from https://www.technologynetworks.com/applied-sciences/articles/fish-vs-fish-oil-supplements-which-is-better-for-your-health-394642
- Healthline. (n.d.). Omega-3 supplement guide: What to buy and why. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/omega-3-supplement-guide

Simple Steps to Love Your Heart
Your heart works tirelessly for you every single day, so why not show it some love? Maintaining heart health is crucial for overall well-being. With heart disease being a leading cause of health concerns worldwide, a few simple lifestyle changes can make a big difference. Here are four loving ways to keep your heart happy and strong:

1. Eat a Heart-Healthy Diet
A balanced diet plays a vital role in maintaining heart health. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals. Avoid processed foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium, as they can contribute to high cholesterol and blood pressure. Choose foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and antioxidants to promote better cardiovascular function.
2. Stay Physically Active
Your heart loves movement! Staying physically active helps strengthen your heart, improve circulation, and keep blood pressure and cholesterol in check. Aim for at least 150 minutes of heart-pumping activity each week, whether dancing, walking, swimming, or cycling—find something you enjoy! Even small changes, like taking the stairs or stretching during breaks, can make a meaningful difference.
3. Get Quality Sleep
Poor sleep habits can lead to high blood pressure, obesity, and increased risk of heart disease. Adults should aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Establish a consistent sleep routine by going to bed and waking up at the same time daily. Reduce screen time before bed, create a comfortable sleeping environment, and manage stress to enhance sleep quality.
4. Bonus Tip: Take Health Supplements
While a well-balanced diet is the foundation of heart health, supplements can provide additional support. Nutrients such as Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, L-arginine and L-citrulline have been shown to support cardiovascular function.1 Scientific study stated that daily dosage of 30-60mg CoQ10 was recommended to prevent CoQ10 deficiency and maintenance purpose.2 Always consult with a healthcare professional before adding supplements to your routine to ensure they align with your health needs.
By following these heart-healthy habits, you can improve your cardiovascular well-being and lead a healthier, more energetic life. Your heart takes care of you, so take a little time each day to care for it too.
References:
1. Nyawose, S., Naidoo, R., Naumovski, N., & McKune, A. J. (2022). The effects of consuming amino acids L-arginine, L-citrulline (and their combination) as a beverage or powder, on athletic and physical performance: A systematic review.
2. Kumar, A., Kaur, H., Devi, P., & Mohan, V. (2009). Role of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) in cardiac disease, hypertension, and Meniere-like syndrome.

Nourishing Ingredients for Hair, Nails, and Skin

Healthy hair, radiant skin, and strong nails rely on specific nutrients, and several scientifically-backed compounds play vital roles in enhancing these features.
Fish Collagen Peptides
Collagen is a structural protein essential for skin elasticity and hydration. Fish collagen peptides are particularly effective at promoting collagen synthesis and improving skin texture. They also support nail strength and hair health by maintaining the protein matrix that underlies these tissues
Hyaluronic Acid
Known for its unparalleled hydrating properties, hyaluronic acid retains moisture in the skin, improving suppleness and reducing fine lines. This hydration benefits not only the skin but also the scalp, fostering an optimal environment for healthy hair growth
L-Cysteine
This amino acid is a precursor to keratin, a fundamental protein in hair and nails. By reducing oxidative stress and enhancing keratin production, L-cysteine supports resilience and growth in both hair and nails
Zinc and Selenium
Both zinc and selenium are critical for maintaining the structural integrity of skin, hair, and nails. Zinc regulates oil production in the skin and strengthens hair follicles, while selenium acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage
Biotin (Vitamin B7)
Biotin is celebrated for its role in metabolic processes, aiding the formation of healthy keratin. This makes it a powerhouse nutrient for combating brittle nails and promoting thicker, shinier hair
Together, these ingredients offer a synergistic approach to enhancing the health of hair, skin, and nails, combining hydration, structural support, and antioxidant protection.

The Power of Nature: Supporting Women’s Wellness Naturally

Herbal remedies have long been revered for their ability to promote health and vitality, especially for women. A combination of potent natural extracts like Cynanchum wilfordii, Angelica gigas, Phlomis umbrosa, and Humulus lupulus offers a holistic approach to addressing the unique health challenges women face at various stages of life.
Key Ingredients and Their Benefits
- Cynanchum Wilfordii
Widely used in traditional Asian medicine, Cynanchum wilfordii enhances blood circulation and boosts energy. This herb is beneficial for supporting bone health and alleviating fatigue, making it an ideal choice for women juggling the demands of daily life
- Angelica Gigas
This herb has a rich history in Eastern medicine and is particularly effective in easing menstrual discomfort and hormonal fluctuations. Angelica gigas has calming properties that help reduce stress and promote emotional well-being.
- Phlomis Umbrosa
Phlomis umbrosa, known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, is used to alleviate joint and muscle pain. Its support for musculoskeletal health is particularly beneficial for women experiencing hormonal transitions.
- Humulus Lupulus (Hops)
Hops extract is a natural source of phytoestrogens, compounds that help balance hormones. This herb is especially helpful in managing menopausal symptoms, such as hot flashes and insomnia, making it a valuable ally during midlife transitions
Holistic Health Benefits: A Natural Solution for Every Stage of Life
The synergy of these herbs provides comprehensive support for women across different stages of life, from hormonal imblances during menstruation to the challenges of menopause. From enhancing energy and managing hormonal changes to supporting bone and joint health, these extracts offer a natural and effective approach to overall well-being. Their use in traditional medicine, combined with modern research, underscores their safety and effectiveness in supporting women’s health.
However, as with any herbal-based supplement, it is important to note that some herbal ingredients may be contraindicated with certain medications, particularly for women in menopause. The older we get, the more health concerns we may encounter, often requiring medication. Therefore, it is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating herbal remedies into your routine, ensuring they are compatible with your current health regimen.
References
- Kim SJ, Jin SW, Lee GH, Kim YA, Jeong HG. Evaluation of Estrogenic Activity of Extract from the Herbal Mixture Cynanchum wilfordii Hemsley, Phlomis umbrosa Turczaninow, and Angelica gigas Nakai. Toxicol Res. 2017 Jan;33(1):71-77. doi: 10.5487/TR.2017.33.1.071. Epub 2017 Jan 15. PMID: 28133516; PMCID: PMC5266372.
- Chun JM, Lee AY, Nam JY, Lee MY, Choe MS, Lim KS, Kim C, Kim JS. Protective effects of Phlomis umbrosa extract on a monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis model and prediction of molecular mechanisms using transcriptomics. Phytomedicine. 2021 Jan;81:153429. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153429. Epub 2020 Dec 1. PMID: 33310311.
- Herbal Remedies for Women's Health: Benefits and Research. Nutraceutical Business Review.
- Phytochemical Effects of Phlomis Umbrosa and Its Use in Traditional Medicine. Herbal Medicine Journal.
- The Role of Phytoestrogens in Menopausal Symptom Management.EstroG100 Journal.

Growing Screen Time, Growing Vision Concerns: Protecting Children’s Eye Health in a Digital World
With digital devices becoming central to both learning and play, children are spending more time than ever in front of screens. Unfortunately, this rise in screen time has led to an increase in vision issues among children worldwide, including in Malaysia.
Studies show that globally, nearly 30% of school-aged children experience myopia (nearsightedness), a statistic that is climbing each year. In Malaysia, a recent survey revealed that over 20% of children have some form of vision impairment. This rise is linked to prolonged screen time, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, when virtual learning became essential.
Several factors contribute to this trend. The blue light emitted from screens can cause eye strain and disrupt sleep, while focusing on close-up screens for extended periods may lead to digital eye strain or even contribute to the development of myopia. Limited outdoor time is another factor; natural sunlight is known to support healthy vision development, and children spending more time indoors tend to have higher rates of myopia.

Parents and caregivers can help protect children’s eyes by encouraging regular breaks with the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. Prioritizing outdoor play also allows children’s eyes to relax from close-up screen focus. Practicing good screen habits—such as setting appropriate brightness, avoiding screens in dark environments, and keeping devices at a safe distance from the eyes—can also reduce strain.
In addition to these habits, eye health supplements and foods that are rich with nutrients thacan support children’s vision are particularly beneficial, such as lutein and zeaxanthin. Lutein and zeaxanthin act as natural filters against blue light, helping to protect the retina and maintain visual sharpness. Vitamins C and E are also powerful antioxidants that shield eye tissues from oxidative stress, promoting long-term eye health.
As digital devices become essential in daily life, it’s crucial to balance their benefits with proactive eye care. By practicing good screen habits and considering dietary support, we can help children maintain bright, clear eyesight in our fast-changing, screen-centric world.
References
-
World Health Organization (WHO): World report on vision. Geneva: WHO, 2019. This report discusses global vision health trends and the impact of screen time on vision issues, including myopia in children.
-
American Optometric Association: Digital Eye Strain and Myopia Management in Children. This provides information on digital eye strain, myopia, and best practices to mitigate eye strain for children.
-
Ministry of Health Malaysia: National Eye Survey (NES) Malaysia. This survey provides statistics on visual impairment in Malaysia, including data on children’s eye health.
-
American Academy of Ophthalmology: Recommendations on children’s screen time and its potential impact on eye health.
-
Research on Eye Supplements: Various studies on lutein, zeaxanthin, and other antioxidants for eye health, such as "Lutein and Zeaxanthin Isomers in Eye Health and Disease" (Nutrients, 2020), which details their benefits for retinal protection against blue light.

Your Prostate Health Matters!
Many men do not care about or even know the importance of their reproductive organs, especially the prostate gland. The prostate gland has an important job, which is to produce a thick, milky-white fluid that becomes part of the semen, the liquid ejaculated during sexual activity. The prostate isn’t that big—about the size of a walnut or golf ball. The prostate is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It also wraps around the upper part of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body. That means prostate problems can affect urination and sexual function.
What are the problems? If your "man" has problems like pain during urination or often urinates at night, you have to check and detect the problem early and take precautions. While you may not have any problems related to this, you have to know ways to prevent them from developing.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Is extremely common in older men. It is not cancerous, but it has the characteristic of enlarging the organ. The prostate goes through a period of rapid enlargement during puberty, but this levelled off once puberty was completed. The prostate will begin to grow again in midlife, but at a slower rate. These periods of growth are thought to be caused by increased levels of male hormones such as testosterone. The prostate grows throughout a man's life because testosterone is produced throughout his life.
The most common symptom of BPH is difficulty urinating or dribbling after you urinate. Also, you may feel the need to urinate a lot, often at night (5).
Prostatitis
It starts with a bacterial infection or prostate inflammation. Prostatitis can result in burning or painful urination, an urgent need to urinate, difficulty urinating, difficult or painful ejaculation, and pain between the scrotum and the rectum or in the lower back. Prostatitis is classified into two types: acute bacterial prostatic and chronic bacterial prostatic. It only causes mild urination difficulties and can cause fever, chills, or pain. A bacterial infection is also the starting point. The second is chronic bacterial prostatic disease, which occurs when an infection recurs frequently. This is a rare and difficult to treat condition. To feel better, you may need to consult your doctor (5).
Prostate Cancer
It is the most common type of male cancer. Prostate cancer typically grows slowly and is initially confined to the prostate gland, where it may not cause significant harm. The development of cancerous cells within the prostate gland, which may spread to other parts of the body. While some types of prostate cancer grow slowly and may require little or no treatment, others are aggressive and spread quickly. It primarily affects older men (1, 5).
Here are a few simple tips on how you can manage or care for your prostate gland. There is also a way to prevent it.
Healthy Eating – Better Health!
First and foremost, you must strive for a healthy eating pattern, which is easier than you might think. Adhering to a heart-healthy, low-animal-fat, low-carbohydrate diet. You must substitute whole-grain bread for white bread, as well as whole-grain pasta and cereal. Choose healthy fats like olive oil, nuts (almonds, walnuts, and pecans), and avocados. Limit your intake of saturated fats from dairy and other animal products. Avoid partially hydrogenated fats (trans fats), which are found in many processed foods and fast foods. Fruits and vegetables high in antioxidants are always beneficial to your body in preventing cancer-causing oxidants. Consume more fish because it contains omega-3 fatty acids. Because obesity has been linked to prostate problems, you should limit your sugar intake as well. Avoid sugar-sweetened beverages such as sodas and many fruit juices (1, 2, 3, 4).
Exercise For Everyone!
You should stay active in addition to eating a healthy diet. Regular exercise will lower your risk of developing certain problems, such as heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer. Although relatively few studies have directly assessed the impact of exercise on prostate health, those that have concluded that exercise is beneficial in the majority of cases.
If you have any kind of symptom, such as pain when urinating, you urinate frequently, especially at night. Screening for prostate problems is recommended between the ages of 55 and 70. Your doctor may perform a rectal exam as a physical test and blood testing for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) (5).
References
- Jennifer H. Cohen, Alan R. Kristal, Janet L. Stanford. (2000). Fruit and Vegetable Intakes and Prostate Cancer Risk. Vol 92. Issue 1 (61-68) https://academic.oup.com/jnci/article/92/1/61/2905797
- Katie M. Di Sebastiono, Marina Mourtzakis. (2014). The Role of Dietary Fat throughout the Prostate Cancer Trajectory. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4277017/
- Paul Turek. (2014). How To Keep Your Prostate Happy https://www.urologyhealth.org/careblog/how-to-keep-your-prostate-happy
- Harvard Health (n.d). 10 Diet & Exercise Tips for Prostate Health. https://www.health.harvard.edu/mens-health/10-diet-and-exercise-tips-for-prostate-health
- MedicineNet (n.d). Prostate Problems. https://www.medicinenet.com/prostate_problem_warning_signs/article.htm

Erectile Dysfunction: Is it taboo or a health concern?
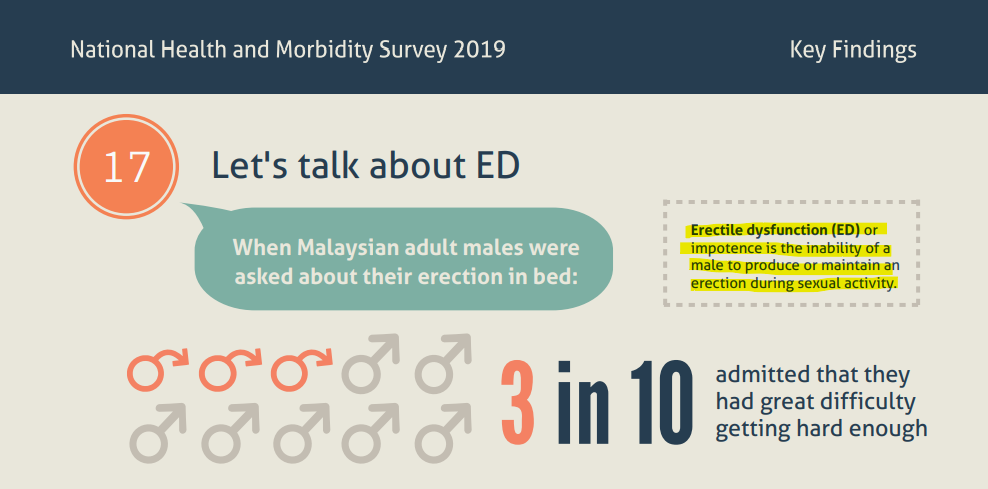
Globally, it is estimated that 100 million men have ED problems, but even with such a figure, ED is considered a taboo topic to discuss because it is considered an embarrassment, and people do not want to seek medical help for it. It is not taboo to discuss ED because it is a health issue. Sexual well-being is one component of overall health, and as we age, our bodies do not function as well as they used to, which is why ED is common in men aged 40 and older.
ED can be caused by a variety of factors, including physical, psychological, and social factors. Physical factors such as heart disease, atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, liver or kidney problems, Peyronie's disease, and alcoholism are common among older men. These medical conditions typically affect the nerves and blood vessels that control erections, which explains why people with such conditions are more likely to develop ED. Psychological factors can also contribute to ED. Worry about being unable to achieve or maintain an erection, as well as prolonged emotional distress related to economic, professional, social issues, relationship conflicts, and depression can all distract a man of any age from becoming aroused.
Stendra (avanafil), Viagra (sildenafil), Cialis (tadalafil), and Levitra or Staxyn (vardenafil) are some of the most commonly prescribed erectile dysfunction treatments. Aside from medication, lifestyle changes such as exercise, healthy eating, stress management, and adequate sleep will also aid in the treatment of this condition.
According to the study, not all types of exercise help with ED; exercise such as cycling might not be helpful for ED, according to the National Health Service, UK; however, weight-bearing exercise can increase the natural production of testosterone, which is a significant factor in erectile strength and sex drive. Apart from weight-bearing exercise, kegel exercises, which improve your pelvic floor, yoga, and aerobic exercise, which are targeted to improve stamina and overall fitness, also help. In general, exercise will improve sexual health as it improves blood circulation, hormone regulation, stamina, and endurance, thus improving sex drive and erection problems.

Apart from exercise, nutrition also plays an important role in ED. A study found that men with a 42-inch waist are 50% more likely developing ED than men with a 32-inch waist. Also, being obese increases men's risk of getting vascular diseases and diabetes, which contributes to ED. Reduce or stop smoking, and consuming alcohol has also shown tremendous positive effects on ED problems. Smoking for a long time affects the vascular health; it causes the blood supply to the penis to become restricted due to blockage or narrowing of the arteries, thus causing the erection problem. While, as for the consumption of alcohol, it suppresses the central nervous system that is responsible for releasing nitric oxide (a chemical that is responsible for producing and maintaining an erection), which is why the more men drink alcohol, the more likely they are to have an ED problem.
In conclusion, talk to your doctor regarding your condition. You might think that your condition is too petty to discuss, but by letting your doctor know about it, it gives a different perspective to your whole treatment plan.
References
- Everyday Health (n.d). Naturqal Treatment for Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.everydayhealth.com/pictures/lifestyle-changes-natural-treatments-erectile-dysfunction/ (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Healthline (n.d). Erection Problems. https://www.healthline.com/health/erection-problems (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Medical News Today (n.d). Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/5702 (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- National Health Service, United Kingdom. Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/erection-problems-erectile-dysfunction/ (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- National Institute of Health (NIH), National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive, and Kidney Disease (NIDDK). Symptoms & Causes of Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/symptoms-causes (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Mayo Clinic. Erectile Dysfunction. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/erectile-dysfunction/symptoms-causes/syc-20355776 (Accessed on March 2, 2021).
- Everything you need to know about ED. https://www.healthline.com/health/erectile-dysfunction#symptoms (Accessed on March 2, 2021).

Menopause in men
While some claim that men go through menopause, others assert that this is not the case for men. Which is accurate? Men can experience this type of menopausal period under certain circumstances, but it would be inaccurate to refer to it as menopause since the process is different from what women go through (6).
The pathway by which men's testosterone levels decline is when older men's testosterone levels fall as a result of declining Leydig cell mass in the testicles or a malfunction in hypothalamic-luteinizing hormone, which in turn results in low testosterone production (6).
In men who are 50 or older, andropause causes a decrease in testosterone production. The term andropause is frequently used by doctors to refer to male hormone changes brought on by ageing. While testosterone production does decrease as men get older, it also does so when they have diseases like diabetes, among others.
Hormone changes occur naturally as we get older. There are several ways in which male menopause differs from female menopause, and not all men go through it. Your reproductive system won't completely shut down as a result. However, because of your lower hormone levels, there might be sexual issues. The decline of testosterone in men happens more gradually than it does in women during menopause, when hormone production completely stops. In contrast to the ovaries, the testes never run out of the substance required to produce testosterone. A healthy male may continue to produce sperm well into his 80s or beyond. Men's testosterone levels vary greatly. The testosterone levels of older men are typically lower than those of younger men. Throughout adulthood, testosterone levels gradually decrease (1, 2).

What are the signs and symptoms of andropause?
Recognizable signs and symptoms of low testosterone levels may include:
-
Changes in sexual function.
Testosterone plays a key role in libido in men. However, someone with low testosterone will likely experience a more drastic drop in their desire to have sex. This might include reduced sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and fewer spontaneous erections. Your testes might become smaller as well.
-
Changes in sleep patterns.
Sometimes low testosterone causes sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or increased sleepiness.
-
Physical changes.
Various physical changes are possible, including increased body fat, reduced muscle bulk and strength, and decreased bone density. Swollen or tender breasts (gynecomastia) and loss of body hair are possible. Rarely, you might experience hot flashes and have less energy. Low testosterone levels in the body can also contribute to smaller-than-average-sized testicles.
-
Emotional changes.
Low testosterone might contribute to a decrease in motivation or self-confidence. You might feel sad or depressed or have trouble concentrating or remembering things.

How do men stay healthy?
The most common type of treatment for symptoms of male menopause is making healthier lifestyle choices. For example, your doctor might advise you to:
-
Eat a healthy diet.
What you eat has a major impact on testosterone as well as other hormone levels. Therefore, you must pay attention to your long-term calorie intake and diet strategy. Constant dieting or overeating may disrupt your testosterone levels. Eating enough protein can help maintain healthy levels and aid in fat loss, which is also associated with testosterone.
-
Get regular exercise.
Exercise is one of the most effective ways to prevent many lifestyle-related diseases. Interestingly, it can also boost your testosterone.
-
Get enough sleep.
-
Reduce your stress.
What are the andropause treatments?
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), men who experience a drop in testosterone level should be offered treatment with testosterone replacement therapy in addition to leading a healthy lifestyle to prevent or reduce the risk of andropause happening.
It is therefore best to seek medical advice if you ever experience any of these symptoms. If a lifestyle or psychological factor is the root of the issue, the appropriate action will be taken to deal with it. It might be brought on by stress, depression, low self-esteem, obesity, being overweight, smoking, or consuming excessive amounts of alcohol.
References
- WebMD (n.d). Male Menopause https://www.webmd.com/men/guide/male-menopause
- Healthline (n.d). What Is Male Menopause? https://www.healthline.com/health/menopause/male#diagnosis-and-treatment
- Adam Fellman. (2018). Is The Male Menopause Real? https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/266749
- Mayoclinic (n.d). Male Menopause: Myth or Reality? Https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/mens-health/in-depth/male-menopause/art-20048056
- NHS. (2019). The ‘male menopause’ https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/male-menopause/
- Duncan, C.G. & Richard, P. (2000). The Male Menopause: Does it exist? For some men need investigation and testosterone treatment. West J. Med. 173(2): 76–78. DOI: 10.1136/ewjm.173.2.76

Oysters and Men’s Health
In general, oysters are a type of shellfish. Not only is it important for ecosystems since one of its functions is to filter pollutants out of the water and provide habitats for other species, like barnacles and mussels, but it is also an excellent source of zinc, copper, iodine, iron, potassium, and selenium. Since oysters are rich in nutrients, they are also used in the supplement product for various reasons.

Oyster supplementation (1, 2, 3)
When it comes to oyster supplementation, people always thought that it came from its shell and not the meat, but the truth is, it comes from its creamy flesh meat!
The creamy flesh of oysters is cleaned and depurated. It is then processed and made into capsules, powder, and tablets. This is actually good news for those who cannot consume slimy, meaty food and thus can take it in tablet or capsule form.
Many people have started to consume oysters for their known ability to increase testosterone levels in men. It is also well known for its benefits in supporting men’s reproductive health as it contains a high level of zinc.
Since oysters are high in zinc, oyster extraction supplementation is highly recommended for those who are deficient in this nutrient. This is a very important nutrient that can help your immune system and improve your body’s metabolism as well.
Zinc is a trace mineral that is essential for various body functions, such as protein synthesis, collagen formation, wound healing, and healthy immune function. Apart from that, it is also needed to support prostate and reproductive health, especially for males. Individuals who have digestive disorders such as Celiac Disease and Chron’s Disease and/or are on a vegan diet are at higher risk of being zinc deficient and thus require zinc supplementation.
Zinc deficiency can lead to fatigue, impaired senses of taste and smell, poor appetite, slow wound healing, poor immunity, and hair loss as well.

What do the study's findings say? (4,5)
In 2003, a study in Japan used oysters, which contain a significant amount of zinc, to investigate whether they could improve the reproductive health of mice. This study was conducted on three groups of mice, where the first group was supplemented with a diet rich in zinc from oysters, the second group was supplemented with zinc from zinc carbonate, and the third group was fed a diet deficient in zinc.
This study found that mice supplemented with zinc either from oyster extraction or zinc carbonate had improved serum levels of zinc, improved sperm motility and maturation, increased successful pregnancy rates, increased maternal weight gain, increased the number of live fetuses, increased fetal body weight, and had better embryonic development as compared to mice fed a diet deficient in zinc. Thus, this study suggested that oyster extraction is a useful supplement that can prevent reproductive defects from zinc deficiency, and the bioavailability of zinc may be identical to zinc carbonate.
Another recent study that was conducted in 2018 with regards to men’s reproductive health and oysters is the review article that concluded that zinc is vital in men’s reproductive health since the adequacy of zinc content in seminal plasma is needed for men’s germination, normal sperm function, and fertilization. The review also noted that seminal fluid deficiency causes infertility, and many studies prove the association of the seminal plasma zinc concentration with the physiology and pathogenesis of sperm and its quality. The study also indicates that men who are smokers have a higher possibility of becoming infertile, as the toxin in cigarettes can lead to oxidative stress that can hinder the efficacy of seminal fluid and sperm parameters.
In conclusion
To date, there has been no meta-analysis or systematic study with regards to oysters specifically and men’s reproductive health. However, randomised controlled trials and review articles from a few studies, such as the two above, are able to portray that zinc deficiency may hinder sperm quality and fertility in men. Since oysters have a significant amount of zinc, they can be used to treat or prevent men’s reproductive health problems. Furthermore, the study also noted that the content of taurine and glycogen will also help alleviate this problem.
References
- Men’s Health Online Magazine. Take This Supplement to Improve you Sex Life. https://www.menshealth.com.au/oyster-and-zinc-supplement-improves-sex-health (Accessed on August 13, 2020).
- Men’s Health Online Magazine. Oyster Nutrition Facts. https://www.menshealth.com/nutrition/a19527227/oysters-nutrition-facts/ (Accessed on August 13, 2020).
- Are Oysters Good for you? Benefits and Danger. https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/oysters#1 (Accessed on August 13, 2020).
_thumbnail-260x200.jpg)
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a condition in which the prostate is enlarged but not cancerous. It is also known by a few other names, such as benign prostatic obstruction, benign prostatic hypertrophy, and enlargement of the prostate. According to the National Health Morbidity Survey Malaysia (NHMS), 16% of Malaysian men over the age of 40 suffer from this problem. The signs and symptoms of this problem usually worsen as men get older, which is why the NHMS reported that the percentage of men with symptomatic BPH increased from 10% among 40-year-old men to 33% among 75-year-old men.
Among the signs and symptoms of this problem are:
- Frequent or urgent urinating problem.
- Increased frequency of urination at night (nocturia).
- Difficulty starting urination
- A weak or interrupted urine stream.
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Urine incontinence
- Pain after ejaculation or during urination
- Unusual urine colour or smell
- Inability to completely empty the bladder.
Most of these symptoms usually come from a blocked urethra or an overworked bladder from trying to pass the urine through the blockage in the bladder. For BPH, the size of the prostate does not necessarily indicate the severity of the problem; men can have a greatly enlarged prostate with little blockage and a few symptoms or a minimally enlarged prostate with greater blockage and more symptoms.
The cause of this condition is rather poorly understood, but there are probably two reasons for this, according to scientists. First, throughout their lives, men produce testosterone (male hormone) and a small amount of oestrogen (female hormone), but as men age, the amount of active testosterone decreases, leaving a higher proportion of oestrogen, which promotes prostate cell growth, hence the enlargement of the prostate. Second, it is due to the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) hormone, which plays roles in prostate development and growth. As men get older, they continue to produce and accumulate high levels of DHT in the prostate, which encourages prostate cells to continue growing. This is also theorised because men who do not produce DHT do not develop BPH.
 There are various treatments that can help with BPH, depending on the individual's severity and condition. Discuss your condition with your healthcare professionals so they may suggest a better treatment plan for you. The treatment plan usually involves lifestyle modifications such as:Urinating as soon as you feel the urge
There are various treatments that can help with BPH, depending on the individual's severity and condition. Discuss your condition with your healthcare professionals so they may suggest a better treatment plan for you. The treatment plan usually involves lifestyle modifications such as:Urinating as soon as you feel the urge
-
Go to the bathroom to urinate, even when you don’t feel the urge.
-
avoiding over-the-counter decongestants or antihistamine medications, which can make it harder for the bladder to empty.
-
Avoid alcohol and caffeine, especially in the hours after dinner.
-
Reduce your stress level, as nervousness can increase the frequency of urination.
-
Exercise regularly, as a lack of exercise can aggravate your symptoms.
-
Learn and practise Kegel exercises to strengthen your pelvic muscles.
-
Keep warm, since being cold can make symptoms worse.
As for the treatment from healthcare professionals, its usually includes prescription of medication (alpha blockers, alpha reductase inhibitors, etc.), minimally invasive procedures (transurethral needle ablation, high intensity focus ultrasound, prostatic stent insertion), and surgery (laser surgery, open prostatectomy, transurethral incision of the prostate (TUIP). Bottom line: talk to your doctor regarding your condition. No matter how insignificant you may think things that occur to you are, they might actually be a symptom of a disease.
References
-
Mayo Clinic. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia/symptoms-causes/syc-20370087 (Accessed on Feb 25, 2021).
-
National Institute of Health (NIH). National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems/prostate-enlargement-benign-prostatic-hyperplasia (Accessed on Feb 25, 2021).
-
What do you want to know about enlarged prostate? https://www.healthline.com/health/enlarged-prostate (Accessed on Feb 25, 2021).
-
Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH). National Health Morbidity Survey (NHMS) (2018) Infographic Booklet

Understanding How Fasting Affects your Digestive System

Fasting, a practice embraced across various cultures and religions, offers a myriad of benefits for physical and mental well-being. While commonly associated with religious observances like Ramadan or Yom Kippur, fasting has also gained traction in health and wellness circles for its potential to detoxify the body, enhance focus, and regenerate immune cells.
Benefits of Fasting
During fasting, the body enters a state called glucogenesis, where it uses stored energy from fats and glucose, promoting weight management and detoxification. This process not only helps to eliminate toxins but also boosts the production of endorphins, enhancing mood and mental clarity. Additionally, fasting allows the digestive system to rest, potentially improving overall gut health.
Fasting and Digestive Challenges
Despite its benefits, fasting can sometimes lead to digestive discomforts like heartburn and indigestion. Reduced food intake lowers stomach acid, which helps digest food and fight bacteria. However, stimuli such as the smell of food or thinking about meals can trigger acid production, potentially causing heartburn. Overeating during iftar or breaking a fast too quickly may also overwhelm the digestive system, leading to bloating or indigestion.
Practical Tips to Prevent Discomfort
-
Break Your Fast Gradually: Begin with light, easily digestible foods such as dates, soups, or yogurt, followed by balanced meals.
-
Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water before and after fasting periods helps maintain hydration and aids digestion.
-
Mindful Eating: Avoid overeating, especially during meals after fasting. Practice portion control to ease the digestive workload.
-
Support Digestive Health: Incorporate supplements like MegaLive GastoEz to address occasional heartburn or indigestion.
Fasting is a holistic practice that nurtures the body, mind, and spirit. By adopting mindful eating habits and addressing potential challenges, you can enjoy its benefits while minimizing discomfort, making the experience both fulfilling and healthful.
References
1. Medical News Today (n.d). What Happens If You Don’t Eat For A Day? Timeline And Effects. [online] Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322065#can-fasting-promote-weight-loss [Accessed 29 April 2020].
2. Medical News Today (n.d). Fasting: Health Benefits And Risks. [online] Available at: https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/295914 [Accessed 29 April 2020].

Why people take Coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10 is a naturally occurring nutrient in human body. It carries variety of vital role including promoting energy production and neutralizing harmful free radicals.
Coenzyme Q10 can be found naturally in foods such as meat, oily fish, eggs, whole grains, and nuts.
Coenzyme Q10 is associated with a variety of health benefits such as for cardiovascular diseases, Alzheimer diseases, migraine and many more.
As we age, study shows that the level of CoQ10 in the body diminished hence, consumption of CoQ10 via supplementation and consuming foods high with CoQ10 level are helpful in maintaining/ increasing CoQ10 level in the body. Other than that, consumption of cholesterol medication – statin also influence the level of CoQ10 in the body, hence why, people consuming statin medication often times are suggested to consume CoQ10 supplementation.

As for individuals who have multiple risk of having heart problem be it due to overweight and obese, strong family history of heart problem, hypertension, and many more are also suggested to consume CoQ10 as it is a potent antioxidant. CoQ10 helps to produce energy during energy synthesis process, however, this process will also release free radicals, which may harm the body.
Under normal condition, free radicals regulate communication between cells and defend body against infectious microbes. However, excess free radical may cause inflammation in the body which can lead to a variety of diseases.
Hence, why CoQ10 is also important in order to help in neutralizing free radicals.
In addition to CoQ10, the consumption of healthy foods, adopting healthy lifestyles like exercise 3-5 times a week and limit consumption of alcohol, processed foods and fast foods will also benefit heart health.
All in all, scientists believe that adopting healthy lifestyles, consumption of healthy and consumption of CoQ10 hand in hand may benefit not only heart health but also whole body in general.

Fruit juice: Is it really good for us?
To answer this, it really is a very tricky one. There are always two sides to a story when it comes to this. One believes that juicing is unhealthy than eating whole fruits due to the loss of fibre throughout the process, which makes fructose (sugar in fruit) absorb even quicker as compared to when it is combined with fibre, thus making it less healthy (1).
Another belief is that juicing is better than eating whole fruits and vegetables because the body can absorb them better and let the digestive tract rest from digesting fibre. If one considers blending fruit, that is even better since the edible fibre in it makes us feel full, so it promotes satiety (1).

So should we consider juicing, blending, or just eating raw fruits and vegetables?
Three longitudinal prospective cohort studies found that greater consumption of fruits such as blueberries, grapes, apples, bananas, and grapefruit reduced the risk of type 2 diabetes, while greater consumption of fruit juice was associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes (2).
When fruit is squeezed for its juice, what is left inside is basically sugar, vitamins, and antioxidants such as carotenoids, etc.; thus, it is healthier in this aspect as compared to frizzy drinks (3). However, the amount of sugar inside both of these drinks is about the same, which is about 20–26 g of sugar per cup (3).
The reason why fruit juice contains a higher sugar content as compared to fresh fruit even when it is 100% fruit juice without the addition of anything else is because, for example, in order to make 250 ml of orange juice, two medium-sized oranges are needed, and that is only 250 ml. Since when it is in liquid form, people tend to consume it even more, thus more fruits are needed. As the number of fruits increases, so does the sugar in them, but not the fibre inside, which in turn makes them have loads of sugar (1, 3, 4, 7, 8).

According to the Singapore Health Promotion Board, many people may think that naturally occurring sugar is healthier than added sugar, but actually there is no chemical difference between the two, and they have the same impact on blood sugar levels when ingested (8).
The same case goes to smoothies, not only because they have a lot of sugar from a large number of fruits, but also because various protein-based foods like yoghurt, milk, almond milk, etc. that are mixed together with them will increase their calories as well (4).
The high sugar levels in both of these drinks make them high-calorie beverages and thus pose the same effect as high-calorie food, which can lead to weight gain. As we know, Malaysia is the fattest country in Southeast Asia, and one of the contributing factors is a lack of knowledge on what can increase weight and what cannot.

Weight gain is linked to many health problems, such as heart diseases, metabolic syndrome, cancer, bone and joint problems, kidney problems, etc. (3).
A study on the composition of grapefruits with different methods of household processing also found out that the composition of antioxidants in blended grapefruit has a higher concentration of the beneficial compound as compared to juicing or hand squeezing (5).
However, as for the absorption of beta carotene, a study found that fruit and vegetable juice makes beta carotene absorb better as compared to blending or eating raw fruit. This is due to the fact that fibre hinders the absorption of beta-carotene (6).
The takeaway message
Eating raw fruit, juicing, and blending all have their pros and cons. What is important is to always take into account the amount of sugar and fibre content. All in all, make sure that you have a balanced, nutritious, and moderate diet as suggested by the Ministry of Health: eat 3 servings of vegetables per day and 2 servings of fruits per day. Vary the way vegetables and fruit are cooked or served and eat them in moderation.
References
-
Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/expert-answers/juicing/faq-20058020
-
MurakiIsao, ImamuraFumiaki, Manson JoAnn E, Hu Frank B, Willett Walter C, van Dam Rob M et al. Fruit consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: results from three prospective longitudinal cohort studies BMJ 2013; 347 :f5001. https://www.bmj.com/content/347/bmj.f5001
-
Healthline (n.d). Is Fruit Juice is as Unhealthy as Sugary Soda? https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/fruit-juice-vs-soda#sugar-content
-
Healthline (n.d). Juicing vs Blending: Which one is better for me? https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/juicing-vs-blending
-
Ram M Uckoo1, Guddadarangavvanahally K Jayaprakasha, V M Balasubramaniam, Bhimanagouda S Patil. Grapefruit (Citrus Paradisi Macfad) Phytochemicals Composition Is Modulated by Household Processing Techniques.
-
Julia K Kolodziejczyk1, Shirley W Flatt, Loki Natarajan, Ruth Patterson, John P Pierce, Gregory J Norman. Associations of Soluble Fiber, Whole Fruits/Vegetables, and Juice With Plasma Beta-carotene Concentrations in a Free-Living Population of Breast Cancer Survivors. Women Health 52(8). DOI: 10.1080/03630242.2012.728189
-
How many orange does it take to make a cup of orange juice? (n.d). https://www.eatdifferentrd.com/blog/2016/8/12/how-many-oranges-does-it-take-to-make-a-cup-of-oj
-
Chanel News Asia (CNA) International (2019). That cup of fresh fruit juice could contain as much sugar as a soft drink. https://www.channelnewsasia.com/news/singapore/fruit-juice-sugar-diabetes-health-risks-soft-drink-11708652

How Much Sugar is Too Much Sugar?!
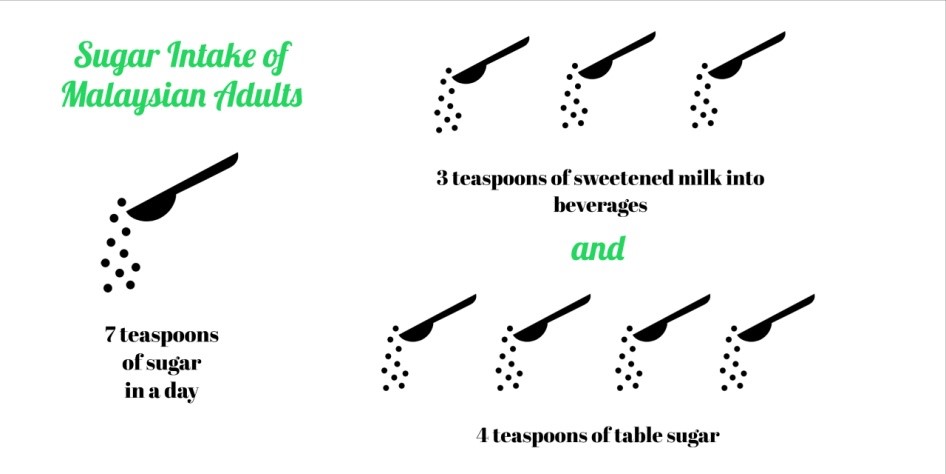
2015 World Health Statistics Report showed that in 2008, Malaysia had the highest obesity prevalence for adults aged ≥20 years among Southeast Asia countries. Increasing availability of sugar or sweeteners coupled with sedentary lifestyles are the contributing factor to Malaysia’s rising problem of obesity and other non-communicable disease problems (11).
On the other hand, Malaysian Adult Nutrition Survey (MANS) 2002/2003, average adult in Malaysia consumes 7 teaspoons of sugar a day comprising 4 teaspoons of table sugar and 3 teaspoons of sweetened milk into beverages. This amount exceeds the recommendation of the World Health Organization and Malaysian Dietary Guidelines (11).

Type of Sugar

Track your consumption of added sugar can be tricky, since packaged foods don’t list the number of teaspoons of sugar and some of us are getting our added sugar by spooning it onto our foods or into our beverages.
Here are the important numbers to remember:
There are 4 calories per gram of sugar and 4 grams per teaspoon. So if the label says it has 20 grams of sugar, that’s 5 teaspoons, or about 80 calories from sugar. Scan the labels for all sources of sugar in processed foods and check the number of grams of added sugars in the nutrition labels (5).
Artificial Sweeteners vs Sugar: Which is better?
Sugar substitute are known as a food additive that provides sweet taste like sugar without excess energy which can promote weight loss and deemed safe for consumption by diabetics (7). They can be either naturally produced or synthesized. Those sugar that are not natural are referred to as artificial sweeteners (9).
American Heart Association labels low-calorie sweeteners, artificial sweeteners and non-caloric sweeteners as non-nutritive sweeteners (NNSs), since they offer no nutritional benefits such as vitamins and minerals. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has given the label “Generally Recognized as Safe” (GRAS) to five non-nutritive sweeteners such as aspartame, acesulfame-K, neotame, saccharin, sucralose and stevia. However, stevia doesn’t have a GRAS distinction but that doesn’t mean it’s dangerous, it just means there isn’t enough evidence yet either way (4).
Artificial sweeteners are thought to be beneficial for diabetics or obese as it provides sweetness without calories and a choice of sweets foods to those who cannot partake refined sugars. This artificial sweeteners may indeed restrict calories but their consumption has been shown to cause mild to serious side effects ranging from nuisance headaches to potentially life-threatening cancer.
However, artificial sweeteners are generally safe to consume but should be avoided by individual with phenylketonuria (a metabolic disorder which cannot metabolize amino acid phenylalanine found in aspartame or allergic to sulfonamides as saccharin belongs to this class of compound. In short, the consumption of artificial sweeteners may poses few health concerns but it is especially beneficial if you use them to decrease the amount of added sugar in diet. The likelihood of negative effects can vary by individual and depend on the type of artificial sweetener consumed (1). If you have bad experience or negative effects after consuming artificial sweeteners try natural sweeteners instead.
Get started cutting down on sugar with these tips
1. Consume foods or beverages low in sugar (3)
2. Focus on whole foods (8)
No sugar diet should focus on eating whole foods as processed foods are more likely to contain refined ingredients or added sugars. Aim to eat foods such as: Fruits and vegetables Lean meat or poultry whole, unprocessed grains and legumes, nuts and seeds
a)Reading the food labels and ingredients list on packaged food is a good way to know and limit how much added sugar you eat.
b) Identify the sugar content claims on packaged foods such as (6).
- Sugar Free: one serving contains less than 0.5g of sugars, both natural and added. Also: free of sugar, sugarless, no sugar, zero sugar or trivial source of sugar
- Reduced Sugar: Has at least 25% less sugars than the older version of the product. Also less sugar, low in sugar or lower sugar
- No Added Sugar: No sugar or ingredients containing sugar was added during processing or packaging. Also without added sugar or no sugar added.
References
- Alina, P. 2019. Artificial Sweeteners: Good or Bad? Healthline. Available from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/artificial-sweeteners-good-or-bad [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- American Heart Association. 2018. Added Sugars [online]. Available from https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/added-sugars [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- American Heart Association. 2018. Life is Sweet with These Easy Sugar Swaps-Info graphic [online]. Available from https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/life-is-sweet-with-these-easy-sugar-swaps-infographic [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- American Heart Association. 2018. Non-Nutritive Sweeteners (Artificial Sweeteners) [online]. Available from https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/nonnutritive-sweeteners-artificial-sweeteners [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- American Heart Association. 2019. By Any Other Name It’s Still Sweetener [online]. Available from https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/by-any-other-name-its-still-sweetener [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- American Heart Association. 2020. What’s the Difference Between Sugar Free and No Added Sugar [online]. Available from https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/difference-between-sugar-free-and-no-added-sugar [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- Arun, S., Amarnath, S., Thulasimani, M. and Ramaswamy, S. 2016. Artificial sweeteners as sugar substitute: Are they really safe? Indian Journal of Pharmacology 48(3): 237-240.
- Johnson, J. 2019. What to know about no-sugar diets. Medical New Today. Available from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/319991#why-cut-out-sugar [Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- Kirtida, R., T. 2011. Sugar substitutes: Health controversy over perceived benefits. Journal of Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics 2(4): 236-243.
- Maria, S., V., A., Khor, G., L. and Pauline, C. 2016. Intake of added sugar in Malaysia: a review: Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition 25(2): 227-240.
- MyHealth Ministry of Health. 2014. Facts About Sugar [online]. Available from http://www.myhealth.gov.my/en/facts-about-sugar/[Accessed on 15 April 2020].
- World Health Organization. 2015. WHO calls on countries to reduce sugars intake among adults and children [press release]. Available from https://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2015/sugar-guideline/en/ [Accessed on 15 April 2020].

Facts on Fiber

“Eat more vegetables and fruits to get your fiber!” You may have heard these words. But what is fiber, really? How it works to improve our health? Let us take a closer look on it!
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate that our body cannot digest undigested. Though most carbohydrates are broken down into sugar molecules but fiber cannot be broken down into sugar and thus it will pass through our body. These carbohydrates often considered beneficial in which mostly come from fruits, vegetables and legumes (1, 3, 6).
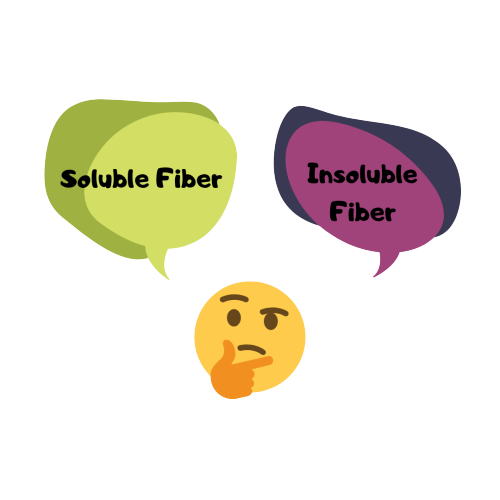
Soluble fiber
Dissolves in water; absorb water to form a gel like substance that slow the digestion and cause you to feel full. They have been shown to decrease cholesterol and lower blood glucose. Common source of soluble fiber includes beans, oat bran, fruits and vegetables. It is also found in pysllium, a common fiber supplement.
Insoluble fiber
Does not dissolve in water; Increase fecal bulk and appear to help food pass more quickly through the digestive tract so it can be of benefit to those who struggle with constipation and irregular stools.
Facts About Fiber (3,4)

#1 Fiber aids in achieving healthy weight.
#2 Fiber fight diseases. It appears to reduce risk of developing various health conditions including heart disease, diabetes, constipation and breast cancer.
#3 Fiber helps to lower cholesterol.
#4 Fiber helps to regulate blood glucose.
#5 Recommended dietary fiber intake per day for all age group is 20-30g/day. However, if a person is not currently eating enough of fiber, he or she should increase his or her fiber intake slowly to avoid gas and bloating.

#6 More fiber needs more water. When eating a high fiber diet, be sure to drink at least eight or more glasses of water every day.
#7 Fiber aids in improving digestion by increasing stool bulk and regularity. A high-fiber diet may help reduce the risk of hemorrhoids and diverticulitis.
#8 Too much fiber is a bad thing. You may experience abdominal cramping, bloating, gas, constipation and even diarrhea.
#9 Fruit and vegetable peels are rich in several nutrients including fiber. Eating unpeeled fruits and vegetables keep you feel full longer due to its high fiber content. However, certain fruit and vegetable peels may be hard to consume or simply inedible. These peels are best removed and not eaten.
#10 Fruits and vegetable juice has less fiber than whole fruits and vegetable. This is because the skin is removed and thus it is more healthful to eat whole fruit and vegetable.
#11 Fiber cannot be cooked out.
Tips to Increase fiber intake (5,7)
Consume products that have whole grain listed as the first ingredients, high fiber content and low fat and sugar content.
Replace white rice, bread and pasta with brown rice and whole grain products.

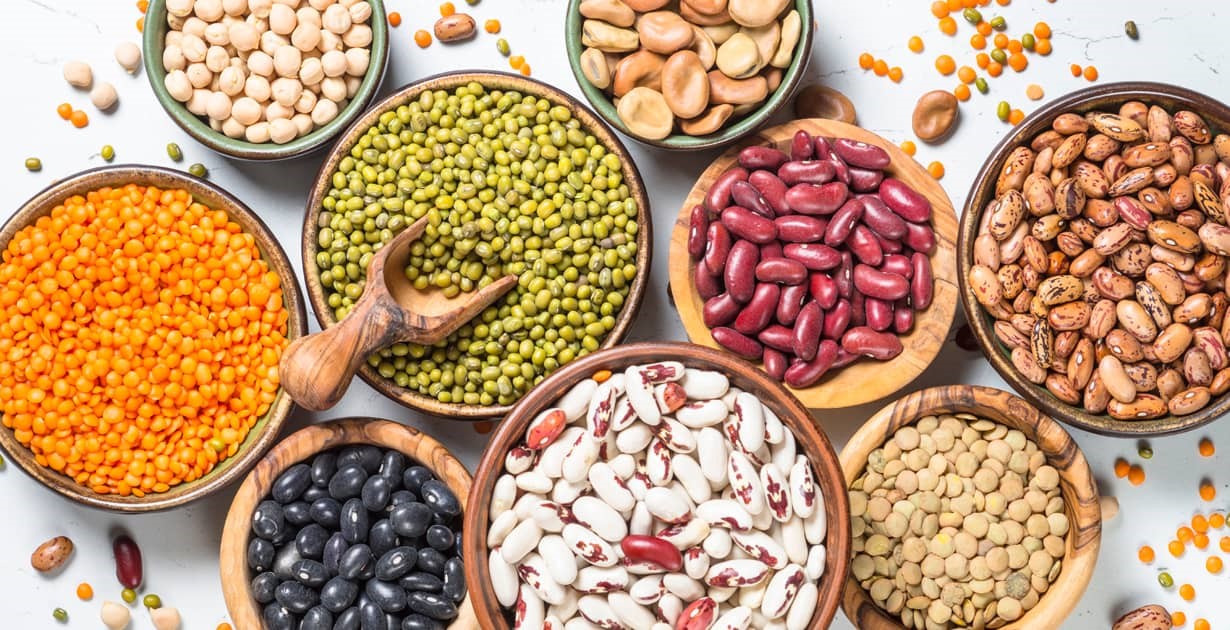
Include legumes in your diet (beans, dried peas and lentils)

Eat unpeeled whole fruit and vegetables not juice.
Snack on fruits and vegetables
Take a fiber supplement (e.g psyllium)
In conclusion,
Fiber is an important dietary substance to your diet. This is because high fiber foods are also good sources of vitamins, mineral and antioxidants which offer many health benefits. Therefore, as one of the key ingredients to healthy eating, fiber is something you cannot skip.
References
- Cleveland Clinic. 2019. Improving Your Health With Fiber. Available from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/14400-improving-your-health-with-fiber [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Danielle, D. 2018. How much fiber is too much. Medical New Today. Available from https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/321286#treatment [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Harvard University School of Public Health. (n.d.). Fiber. Available from https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/fiber/ [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Karin, L. 2016. 45 Interesting Facts about FIber. Fact Retriever. Available from https://www.factretriever.com/fiber-facts [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Kerri, A., J. 2016. 16 Easy Ways to Eat More Fiber. Healthline. Available from https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/16-ways-to-eat-more-fiber [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- Mayo Clinic. 2018. Dietary fiber: Essential for a healthy diet. Available from https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/fiber/art-20043983 [Accessed on 23 April 2020].
- My Health Ministry of Health. 2012. SERAT DAN KAWALAN DIABETES. Available from http://www.myhealth.gov.my/serat-dan-kawalan-diabetes/ [Accessed on 23 April 2020].

Diabetic Neuropathy
Blood glucose is the primary source of energy, and it is derived from the food that we eat. To convert this energy from food that we consume to cells, our bodies require a hormone called insulin, which is produced in the pancreas. With the help of this insulin hormone, energy from food is then converted into cells. When the body is unable to produce enough or any insulin, or when insulin is not used effectively, glucose or sugar remains in the blood and does not reach the cells (2).
Too much glucose in the blood can cause health problems over time. Although there is no cure for diabetes, individuals can take steps to manage their diabetes and stay healthy. Diabetes complications include cardiovascular disease, diabetes neuropathy (nerve damage), nephropathy (kidney damage), retinopathy (eye damage), and many others.
In this article, we will concentrate on the complication of nerve damage, also known as neuropathy. Excess sugar can cause damage to the walls of the tiny blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish nerves, particularly in the legs. This can cause tingling, numbness, burning, or pain, which usually starts at the tips of the toes or fingers and spreads upward. If left untreated, the individual may lose all feeling in the affected limbs (4).
Many studies are being conducted in an effort to reduce the risk of diabetic neuropathy complications, one of which is the use of Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA). ALA is a type of antioxidant found in a variety of foods, but in very small amounts. Foods containing it include spinach, broccoli, yams, tomatoes, potatoes, carrots, beets, and rice bran. Whereas in animal-based food, the heart, liver, and kidney have higher concentrations of lipoic acid (LA) (5).
Lipoic acid (LA) can be synthesized by the human body in the liver. LA or ALA performs functions such as glucose and lipid metabolism, anti-inflammation, antioxidant property that can be used to regenerate other antioxidants, protein repair, and metal ion chelation. ALA, on the other hand, increases insulin sensitivity in people with diabetes (6).
As an antioxidant, ALA or LA aids in the fight against free radicals or oxidative stress caused by three pathways in the body of people with diabetes mellitus: mitochondrial, enzymatic, and non-enzymatic. Concerning the function of ALA in diabetes, several clinical trials have discovered that ALA may increase insulin sensitivity and help to reduce blood sugar and lipid levels.
There are two detailed studies involving this, in which ALA is administered for two weeks to 22 patients and improvements in fasting and average glucose levels, insulin sensitivity, LDL and HDL, and total cholesterol are seen, but the study is too short to measure the HBa1C level. So, another study related to this is the one that administered ALA orally to 74 patients for 4 weeks and discovered improvements in insulin resistance and fasting glucose (7).
Regarding the sole function of ALA on diabetic neuropathy, it is a possible alternative treatment for diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes causes neuropathy, or nerve damage, which is a permanent and common complication. However, ALA can help to alleviate the symptoms (8).
There are two types of neuropathy, the first of which is peripheral neuropathy, which most commonly occurs in the feet and legs but can also sometimes occur in the hands and arms. It can also cause numbness or the inability to feel changes in temperature, tingling or burning sensations, muscle weakness, a loss of balance, foot problems including ulcers or infections, sharp pain, or cramps. Whereas autonomic neuropathy can affect your autonomic nervous system, such as your heart, bladder, lungs, stomach, and intestines, this includes difficulty swallowing, constipation or uncontrollable diarrhea, bladder problems, erectile dysfunction, a decrease or increase in sweating, sharp drops in blood pressure, and many more (8).
In conclusion, studies show that ALA is able to help alleviate the symptoms of diabetes and diabetic neuropathy. However, the right management of diabetes, such as the intake of its medication, such as metformin, and diet control, together with physical activity, must be done side by side.
References
- National Institute if Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Disease (NIDDK). United States Department of Health and Human Services. What is Diabetes? https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes#:~:text=Diabetes%20is%20a%20disease%20that,to%20be%20used%20for%20energy. (Accessed on June 16, 2020).
- National Diabetes Institute of Malaysia (NADI). https://www.diabetesmalaysia.com.my/article.php?aid=8#:~:text=Your%20target%20blood%20glucose%20levels,in%20the%20last%203%20months. (Accessed on June 16, 2020).
- Clinical Practice Guideline (CPG) for Management of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2. 5th Ministry of Health Malaysia (MOH). https://www.moh.gov.my/moh/resources/Penerbitan/CPG/Endocrine/3b.pdf (Accessed on June 16, 2020).
- Mayo Clinic. Diabetes. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes/symptoms-causes/syc-20371444 (Accessed on June 16, 2020).
- Alpha Lipoic Acid Supplement. https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/supplement-guide-alpha-lipoic-acid (Accesed on June 16, 2020).
- Saeid Golbidi, Mohammad Badran and Ismail Laher. Diabetes and Alpha Lipoic Acid (2011). Frontiers in Pharmacology. Journal of Pharmacology.NCBI. DOI 10.3389/fphar.2011.00069
- Diabetes Action. Alpha Lipoic Acid. https://diabetesaction.org/article-alpha-lipoic-acid#:~:text=While%20most%20of%20the%20research,of%20oxidative%20stress%20and%20inflammation. (Accessed on June 16, 2020).
- Alpha Lipoic Acid (ALA) and Diabetic Neuropathy. https://www.healthline.com/health/alpha-lipoic-acid-and-diabetes (Accessed on June 16, 2020).

DURIAN!!! Eat whole durian is equivalent to 3 bowl of rice?
Durian or ‘King of fruit’ is a well-known fruit for its smell. Anthony Bourdain, the late renowned food critic describes durian as “It smelled like you buried someone holding a big wheel of Stilton (cheese) in his arms, then dug him few weeks later” (1). That is to describe how horrible the smell of durian is, but to certain people who like to eat durian the smell of durian to them is heaven!
Durian actually has more than 30 species but the one that people usually eat are about 8 species only, due to its exotic nature, people have started to commercialized durian even to the international level. The most common durian being exported and widely consumed is Durio Zibethinus (2).

Due to its popularity, people started to questioning about durian health benefits, whether it is good or bad for health? Unlike apple, orange, guava and many other common fruits where people always equate it to “an apple a day keeps the doctor away” which means, consuming all these fruits are going to make you healthier, since it is packed full with nutrients that is good for body. For durian, the opinion regarding its health effect is mixing, some people say that it is good for health and can even be used to alleviate infertility or PCOS, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and some people say that it is heaty thus cannot be consumed too much etc. (3).
In general, durian is considered a safe fruit to eat just like any other fruit, but since durian has high calorie value, thus it is not advisable to consume in large amount unlike other fruits. Look at the infographic below to understand, calorie in durian in comparison with other fruits (4).
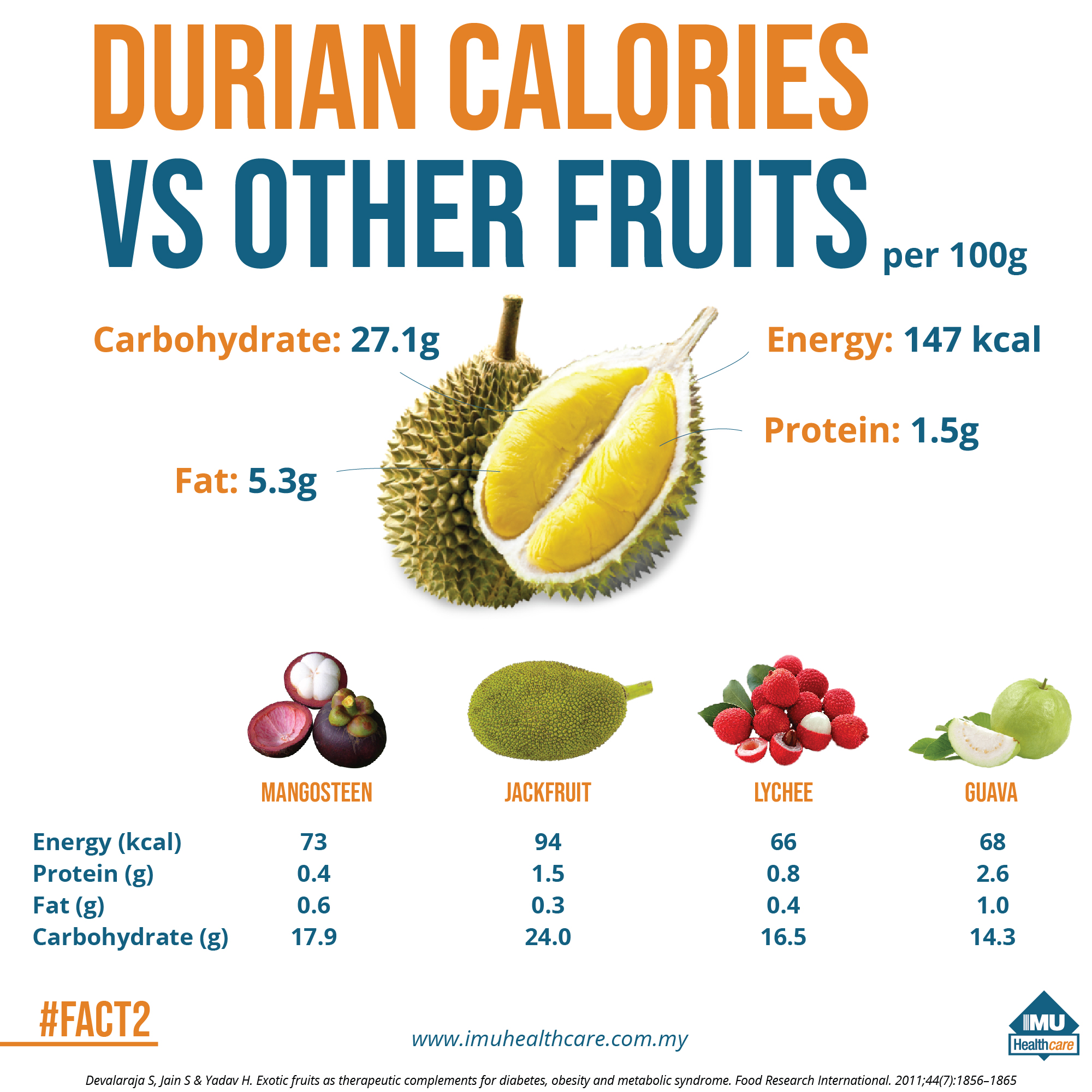
Here is the calorie of durian per seeds, surprisingly eating 5 seeds of durian is equivalent to a bowl of rice! ANDDDD IF A DURIAN CONSISTS OF 15 SEEDS IT IS EQUIVALENT TO 3 BOWL OF RICE! Thus, the recommended intake of durian is only 2-3 seeds, which is equivalent to about per serving of fruits or 90 kcal.

Though, it is crystal clear here that it is safe to eat durian within recommended amount, but there are people who should be even more cautious in consuming durian, that is people who are obese, people who have diabetes and people who have kidney problem. As for people who are obese and diabetes, it is due to its high calorie, high carbohydrate and high fats value thus should be extra careful on the consumption of durian. Whereas for people with kidney problem or undergoing dialysis, due to high potassium content in durian and it is difficult for their body to excrete potassium, thus, they must avoid eating TOO MUCH durian at all cost (4)!

Apart from its high calorie content durian has many benefits as well. It has high antioxidant effect, which makes it a potent fruit to fight against cancer. Durian contains high vitamins, nutrients and organic chemicals that function as antioxidant. All these antioxidants are vital in scavenging the free radicals, that potentially mutated and becoming cancer cells. Which is why it is very important to consume food that is high in antioxidant. It also contains high vitamin C, vitamin B complex and vitamin E, as well as phytonutrients that battle cancerous cells (2).
Durian also, is found to helps in maintaining healthy bones due to its high potassium content. It can help in alleviating depression and sleeping problem, for it contain tryptophan – a natural sleep-inducing compound, that can increase level of serotonin and melatonin for better sleep and emotion management. Durian also contain high fibre which can aids in digestion and helps in infertility for it has high estrogen hormone for conceiving (2).
Albeit durian has many health benefits, when it comes to its consumption with other foods and beverages such as alcohol, it is said that it can interfere with liver function. In detail, durian contain sulphur-containing volatiles which can inhibit the enzyme aldehyde dehydrogenase (enzyme that helps in process alcohol), thus explaining why consuming durian together with alcohol is a deadly mixed (4).
As for the consumption of durian with paracetamol, there is no study on human has been conducted, so far. But there is study on lab rat regarding this. The study shows that, rat that receive paracetamol and durian gives sign of hypothermic effect (significant drop in temperature) thus explain that the two mixture is toxic. However, the mechanism of toxicity is still unknown. To be safe, it is not safe to consume durian together with paracetamol (5).
In conclusion, for people who does not have any health concerns, consume durian within the recommended intake and consume it in moderation, is very much advisable. While for those who have health concerns, eat durian very minimally, it is advisable to eat other types of fruit that have lower calorie count as compared to durian, but since it is in the season thus consume it very minimally with caution towards calorie intake from other food types as well is recommended.
References
- The Star. Benefits of eating durian? Its rich in antioxidant but its fattening (2019). https://www.thestar.com.my/lifestyle/health/2019/09/10/eating-durian-healthy-or-not/ (Accessed on June 17, 2020).
- Tan M.C & Shyamala A. (2018). Exploring the Nutritional Content and Benefits of Durian (Durio Zibethinus). Institute of Bioproduct Development, Universiti Teknologi Mara. https://www.utm.my/ibd/project/exploring-the-nutritional-contents-and-benefits-of-durian-durio zibethinus/#:~:text=Durian%20is%20widely%20celebrated%20for,and%20protect%20against%20cardiovascular%20diseases. (Accessed on June 17, 2020).
- Reshma M. Ansari (2016). Potential Use of Durian Fruit (Durio Zibenthinus linn) as an Adjunct to treat Infertility in Polycystic Ovarian Synrdome (PCOS). PubMed. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26778225/ (Accessed on June 17, 2020).
- International Medical University (IMU). Can A Durian A Day Keep the Doctor Away? http://imunews.imu.edu.my/people/can-a-durian-a-day-keep-the-doctor-away/ (Accessed on June 17, 2020).
- A. Chua., H. Nurhaslina., S.H. Gan. (2008). Hyperthermic Effect of Durio Zibethinnus and Its Interaction with Paracetamol. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19271022/#:~:text=Because%20durian%20(Durio%20zibethinus)%2C,a%20risk%20of%20toxic%20effects

L – Carnitine: Can It Improve Diabetes?
L-Carnitine is an amino acid that the body produces. L-carnitine assists the body in converting fat into energy. In other words, L-carnitine aids the body's energy production. L-carnitine is essential for heart and brain function, muscle movement, and a variety of other processes in the body (1).
How does it work?
Many studies have found that L-carnitine can improve insulin sensitivity. It improves insulin sensitivity, allowing the body to convert food into energy. Here's a general overview of how food is converted into energy or fat in the body.
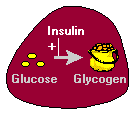
Glycogen is created when food is consumed and stored in the body until it is needed again (2). Insulin is an enzyme that converts the glucose in the food into glycogen.
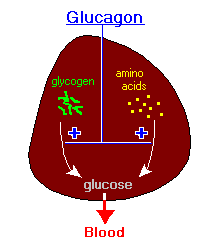
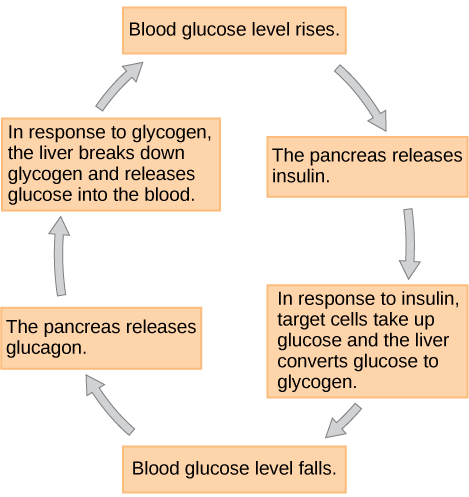
The Overall pathway
This is where L-carnitine plays its role. Mice fed a high-fat diet are able to lower their blood glucose levels when L-carnitine supplementation is given to them, as opposed to mice fed a high-fat diet without the supplement (3).
Another human study found the same result, which is that L-carnitine supplementation reduces insulin resistance and improves insulin sensitivity. The study also suggests that current diabetes patient management, which includes diet modification, medication administration, and physical activities, may be improved in the future with the consumption of supplements such as L-Carnitine (4). The study also suggests that consuming 3g of L-carnitine per day may improve diabetes symptoms, but this must be accompanied by medical professional consultation (4). However, some studies suggest that L-carnitine consumption may have some side effects, so the safe consumption level is less than 2g/day.

Due to the possibility that the general public might mistake it for a "magic pill" that would allow diabetes patients to eat whatever they wanted after taking it. The answer is no! A diabetes patient must still adhere to the diabetes diet, physical activity, and diabetes medication, but because diabetes is a progressive disease where the condition can worsen progressively, all actions, including supplement intake, may slow its progression (4).
Where can L-carnitine be found?
Apart from supplemented products, L-carnitines can be found naturally in foods such as beef and fish.
Beef: 81 mg/ 3 ounces
Pork: 24 mg/ 3 ounces
Fish: 5 mg/ 3 ounces
Chicken: 3 mg/ 3 ounces
Milk: 8 mg/ 3 ounces
References
-
WebMD. L – Carnitine. https://www.webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1026/l-carnitine (Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Feedback Loop of Insulin and Glucagon. https://www.biologycorner.com/2017/08/22/feedback-loops-insulin-andglucagon/ (Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Randall L. Mynat (2009). Carnitine and Type 2 Diabetes. NCBI. PMC Journal. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5707127(Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Mingroe, Graco et al., (1999). L- carnitine Improves Glucose Disposal in Type 2 Diabetes Patient. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10067662/#:~:text=Conclusions%3A%20L%2Dcarnitine%20constant%20infusion,also%20observed%20in%20normal%20subjects (Accessed on July 13, 2020).
-
Healthline. L – Carnitine: Benefits, Sides Effects, Sources and Dosage.https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/l-carnitine (Accessed on July 13,2020).

Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetes is a type of chronic disease; it occurs when the glucose level in the blood is higher than normal. It is one of the leading causes of heart problems as well. In Malaysia, according to the National Health Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2019, there are about 3.9 million people aged 18 years and older who have diabetes. Diabetes affects one out of every five adults, and the prevalence is higher in states such as Negeri Sembilan (33.2%), Perlis (32.6%), and Pahang (25.7%). The prevalence of people who have undiagnosed diabetes in Malaysia is high as well; undiagnosed diabetes occurs when people have never checked their blood glucose level in their entire life or check it rarely (1).
To understand diabetes better, it occurs when the pancreas in the body does not produce enough insulin anymore, or when the insulin is not working well anymore. Insulin is needed in order to transport glucose from the blood vessels to cells and tissues. When insulin is insufficient, glucose cannot be transported to the intended organ, thus causing a high glucose level in the blood vessels and causing damage to the organ and tissue that do not get sufficient glucose to function, and also causing damage to the blood vessels that are exposed to a high glucose level (2).
There are various complications due to diabetes, such as kidney problems, heart problems, diabetic food disease, nerve problems, and eye problems. A nerve problem is when a diabetic person starts to feel tingling and numbness in their peripherals (legs and hands), which is commonly referred to as diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic foot disease, or gangrene, occurs when a diabetic person is exposed to a wound. It must be handled with care since it can be dangerous to the extent of amputation. Eyes problem or diabetes retinopathy is the one that can lead to blindness, that we are going to discuss in detail in this article (2,3).
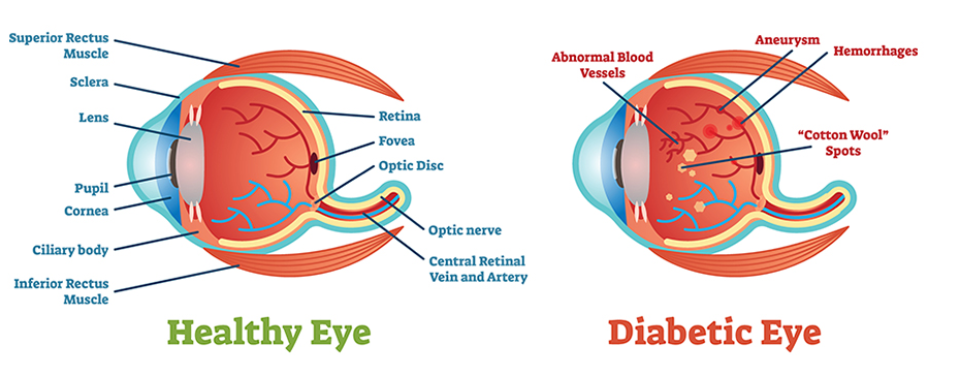
Diabetes retinopathy is the condition in which the retina is damaged, and it is a diabetic complication. When the glucose level in the blood is high, it causes a blockage in the blood vessels, causing the blood vessels to rupture easily. thus causing impaired vision and blindness (2, 3).
In the early stages, there are no significant symptoms associated with this problem; however, as things get more serious, people will experience seeing floaters or black dots in their vision. They will then start to experience obscure vision, night blindness, and diplopia (seeing a double image) (2, 3).
Risk factor to this problem includes those who have been diagnosed with diabetic in the long time (more than 5 years), those who have poor control of blood glucose level, cholesterol level, blood pressure level and low haemoglobin. Those who have gestational diabetes are also at high risk of getting diabetes retinopathy (2, 3).
There are two types of diabetic retinopathy (2,4);
Non – Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) is the early stage of the disease, in which symptoms will be mild or non-existent. In NPDR, the blood vessels in the retina are weakened. Tiny bulges in the blood vessels, called microaneurysms, may leak fluid into the retina. This leakage may lead to swelling of the macula.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
The more advanced form of the disease is proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR). Circulation issues deprive the retina of oxygen at this stage. As a result, new, vulnerable blood vessels can form in the retina and the vitreous, the gel-like fluid that fills the back of the eye. Blood from the new blood vessels may leak into the vitreous, clouding vision.
In order to prevent diabetic retinopathy from occurring, it is recommended for individuals with diabetes to control their blood sugar level, control their blood pressure level, stop smoking, regularly exercise, and maintain their ideal weight. Apart from these, people with diabetes may as well conduct yearly eye screenings. Eye screening for diabetics will be conducted using a fundus non-mydriatic camera, where an image of the eyes will be captured. Optometrist, eyes doctor, or eye specialist will then grade the image to see whether the eye's codition is normal or abnormal. Bleeding and swelling in the retina, an abnormal optic disk, a torn retina, and other abnormal conditions are examples of abnormal conditions.
References
- National Health Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2019. Institute Kesihatan Umum (IKU), Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia.
- Fatanah Ismail. Diabetes Mellitus (2008). MyHealth Portal. Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia. http://www.myhealth.gov.my/en/diabetes-mellitus-3/ (Accessed on August 21, 2020).
- Ainayanti Adnan. Diabetis: Mesti Jalani Pemeriksaan Mata (2016). MyHealth Portal. Kementerian Kesihatan Malaysia. http://www.myhealth.gov.my/diabetes-mesti-jalani-pemeriksaan-mata/ (Accessed on August 21, 2020).
- Diabetic Retinopathy (n.d). American Optometric Association (AOA). https://www.aoa.org/healthy-eyes/eye-and-vision-conditions/diabetic-retinopathy?sso=y (Accessed on August 21, 2020).




