Calcium Supplementation, Who Needs it?
Function of Calcium?
Body needs calcium for strong bones and teeth. Calcium is also required to carry out important function such as for muscle to move, for nerves system to carry messages between brain and body parts, for blood vessels to move blood throughout the body, and for body to help release hormones and enzyme that affect almost every function in the human body (1,2,3).
How much calcium is needed?
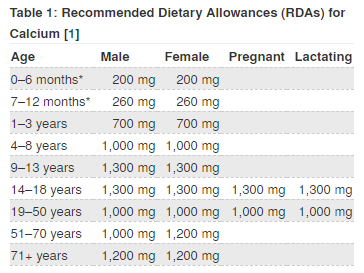
Normal adult need about 1000 mg of calcium daily, however there are certain condition which require to consume up to 1300 mg of calcium daily such as for pregnant lady, lactating mother, post-menopausal women, and man who is above 70 years old of age (1,2,4).
Calcium and diet
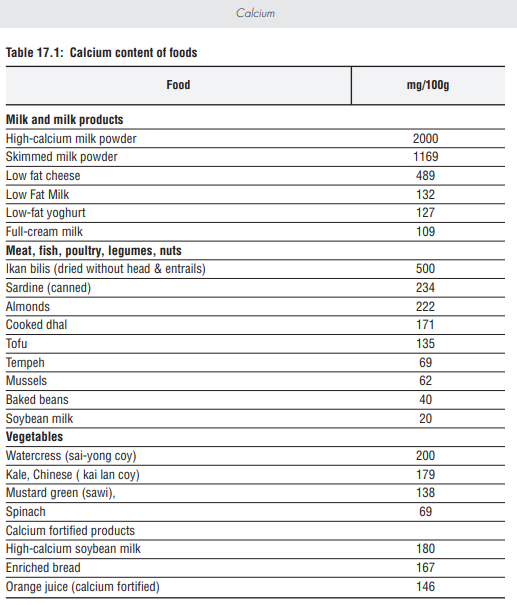
Body does not produce calcium, so it needs to be consumed from foods. Luckily, calcium can be found in variety of foods such as dairy products, dark leafy vegetables, fish, and many other fortified food products (1,2,3). As for our local food products sardine, anchovies, cencaluk, budu, tofu, tempeh, broccoli, kalian, and tapioca leaves are among food that is high with calcium (4).
It is also important to take note that in order to absorb calcium, body needs vitamin D. Only a few foods containing small amount of natural vitamin D, such as egg yolks and salmon with bones. Mostly, we rely on the exposure to sunlight in order to get enough vitamin D, of course in Malaysia the country with sun all year long have no problem with this! However, as currently we are still in the so to say the ‘lockdown’ phase thus it is very important to remind everyone to get the sunlight every day at least 20 minutes for its vitamin D and calcium absorption (1,2,4).
Though all the foods stated above are easily found, but there are conditions which hinder individuals from getting enough calcium from diet thus require it from calcium supplementation.
Condition for calcium supplementation
Before considering calcium supplement, individuals must understand how much calcium needs by the body (stated above). Then individuals must seek help from nutritionist, dietitian, pharmacist, or doctors, where they will assess your calcium consumption from your diet through diet recall. If the calcium intake falls short thus you need to top up calcium from supplement.
Hypertensive individuals and diet with large amounts of sodium.
Several literature reviews on topic of total calcium intake from food and supplements with regards to hypertension suggested that there is possible link to lowering high blood pressure. However, since most of the study design have small number of subjects, and were tested with people from different background, and not to mention possess various kind of biases thus making it difficult for scientist to draw conclusion (1,2).
However, a large study subject (Women’s Health Study), found out that calcium intake was inversely associated with risk of hypertension in middle-aged and older women, in terms of preventing hypertension (1,2).
The consumption of high sodium food lead to more calcium excretion through the urine, which will lead to constriction of blood vessels, which in the end resulting in high blood pressure. Drinking large water after consuming salty food, is not enough, as it may be making blood pressure return to its slightly normal condition, but it is not helping with the loss of calcium (1,2,5).
Pregnant and lactating mother
Often times, pregnant women is being reminded of how important is folic acid for the baby, even from the trying to conceive period, healthcare providers already advise them to consume folic acid, in order to prevent spina bifida to the baby. However, calcium is as well very important for mothers throughout pregnancy and lactating period especially for mother who is lack of calcium from diet (1).
Several professional organizations recommend calcium supplements during pregnancy for women with low calcium intakes to reduce the risk of preeclampsia (a condition where gestational hypertension always occur). For example, the American College of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (ACOG) states that daily supplementation with 1,500–2,000 mg calcium may reduce the severity of preeclampsia in pregnant women who have calcium intakes less than 600 mg/day. Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 1,500–2,000 mg calcium for pregnant women with low dietary calcium intakes, particularly those at higher risk of gestational hypertension (1).
As for normal healthy mother, the consumption of calcium is especially important during lactating period, mother may notice symptoms such as cramps which indicates lack of calcium during pregnancy and lactation period. Also if a mother is on iron supplementation as well, it is advisable to not consume both at the same time, it is best to gap several prior the consumption of these two since it can interfere with the absorption (1,2).

Post-menopausal women and elderly
Throughout the lifespan, bones are constantly being broken down and built up in a process known as remodelling. Bone cells called osteoblasts build bone, while other bone cells called osteoclasts break down bone if calcium is needed. In healthy individuals who get enough calcium and physical activity, bone production exceeds bone destruction up to about age 30. After that, destruction typically exceeds production. This is sometimes called “negative calcium balance,” which can lead to bone loss. Women tend to experience greater bone loss than men later in life due to menopause, a condition that lowers the amount of hormones that help to build and preserve bone (5).
Getting enough dietary calcium at all ages may help to slow the degree of bone loss, but calcium intakes at any level are not known to completely prevent bone loss. Calcium is less easily absorbed at later ages, and therefore eating a very high amount of calcium will not always resolve the problem (5).
Studies on calcium intake and bone density in postmenopausal women have mixed results that could be due to various reasons. Because the results of some large trials found that higher calcium intakes (usually achieved with a supplement) was associated with improved bone density and slightly lower risk of hip fractures, the RDA for calcium for postmenopausal women is higher than at younger ages. Some studies suggest that frail elderly (80 years and older living in institutions) may benefit from supplementation more than “younger” elderly who live independently in the community (5).

Individuals with lactose intolerance and limit dairy products
Individuals with lactose intolerance usually, is unable to consume food that has high amount of calcium especially if it come from milk and dairy source of food. Thus, lactose intolerance individuals need to consume it form dark leafy vegetables and soy-based product. However, in most cases the consumption is not enough or individuals with lactose intolerance consume not enough vegetable rich with calcium or other food source rich with calcium, thus for this specific population calcium supplementation is needed either from fortified food product such as ready to eat cereals or from calcium supplementation tablet itself.
Individuals receiving treatment on certain medication in the long period
Well, there are certain medication which can influence the absorption of calcium. Medication such as to treat osteoporosis (bisphosphonates), antibiotics (fluroquinolone), medication to treat low thyroid problem (levothyroxine), anticonvulsant (phenytoin), diuretic medication (Lasix and bumex), antacids containing aluminium and magnesium and also glucocorticoids (prednisone). These are all either causing calcium loss in the urine or cause calcium depletion in the bone. Thus, if you are on these medication, it is advisable to take calcium rich foods four hours prior or after the intake of medication, so that it would not interfere with the absorption of calcium, it is also best if you consume calcium supplementation if you do have poor intake of calcium rich food as well (2).
In conclusion, in all these conditions, calcium supplements may help you meet your calcium requirements. Talk with your doctor or dietitian about whether calcium supplements are right for you.
References
- National Institute of Health (NIH). Department of Health and Human Service. Calcium. Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-HealthProfessional/ (Accessed on November 18, 2020).
- National Institute of Health (NIH). Department of Health and Human Service. Calcium. Fact Sheet for Consumers. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-Consumer/ (Accessed on November 18, 2020).
- Mayo Clinic. Nutrition and Healthy Eating. Healthy Lifestyle. Calcium and calcium supplements: Achieving the right balance. https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/nutrition-and-healthy-eating/in-depth/calcium-supplements/art-20047097 (Accessed on November 18, 2020).
- Ministry of Health (MOH). National Coordinating Committee on Food and Nutrition. Recommended Nutrient Intake (RNI): A Report of the Technical Working Group on Nutritional Guidelines (2017).
- Harvard T.H. Chan. School of Public Health. The Nutrition Source. Calcium. https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/calcium/ (Accessed on November 18, 2020).




